Partition
Eukaryotic genomes often consist of multiple chromosomes, which are distinct sequences. However, they are often visualized as one contiguous sequence by placing them end-to-end of each other. Some visualizations, especially when comparing genomes, treat chromosomes as separate elements. While different chromosomes are the most common reason to display a sequence in separate parts, one could imagine partitioning a sequence based on other factors too, such as partitioning it in equally sized subsequences to show the entire sequence in multiple rows (similar to space-filling layouts).Contiguous

Segments, typically individual chromosomes, of the genome are joined together end-to-end.
3dViewer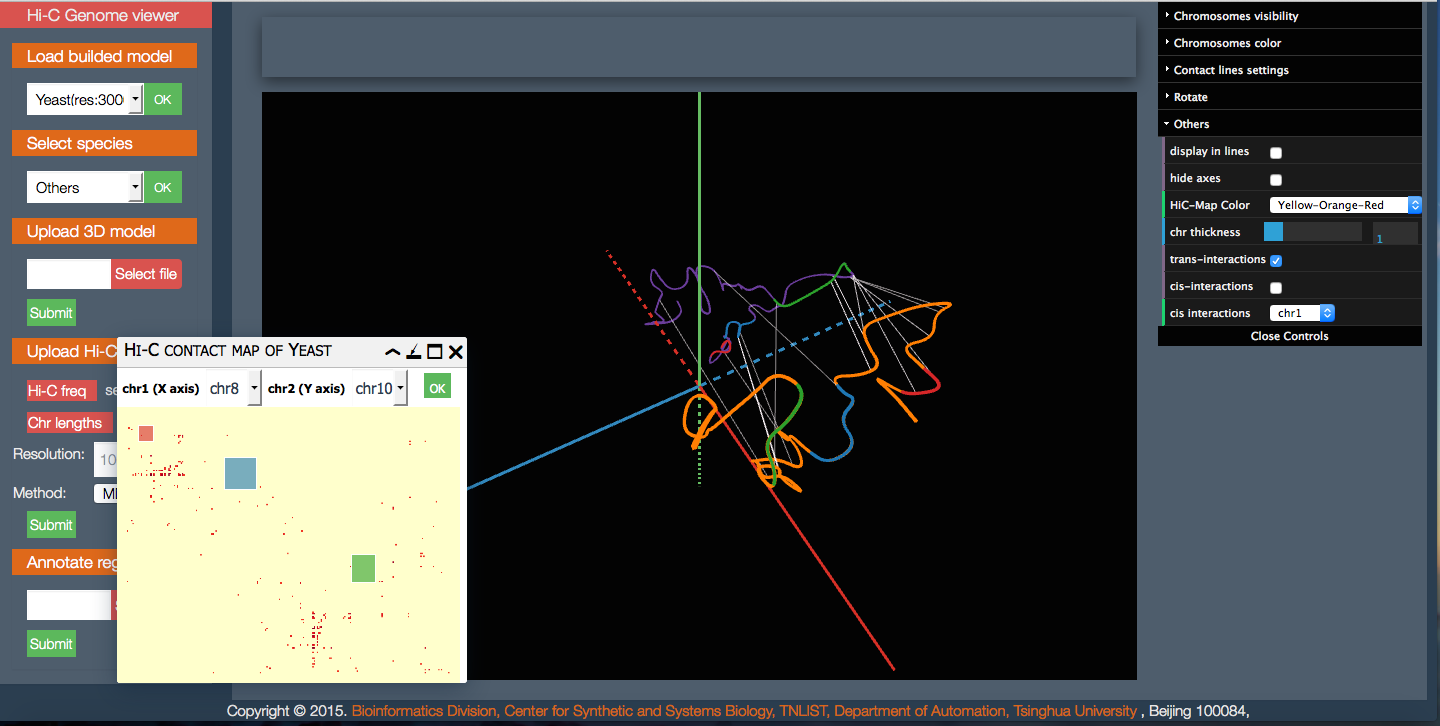 Alvis
Alvis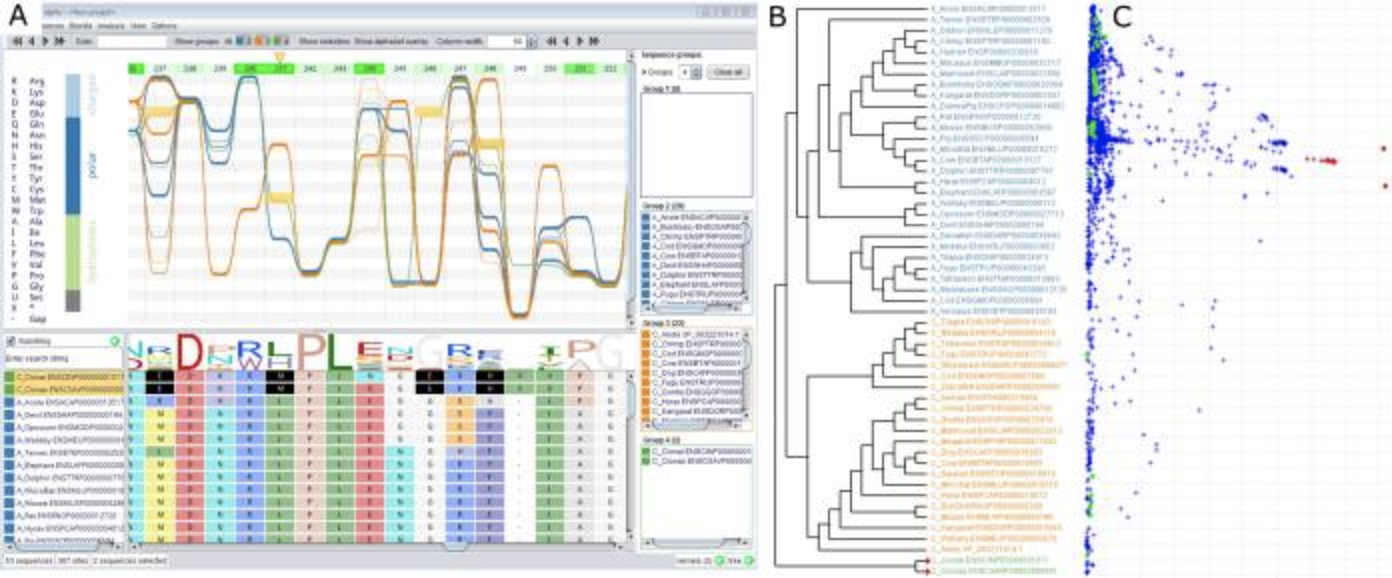 Apollo
Apollo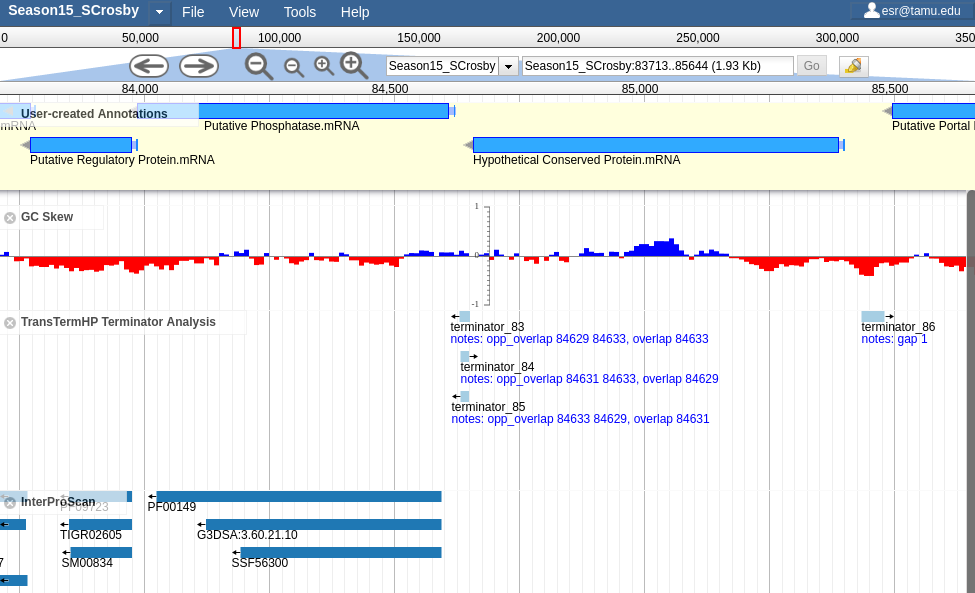 BactoGenie
BactoGenie BedSect
BedSect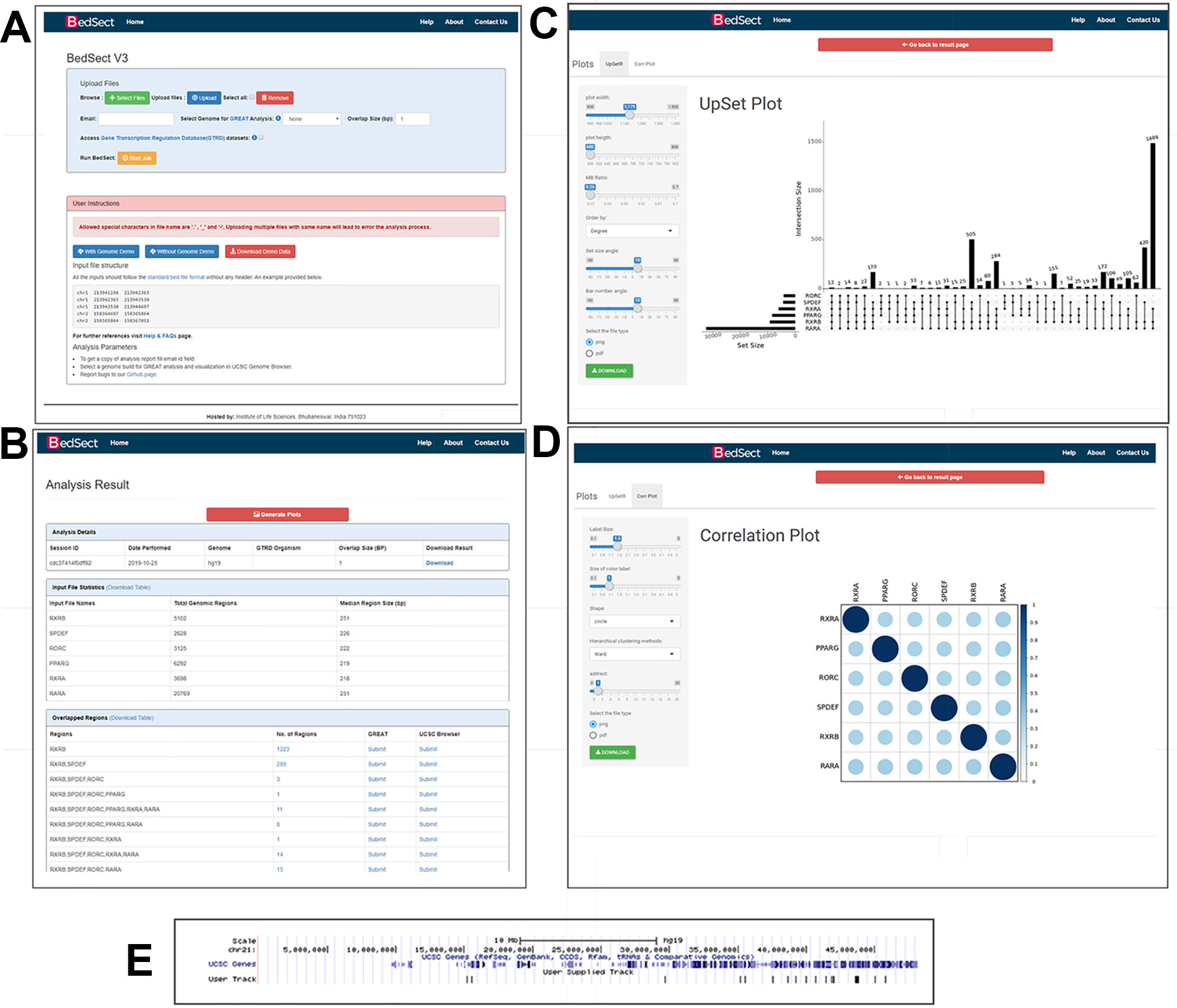 Circos
Circos Civi
Civi ClicO Free Service
ClicO Free Service CNVkit
CNVkit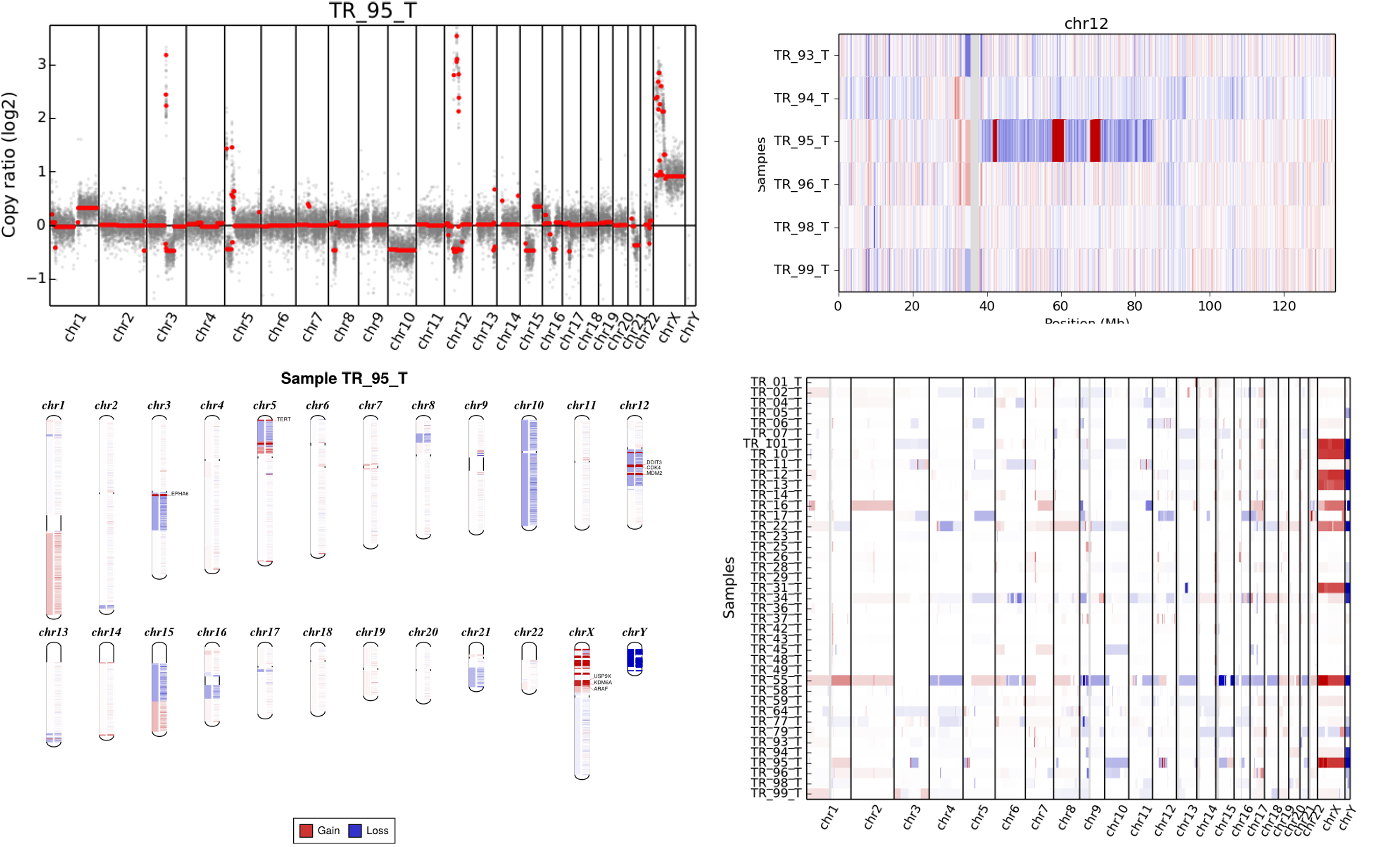 Cooler
Cooler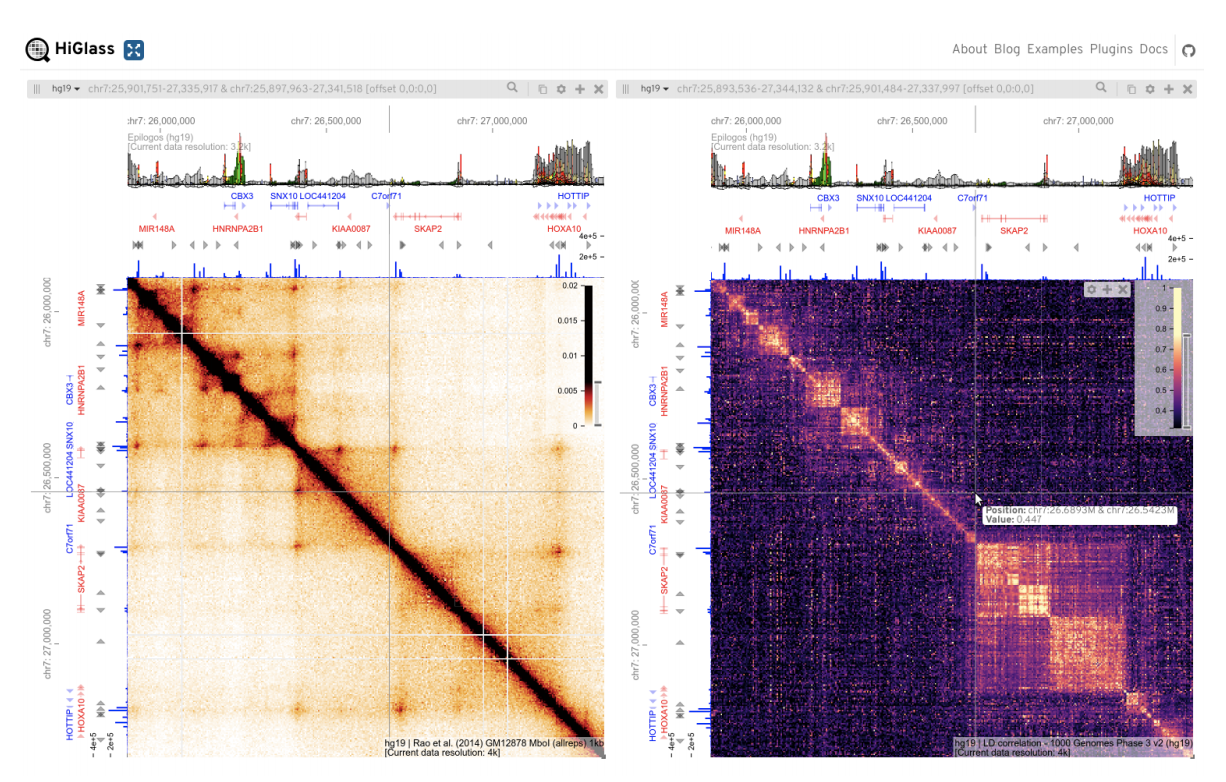 CRAMER
CRAMER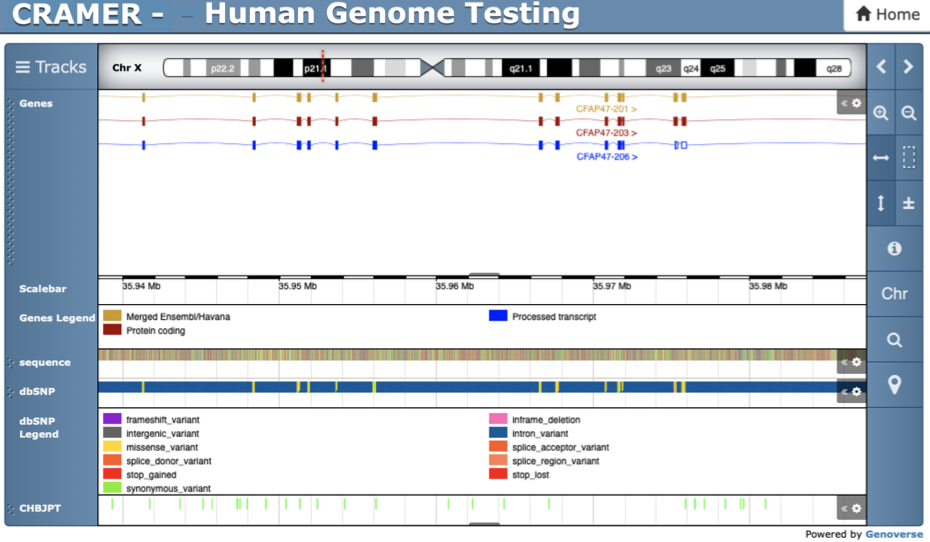 CRISPResso2
CRISPResso2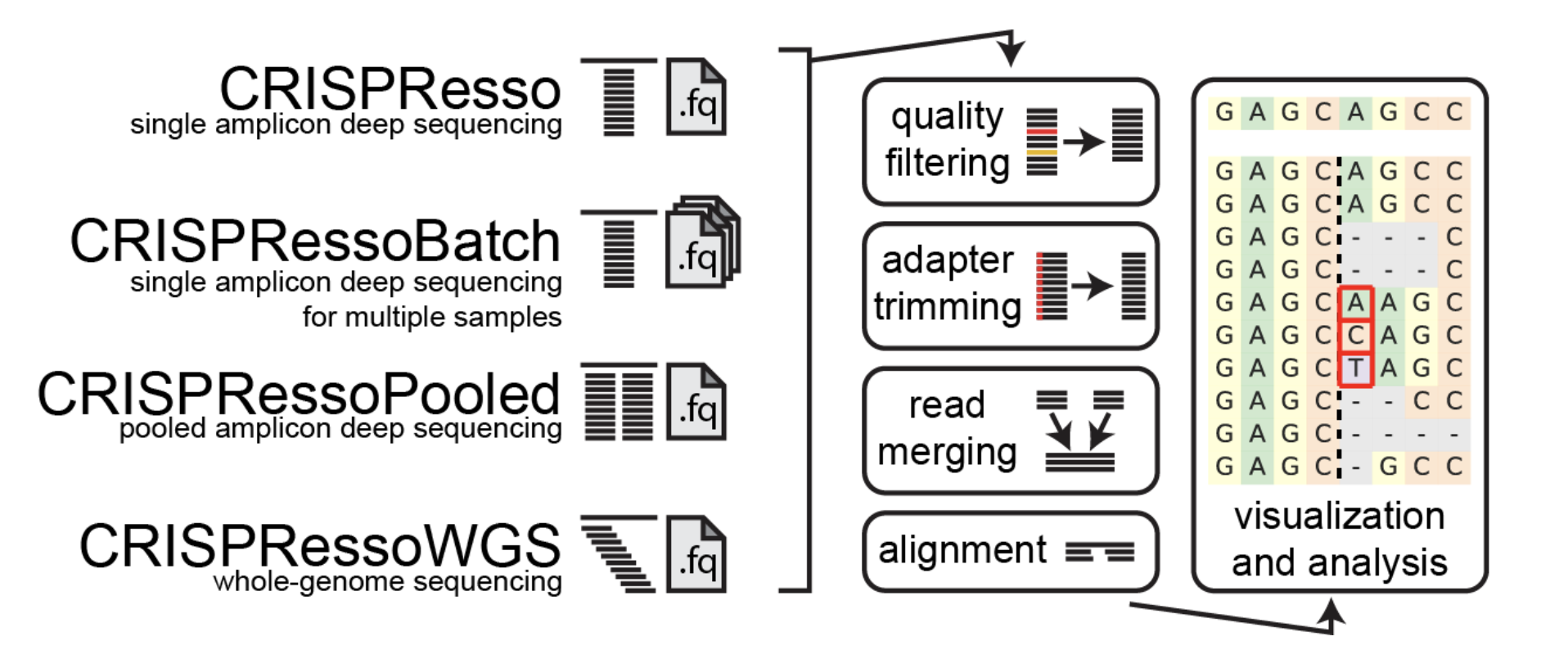 Deep Motif Dashboard
Deep Motif Dashboard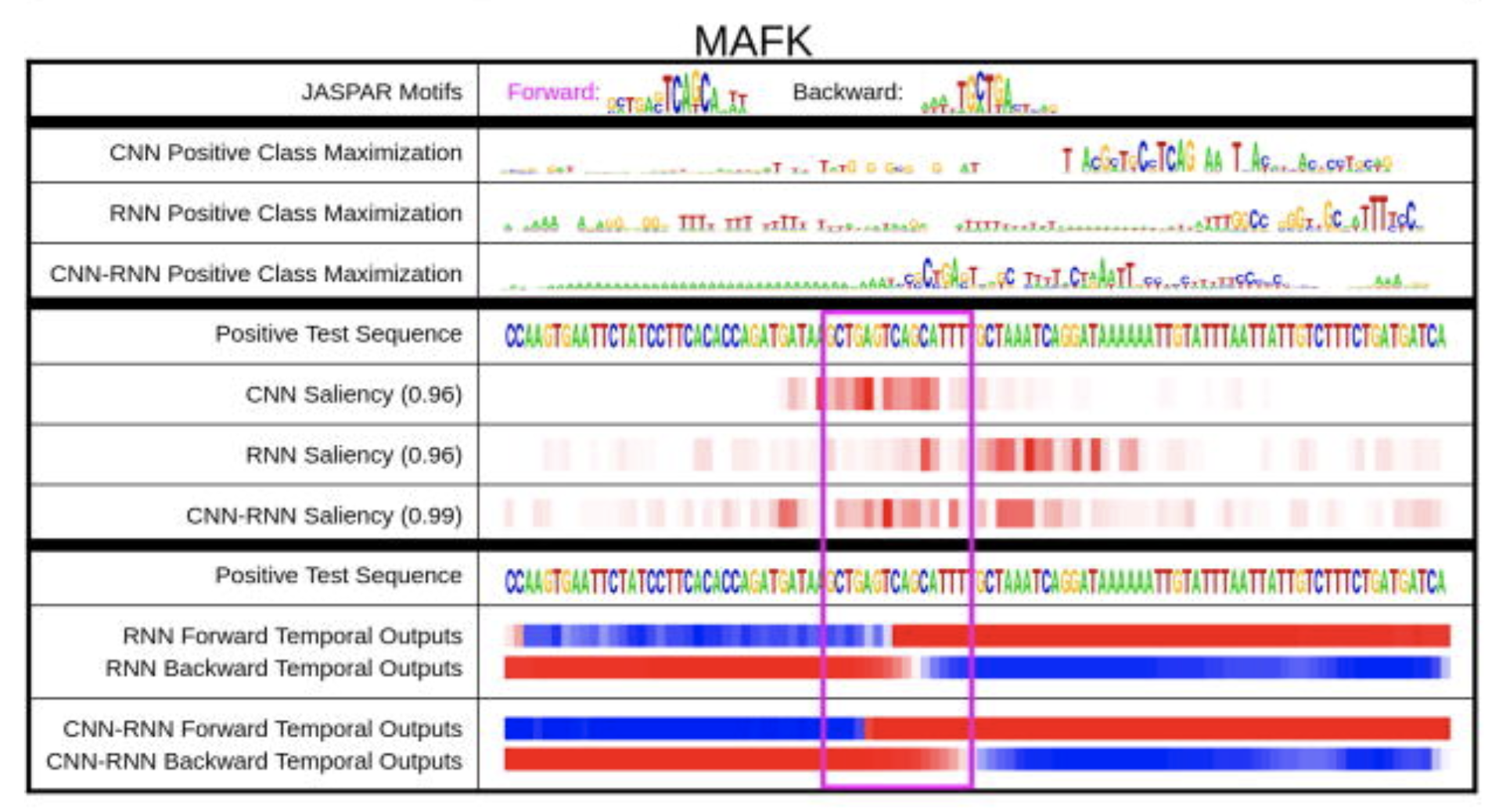 DNAPlotter
DNAPlotter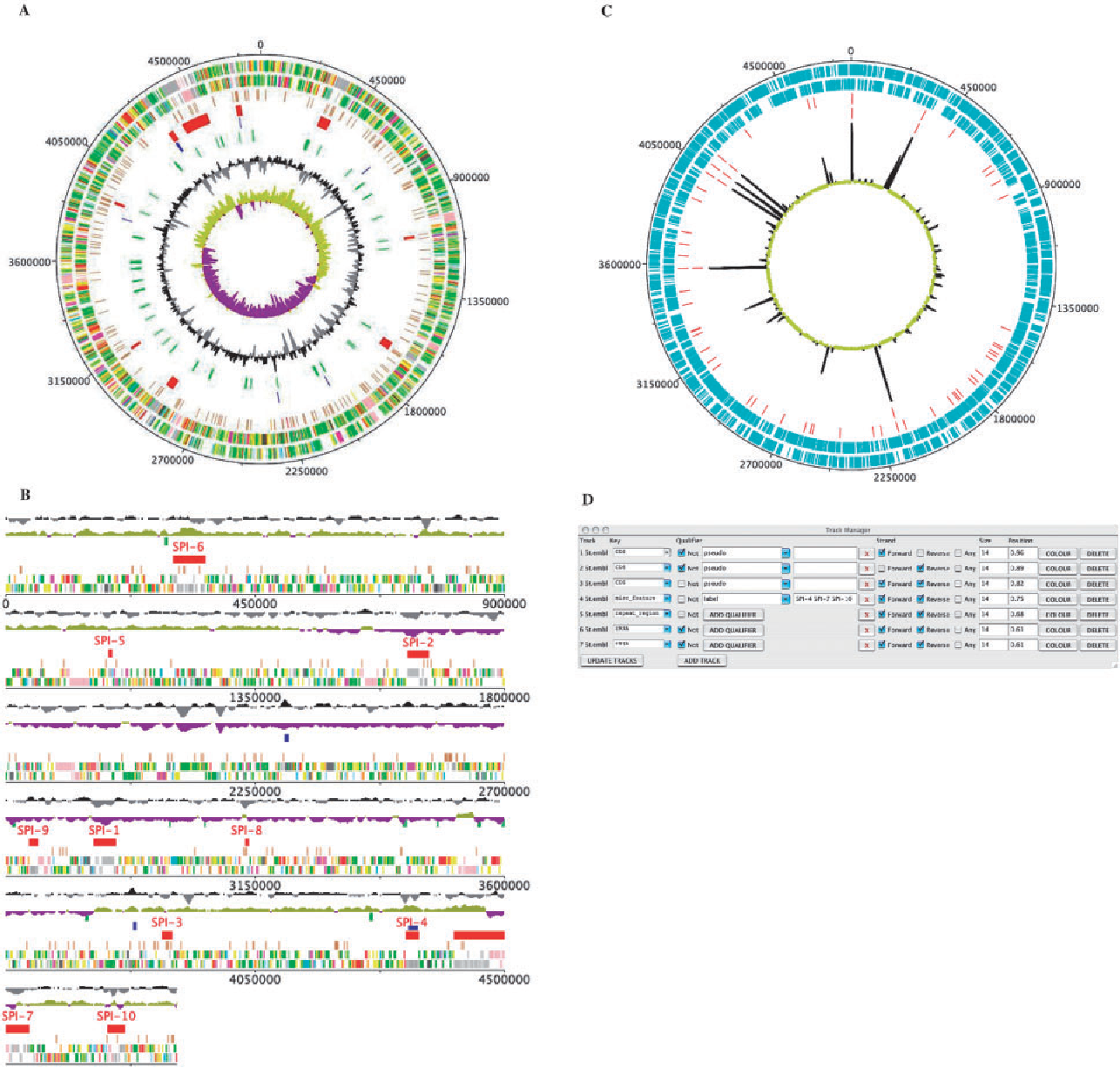 Edgar Genome Browser
Edgar Genome Browser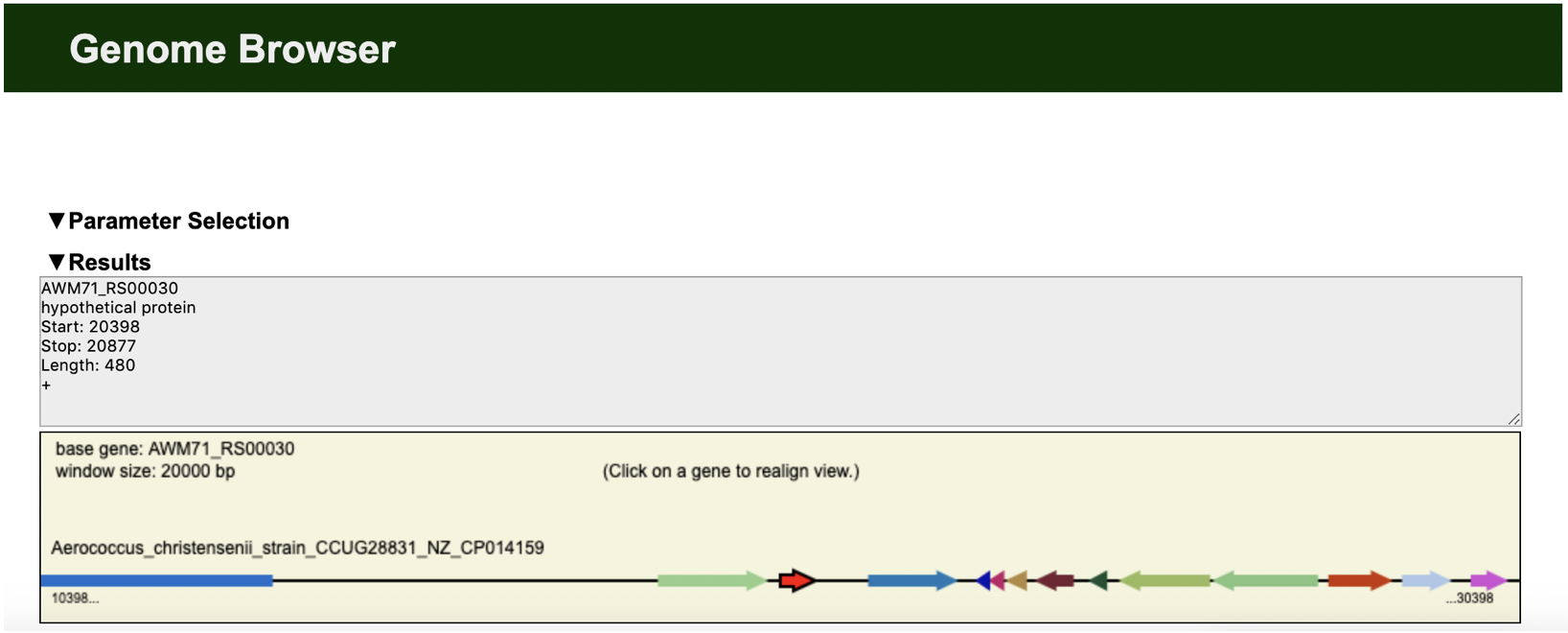 Edgar Synteny Plots
Edgar Synteny Plots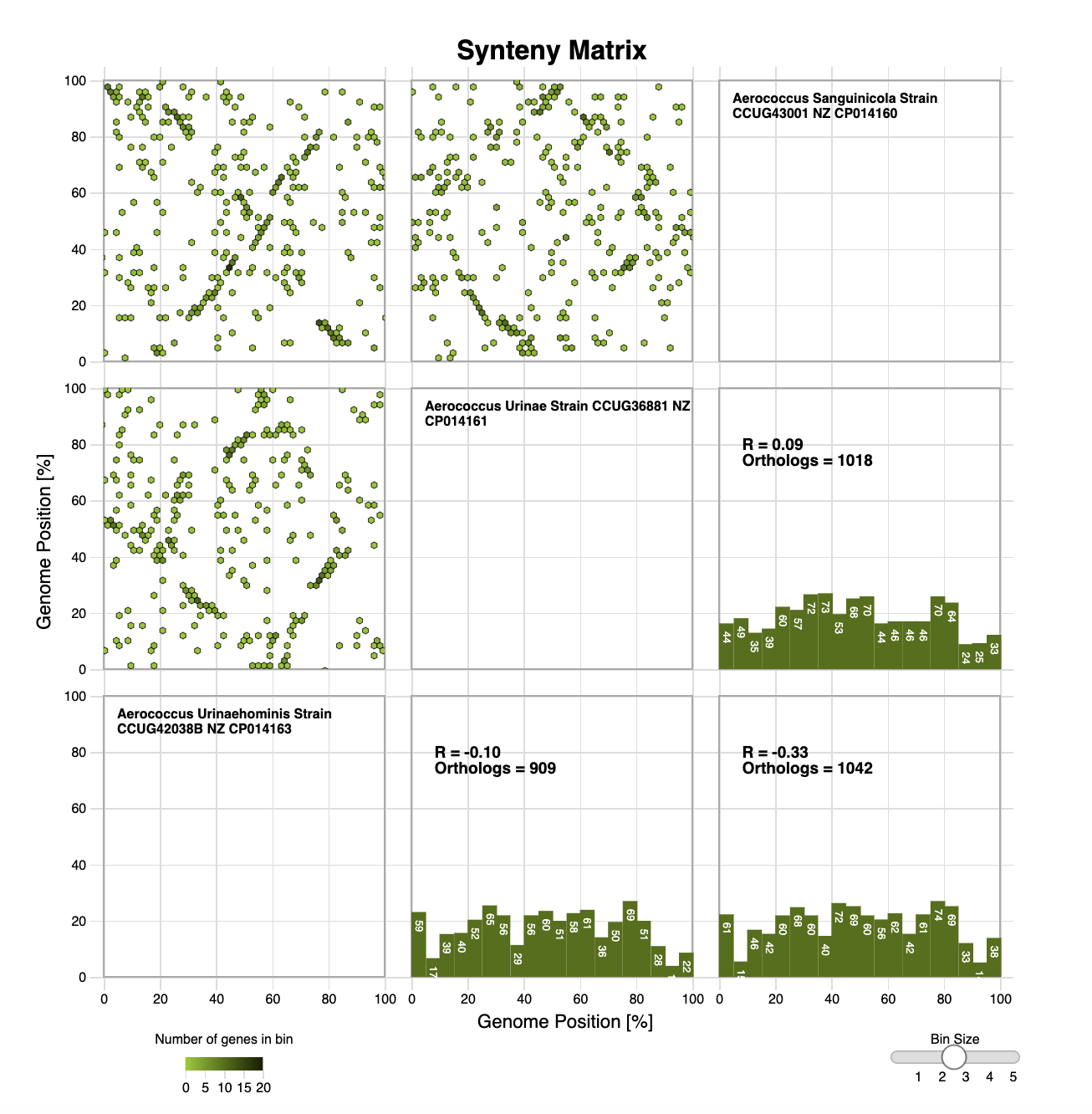 Galaxy HiCExplorer
Galaxy HiCExplorer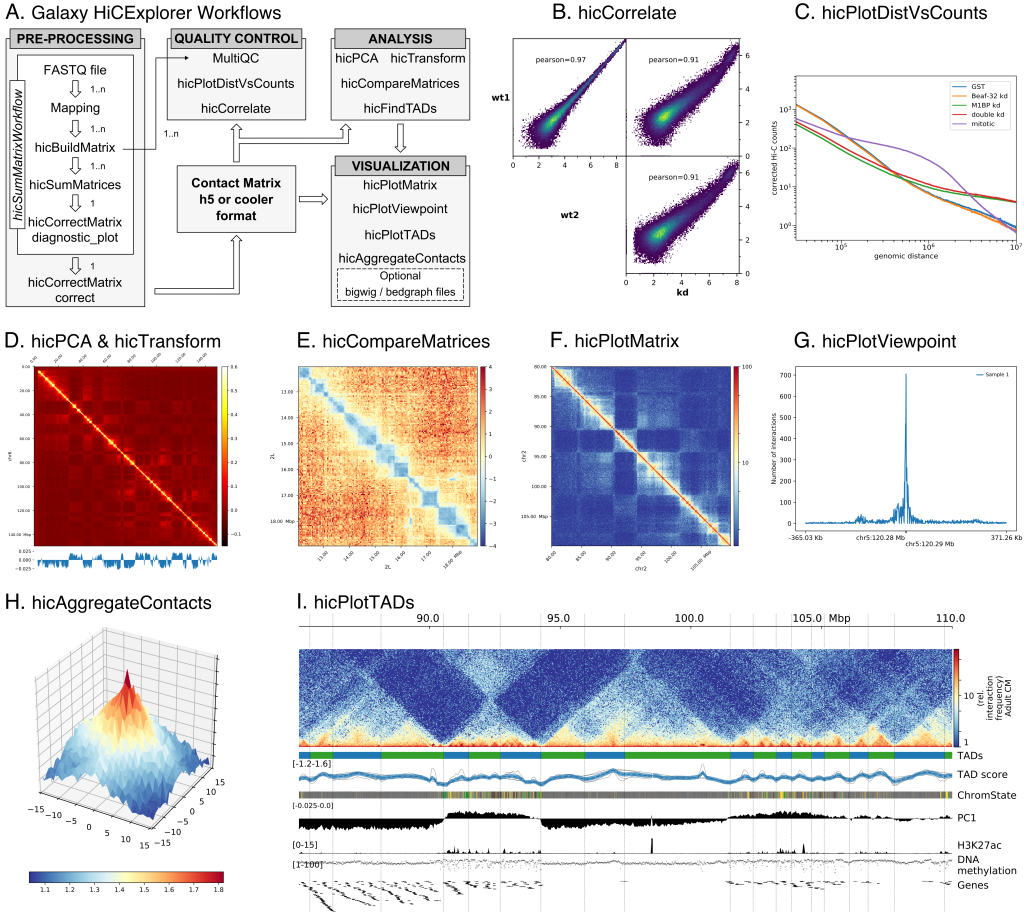 GenomeRing
GenomeRing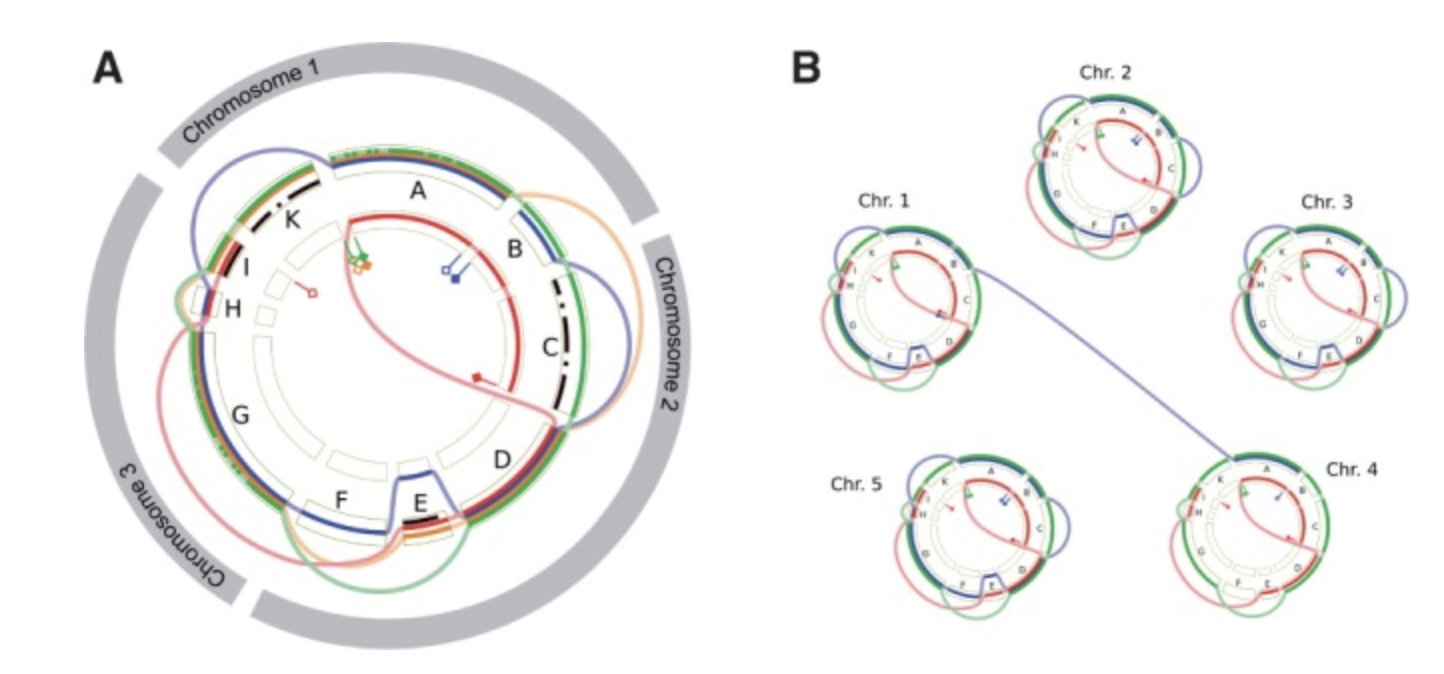 Gepard
Gepard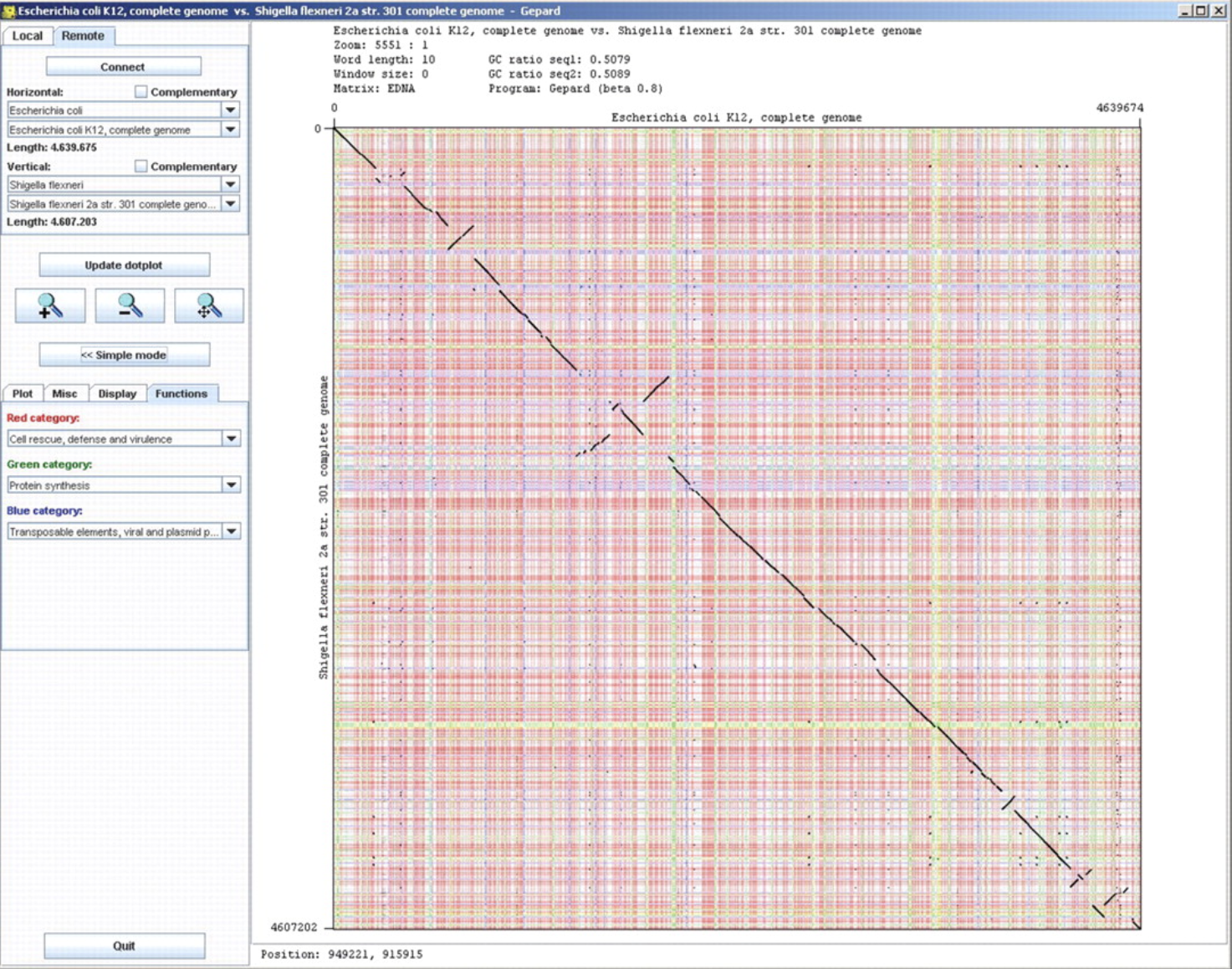 ggBio
ggBio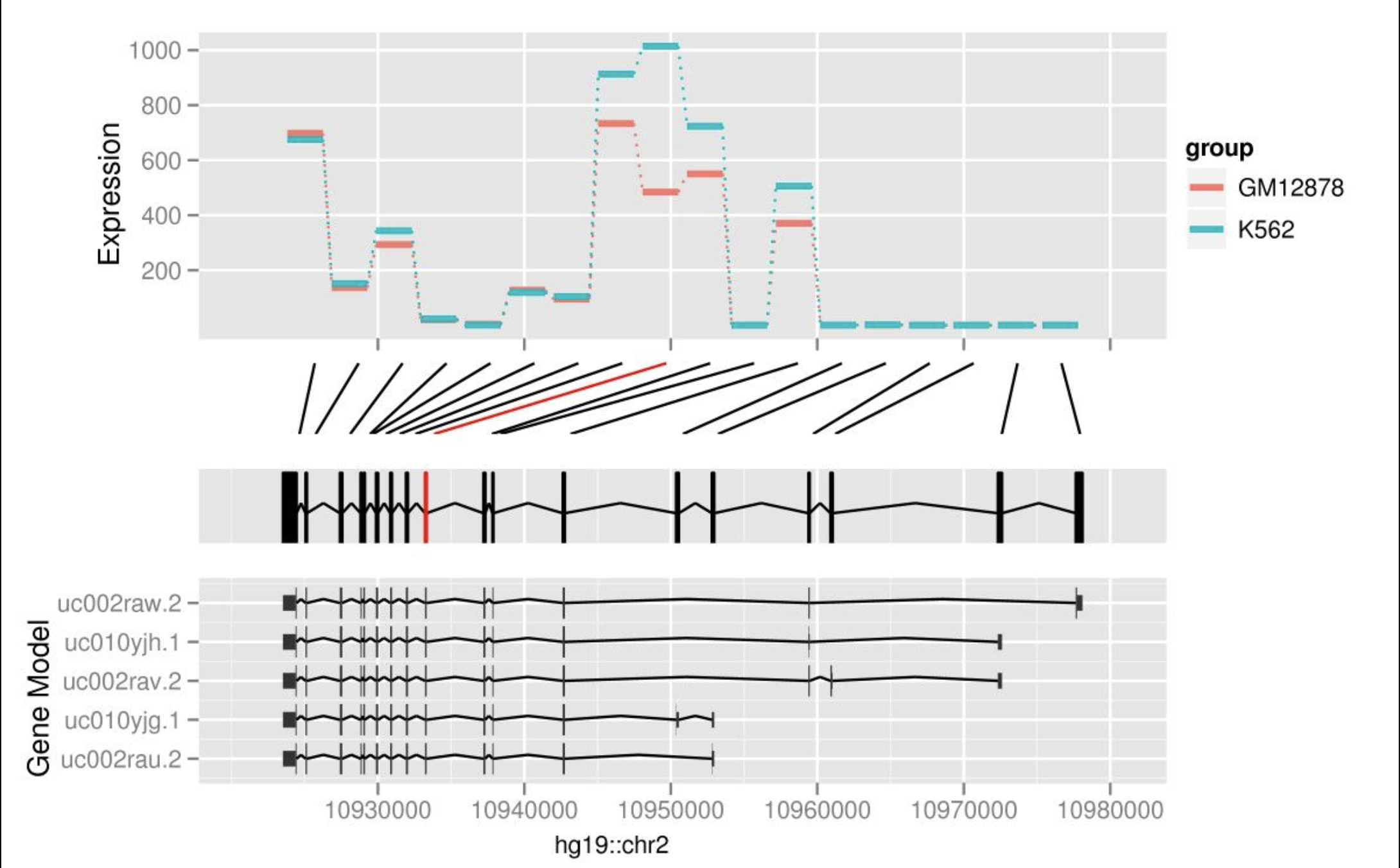 Gremlin
Gremlin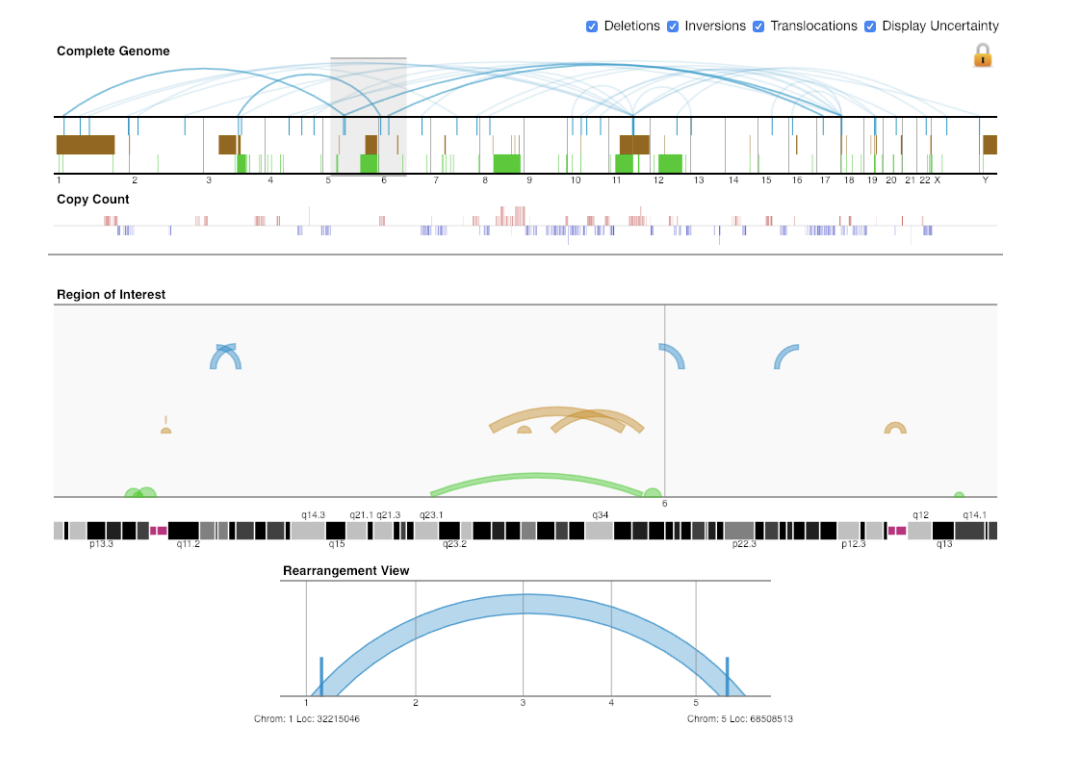 HiGlass
HiGlass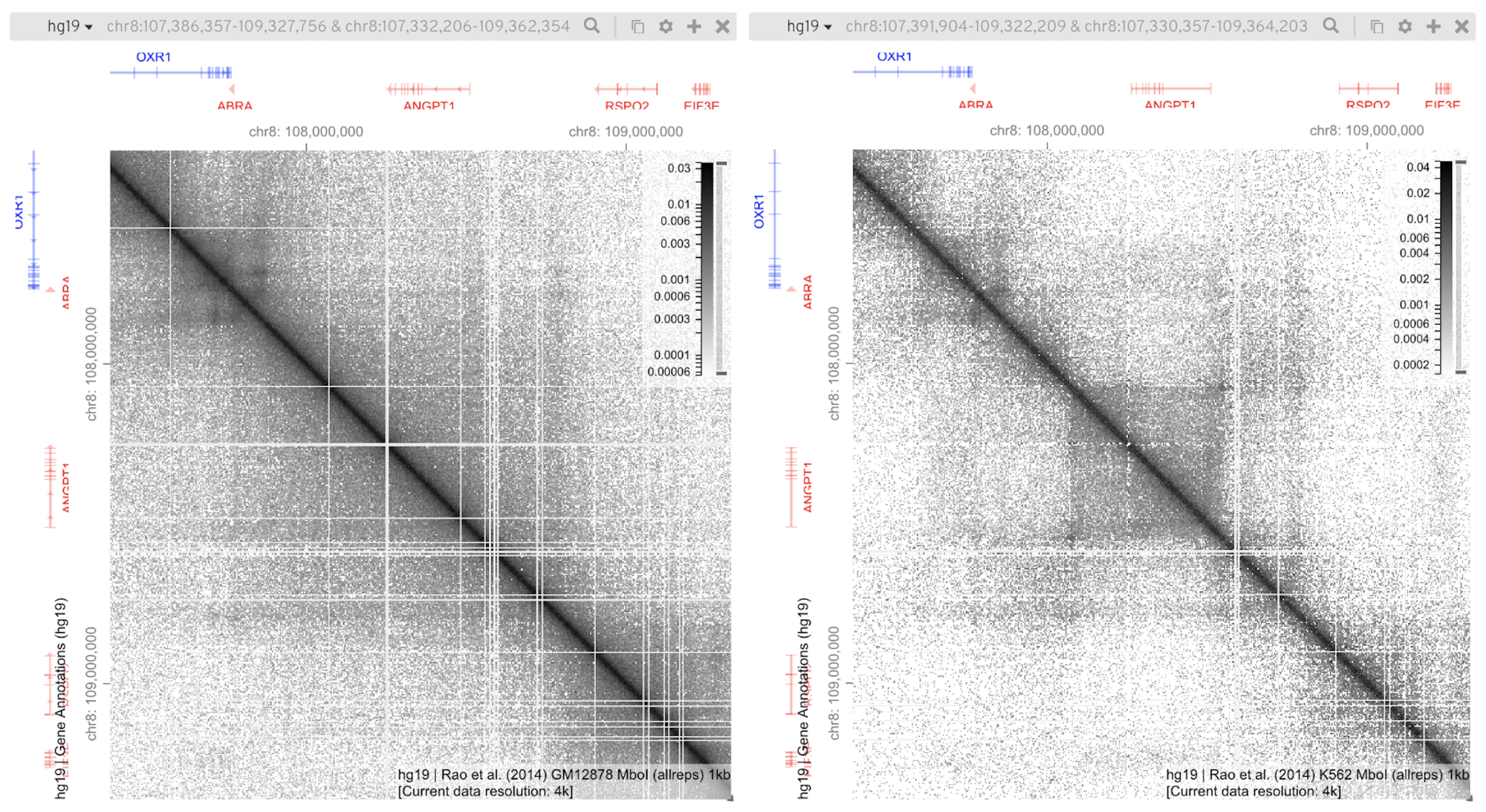 HilbertCurve
HilbertCurve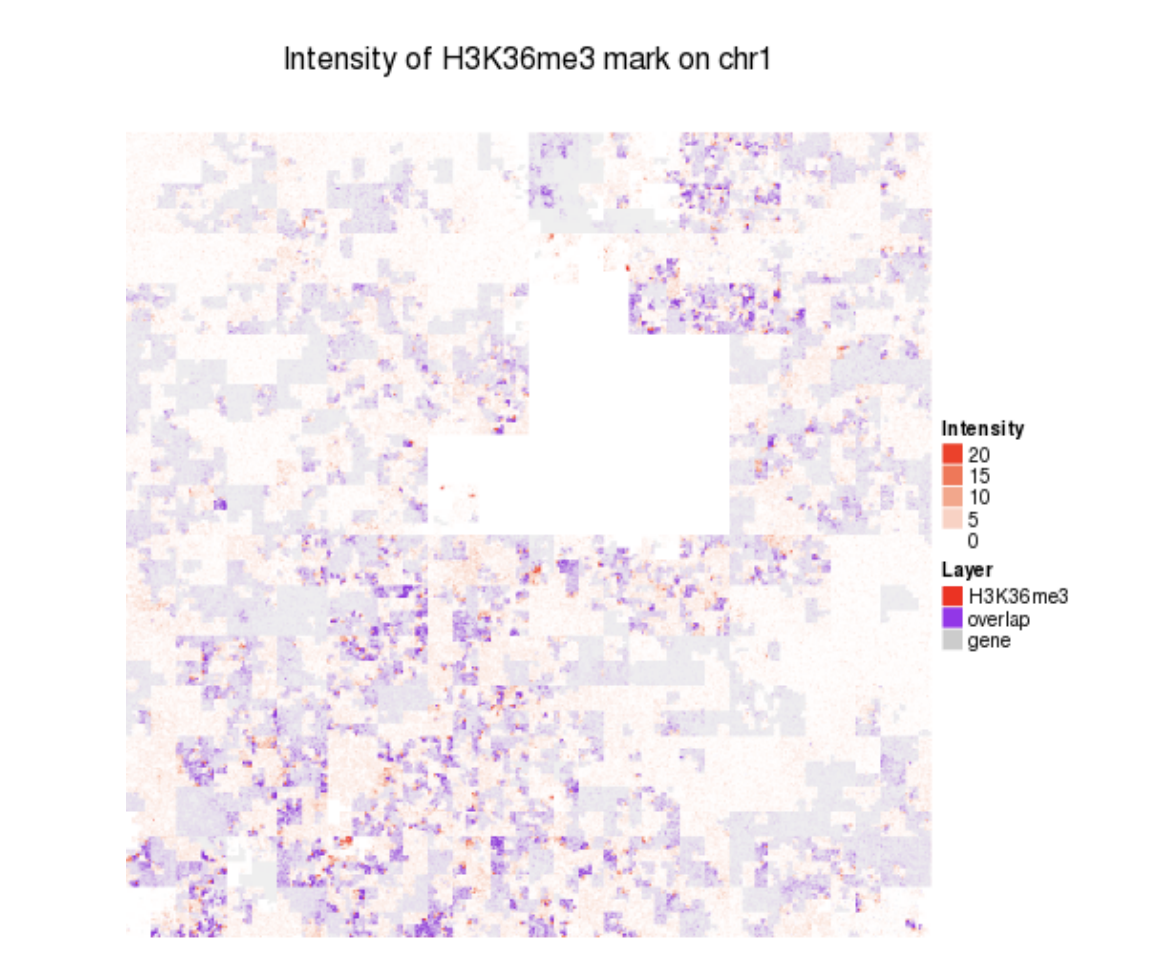 HilbertVis
HilbertVis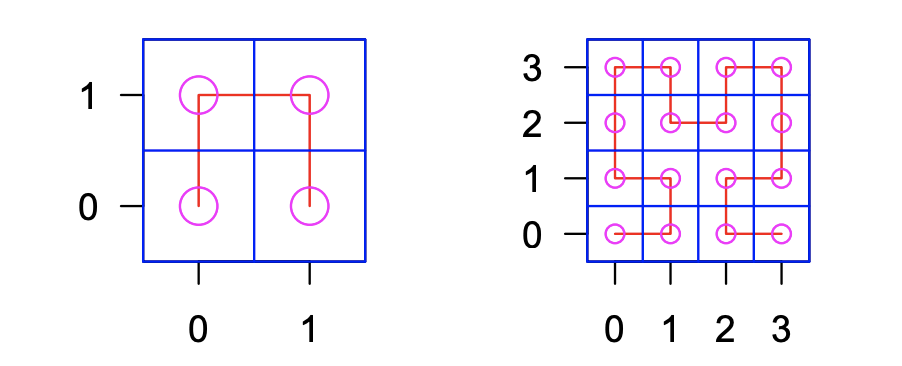 HiPiler
HiPiler IGB
IGB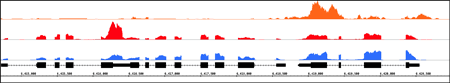 Integrative Genomics Viewer
Integrative Genomics Viewer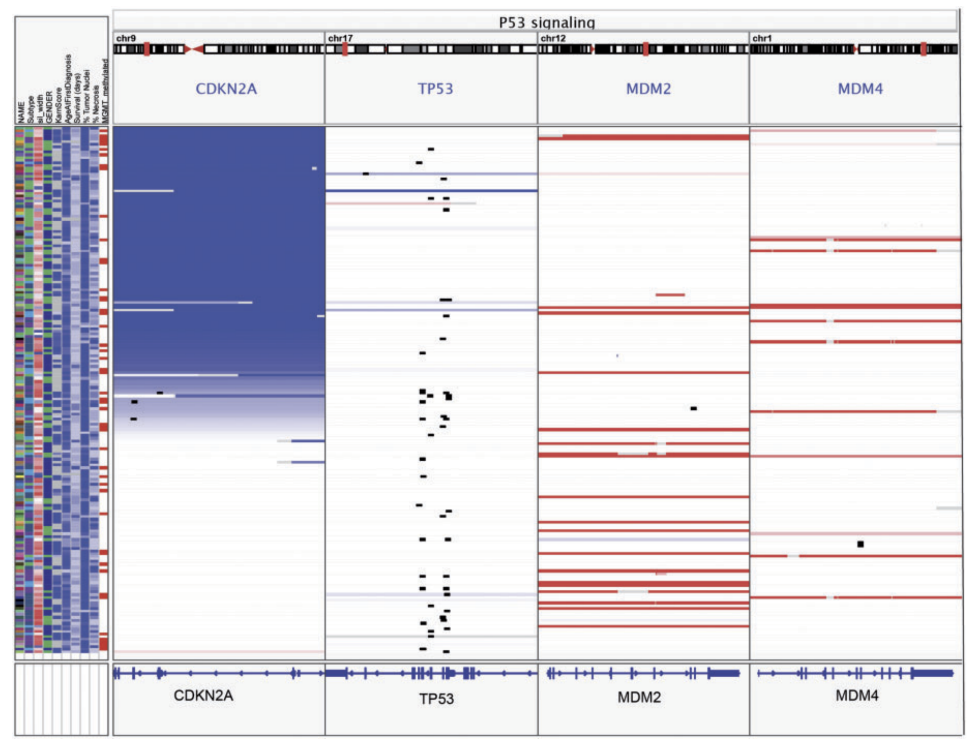 J-Circos
J-Circos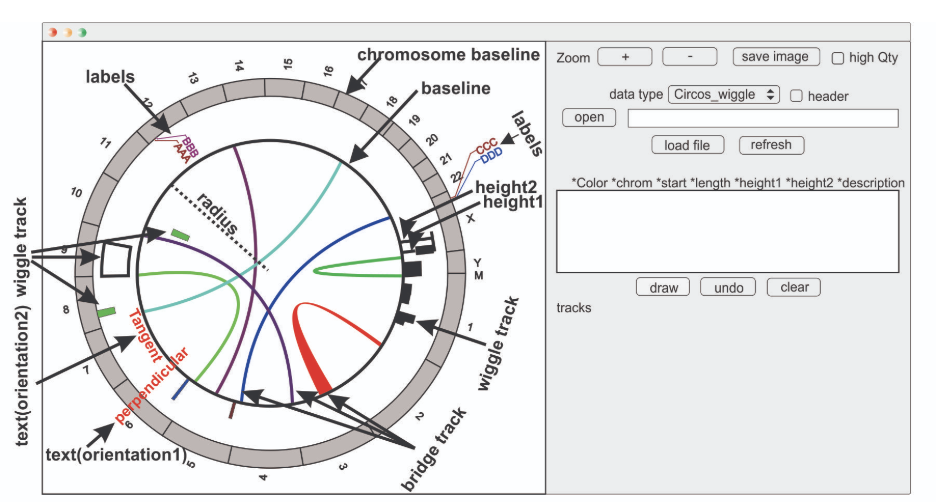 JuiceBox
JuiceBox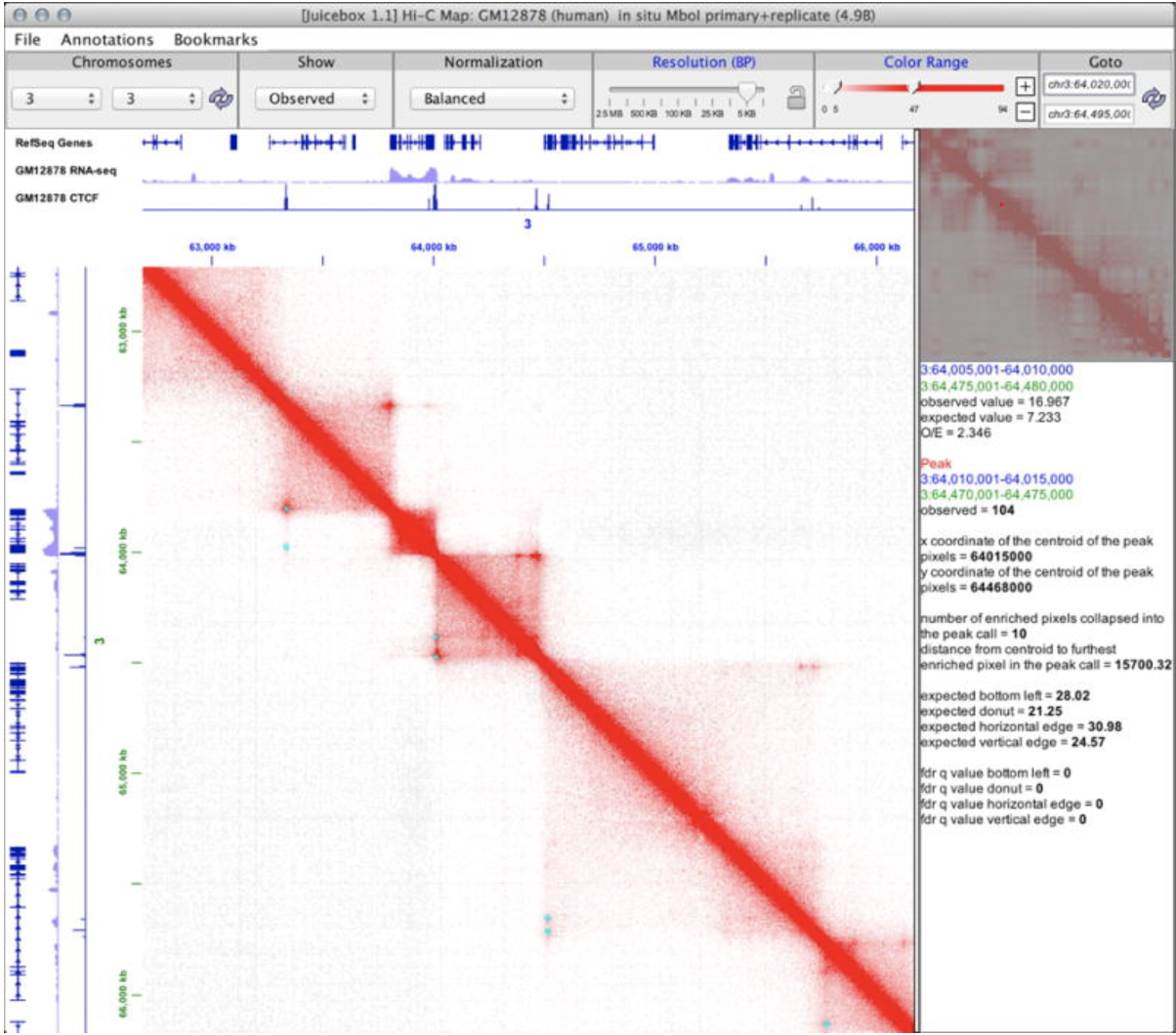 Juiceboxjs
Juiceboxjs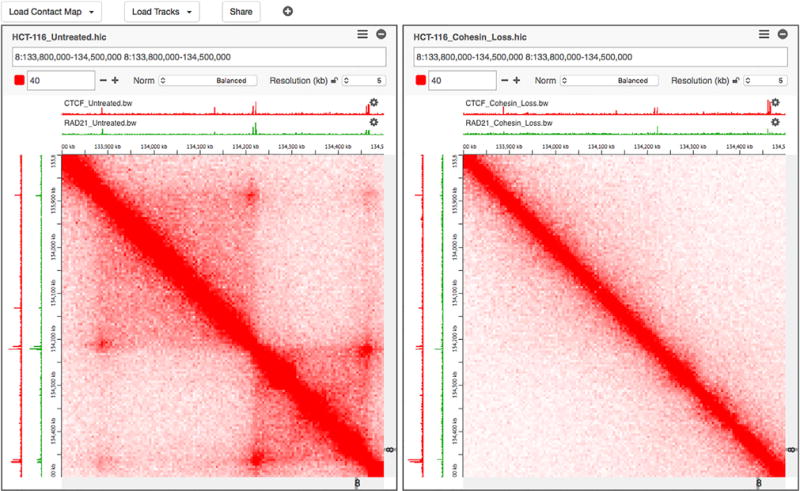 Lollipop Plot cBio
Lollipop Plot cBio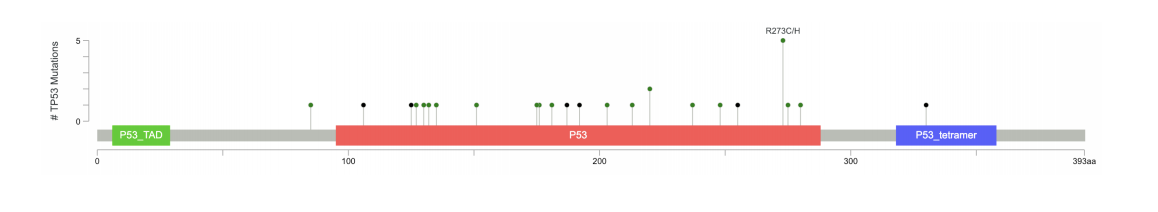 MEME
MEME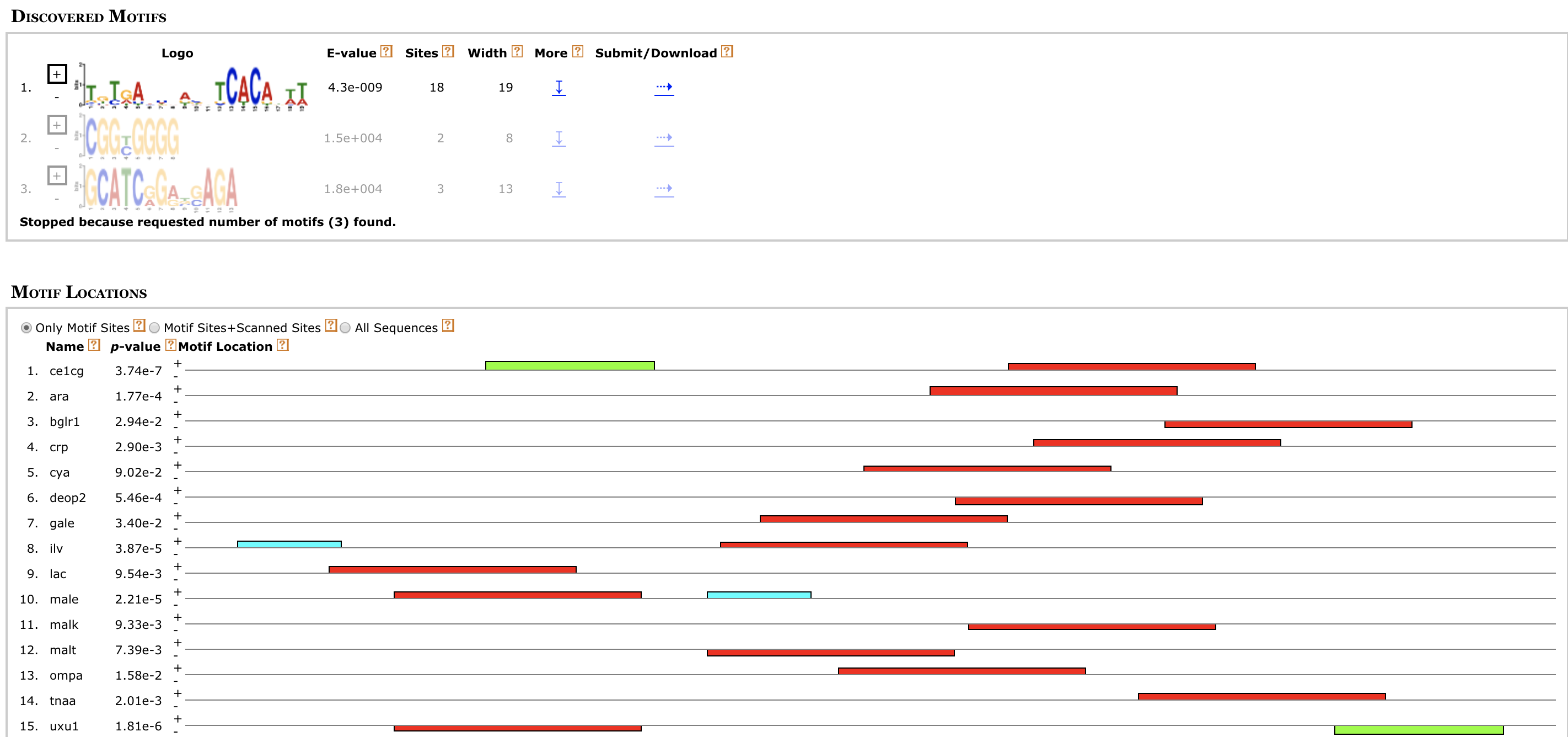 MEXPRESS
MEXPRESS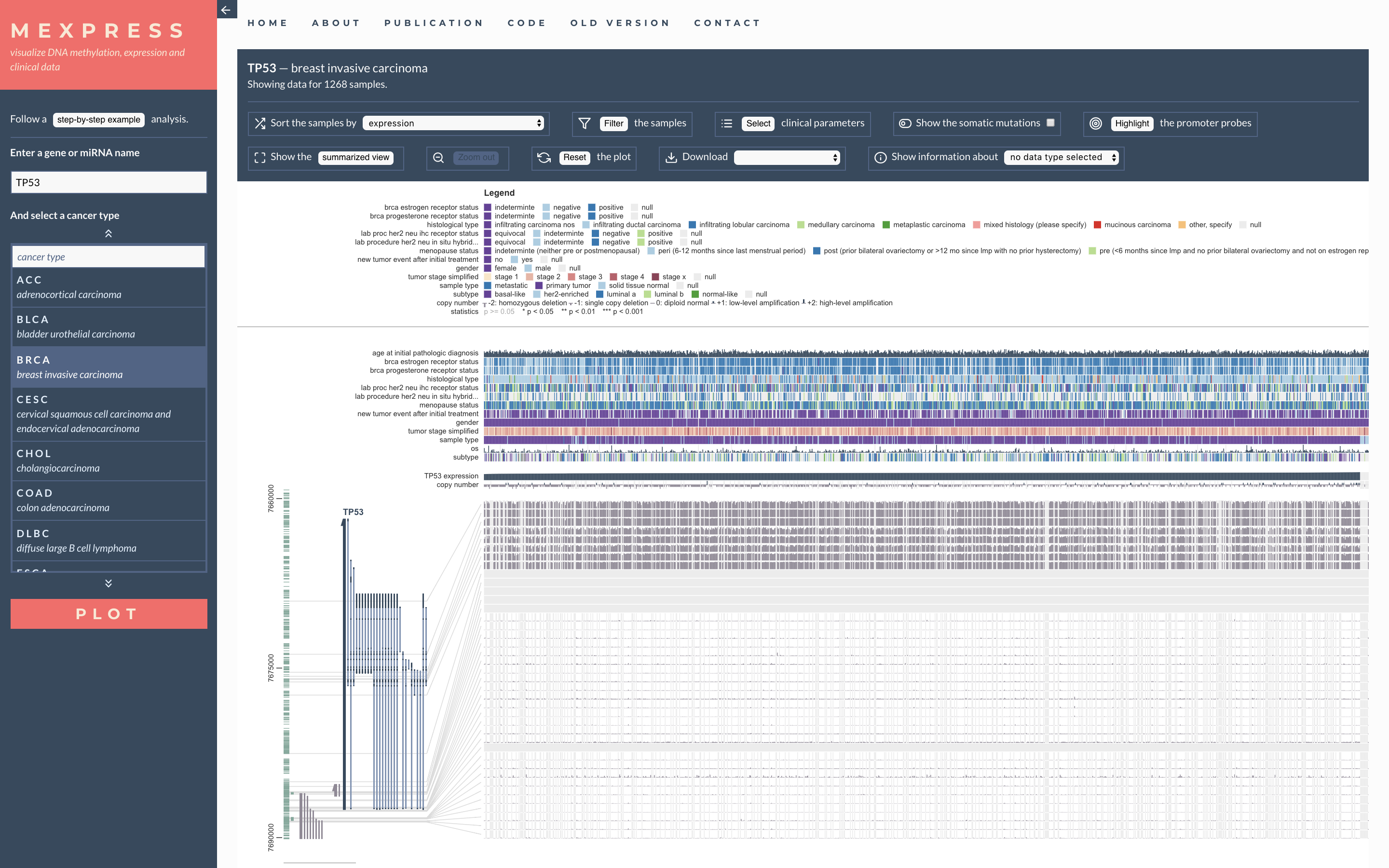 MGcV
MGcV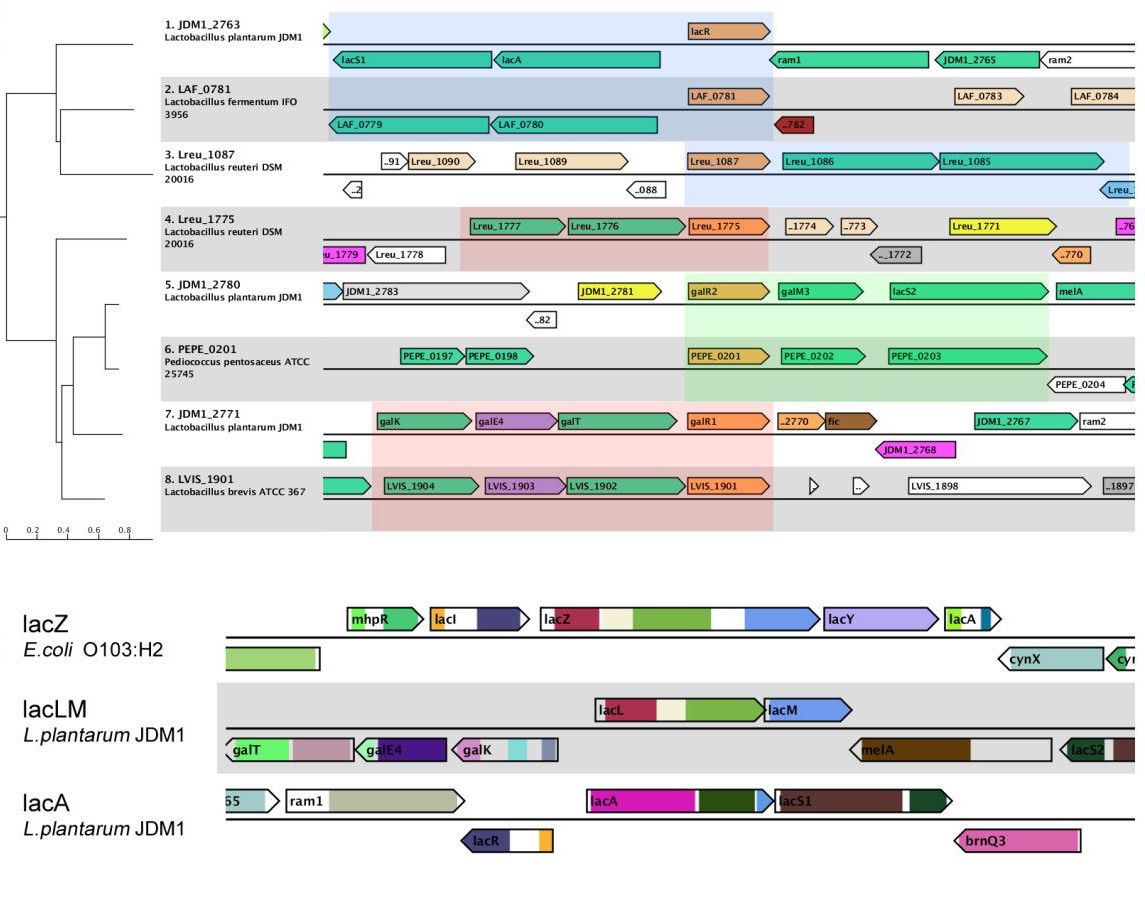 MicroScope
MicroScope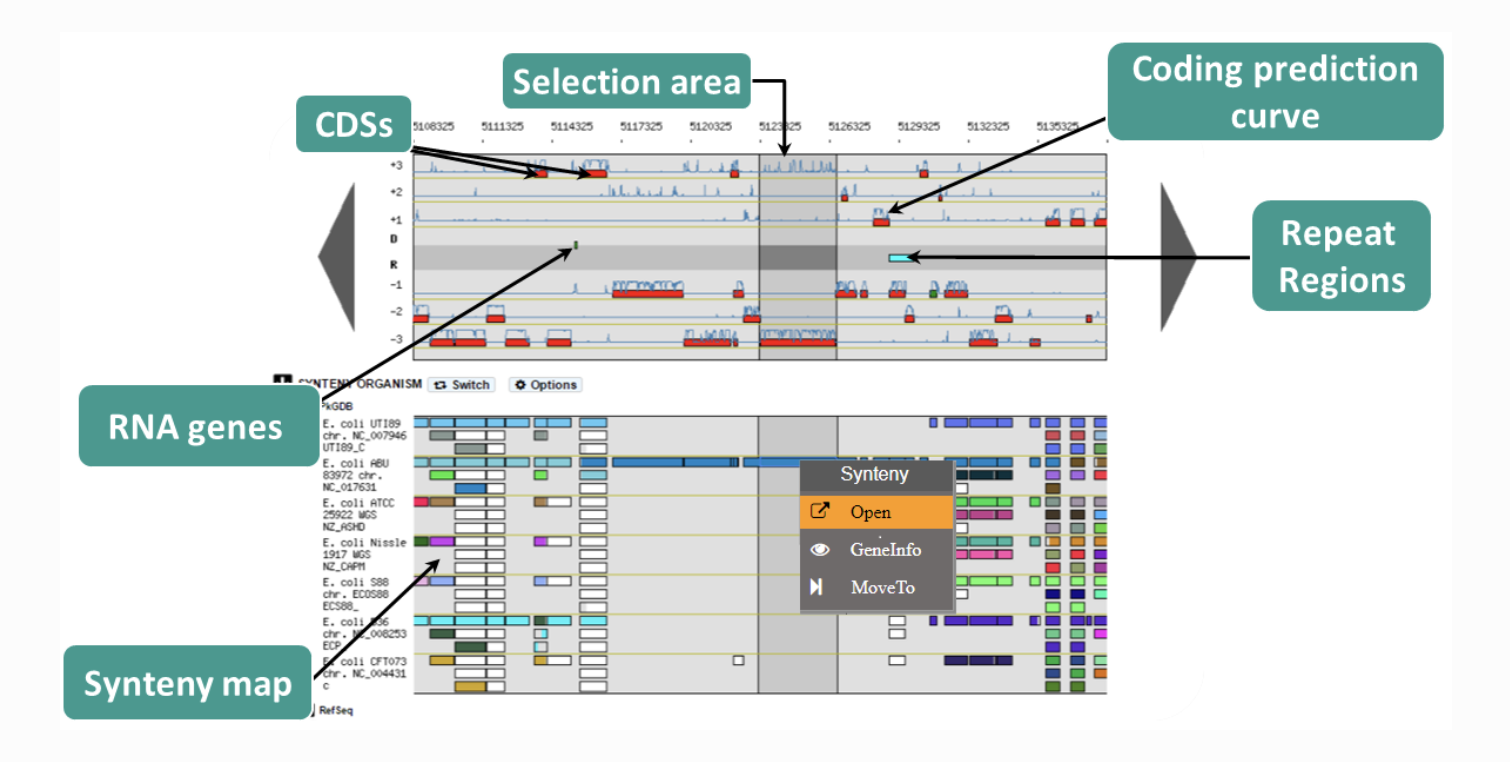 MizBee
MizBee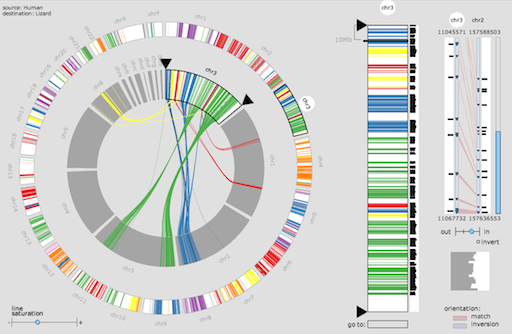 MSAViewer
MSAViewer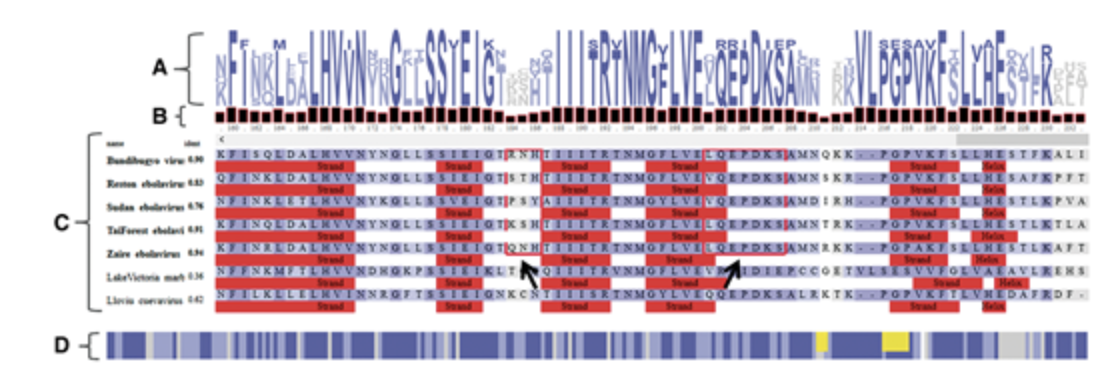 my5c
my5c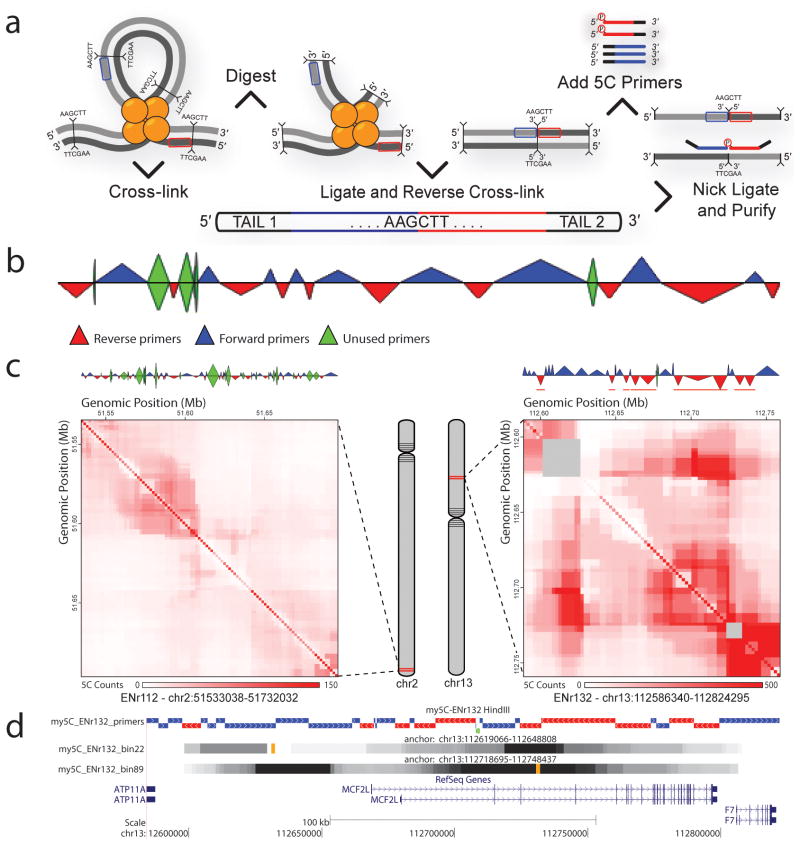 ngs.plot
ngs.plot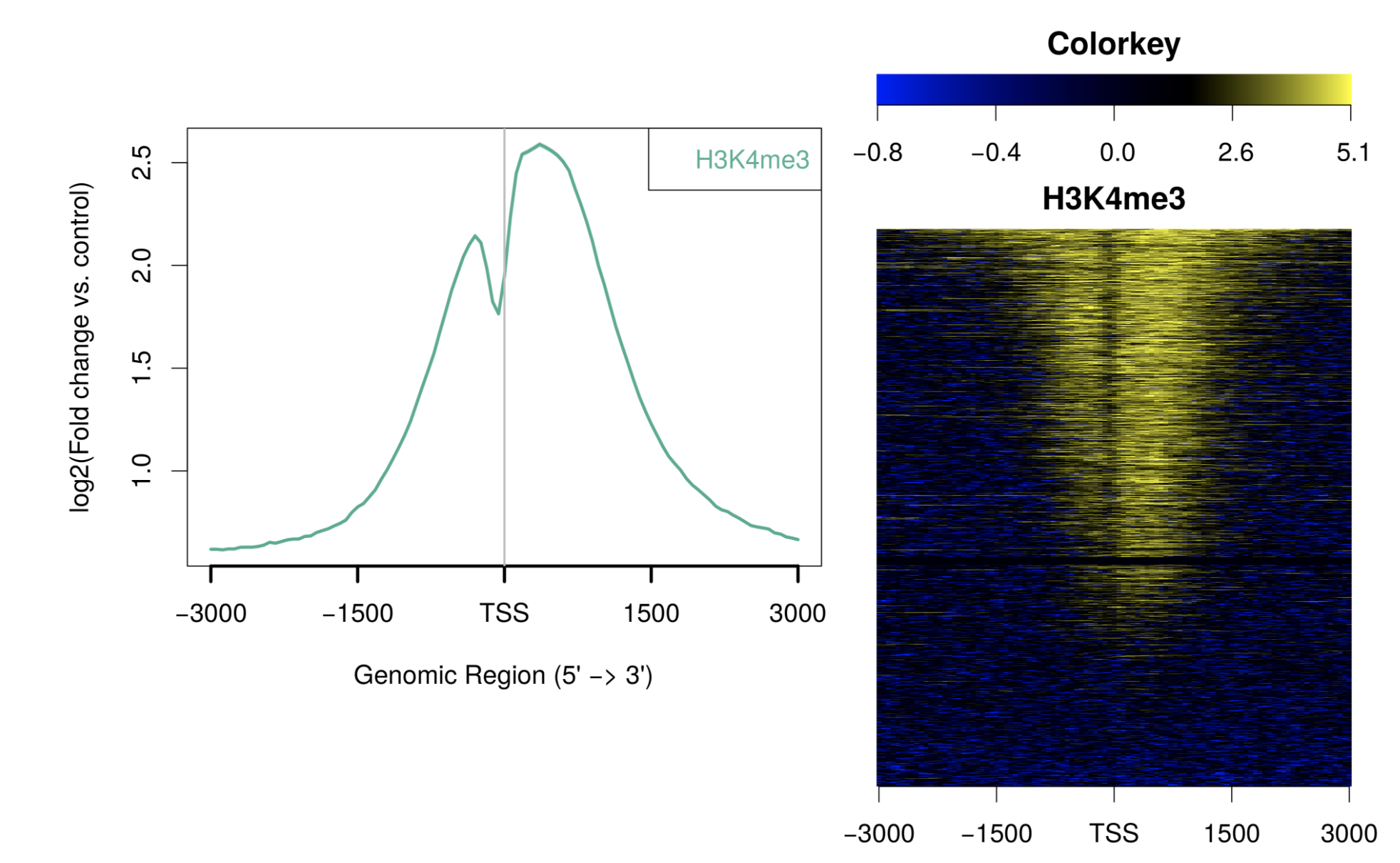 Oviz-Bio
Oviz-Bio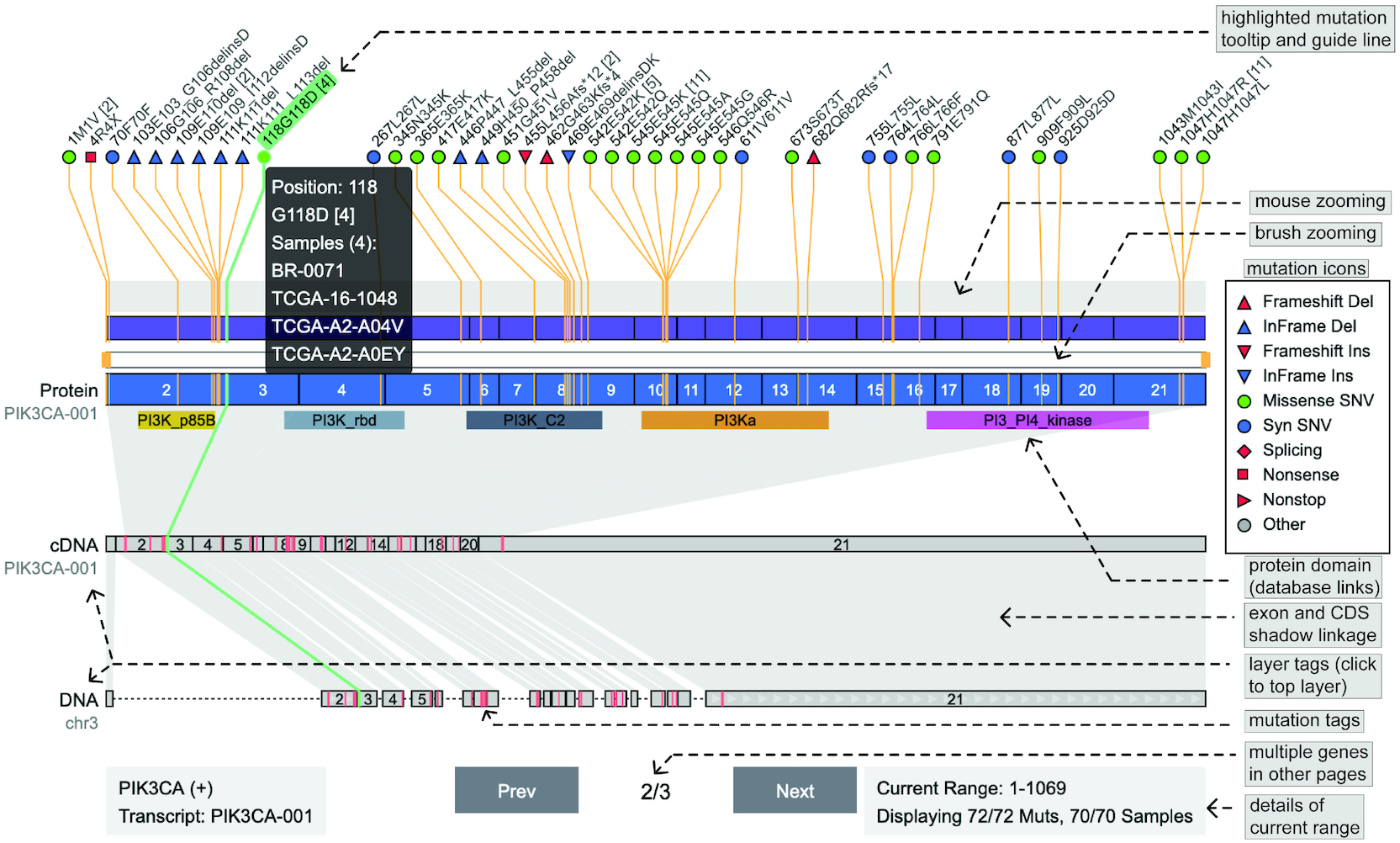 pLogo
pLogo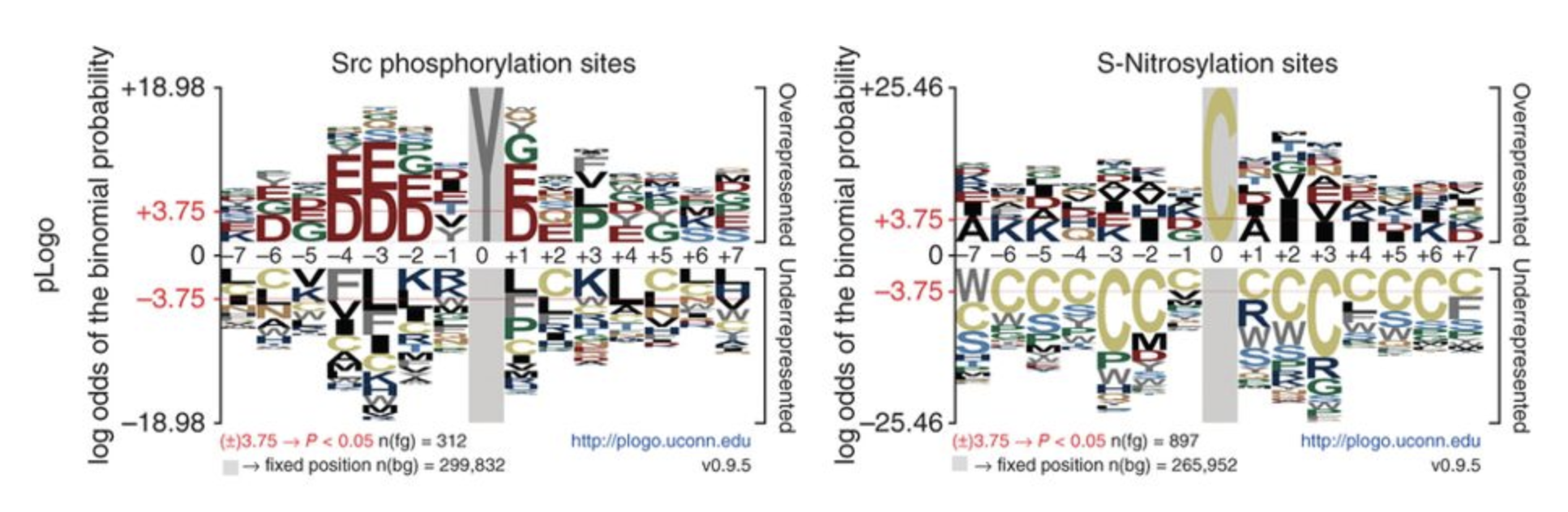 Rondo
Rondo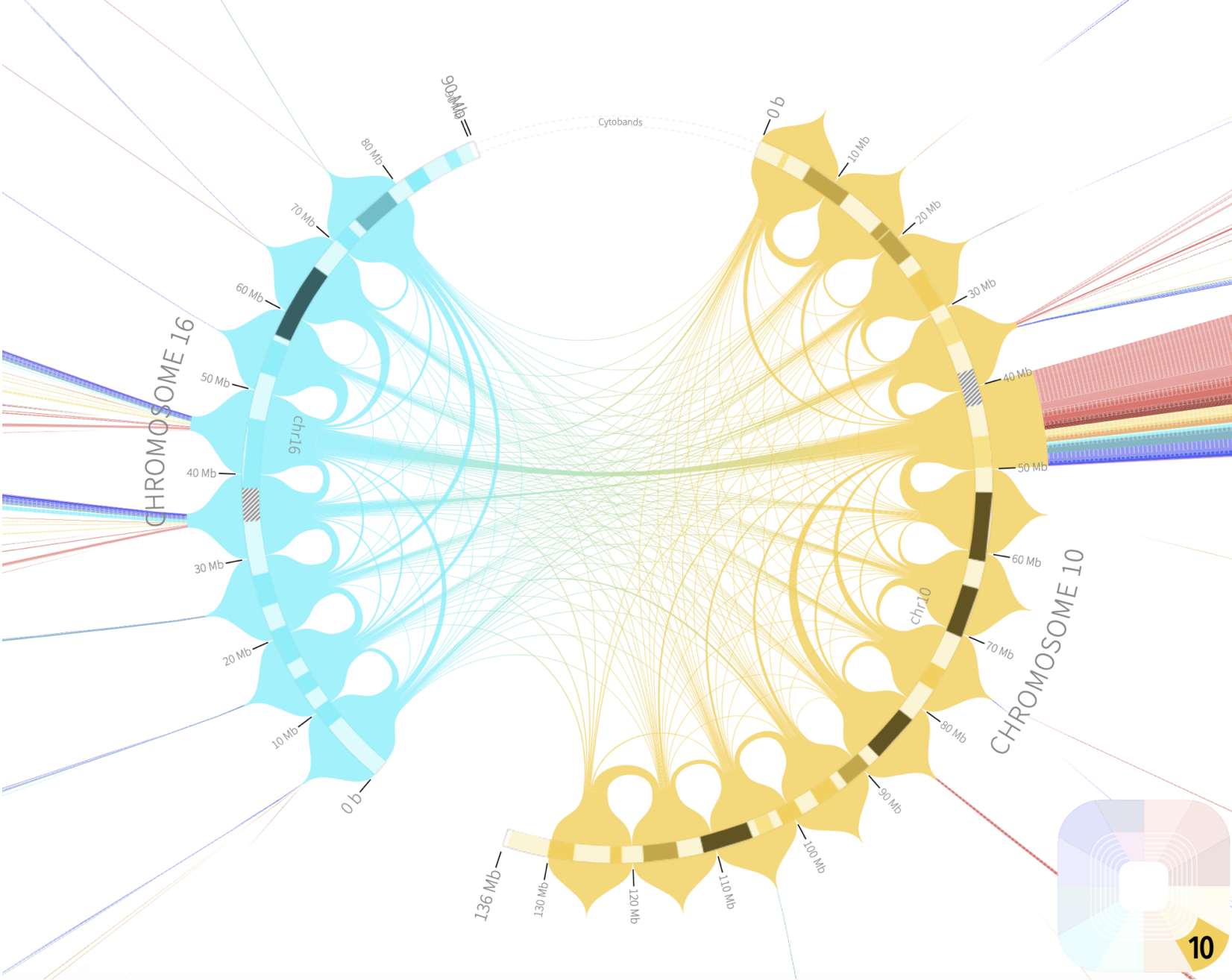 Sashimi Plot
Sashimi Plot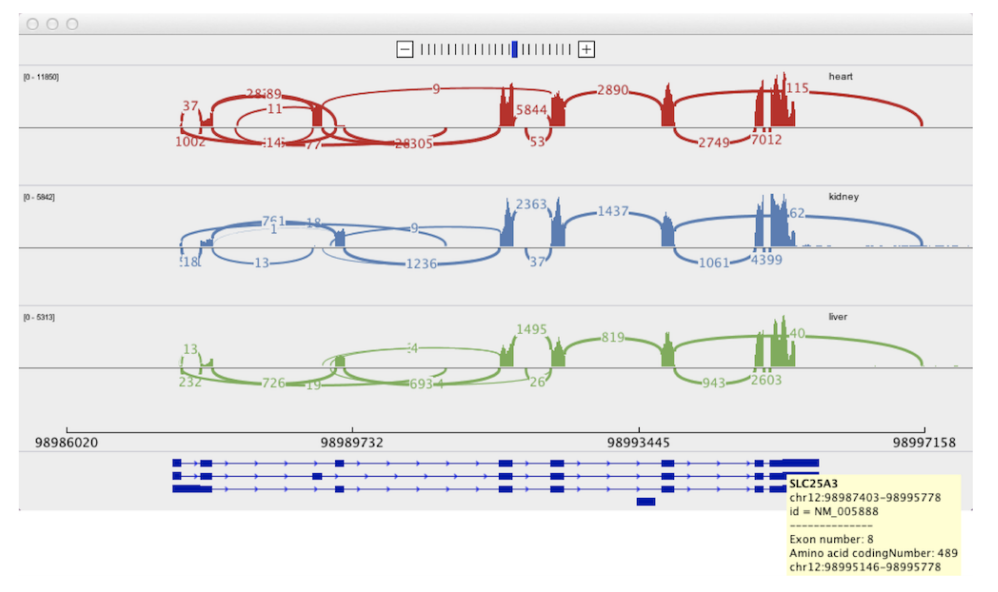 SCGV
SCGV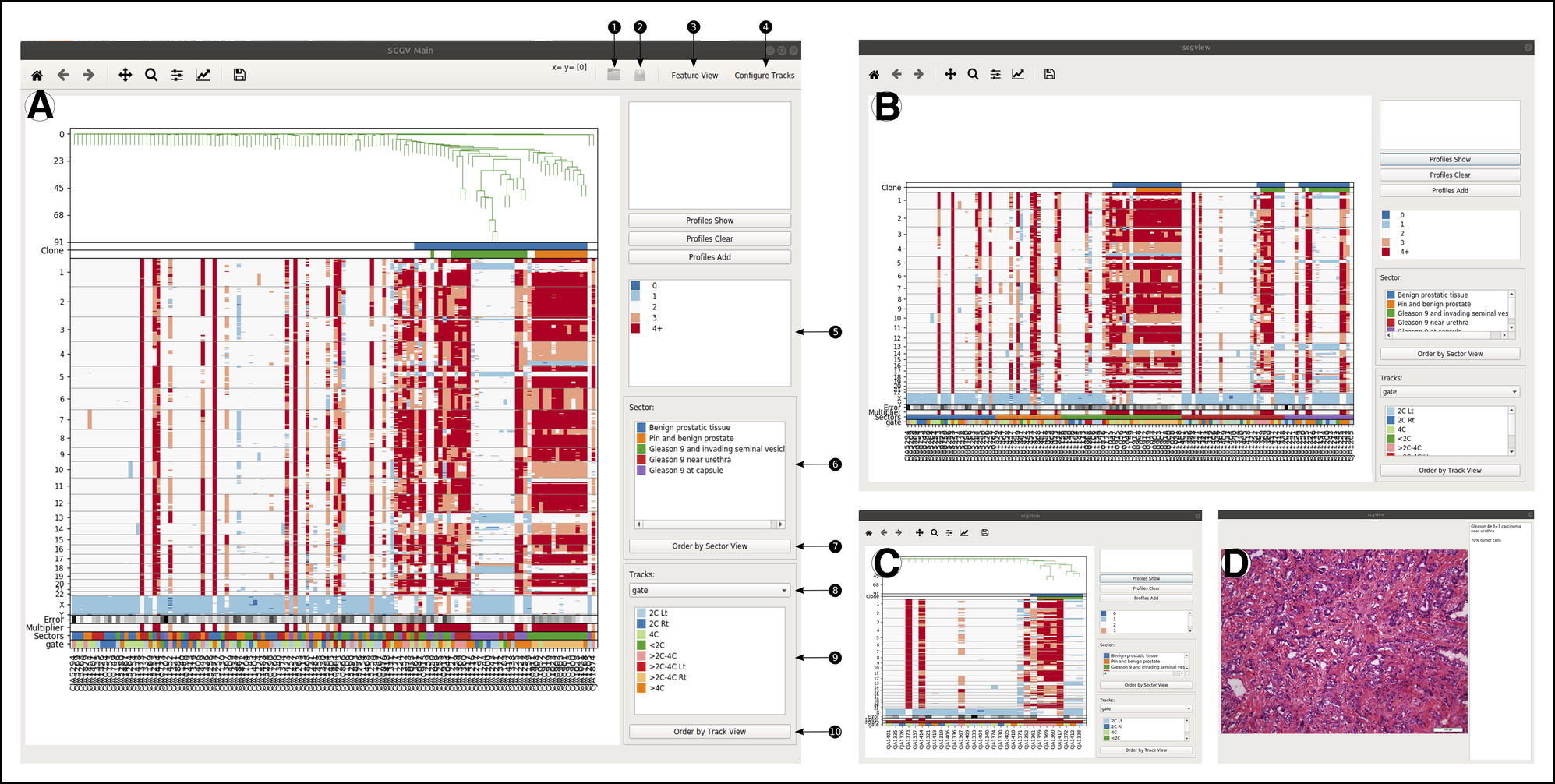 Sequence Bundles
Sequence Bundles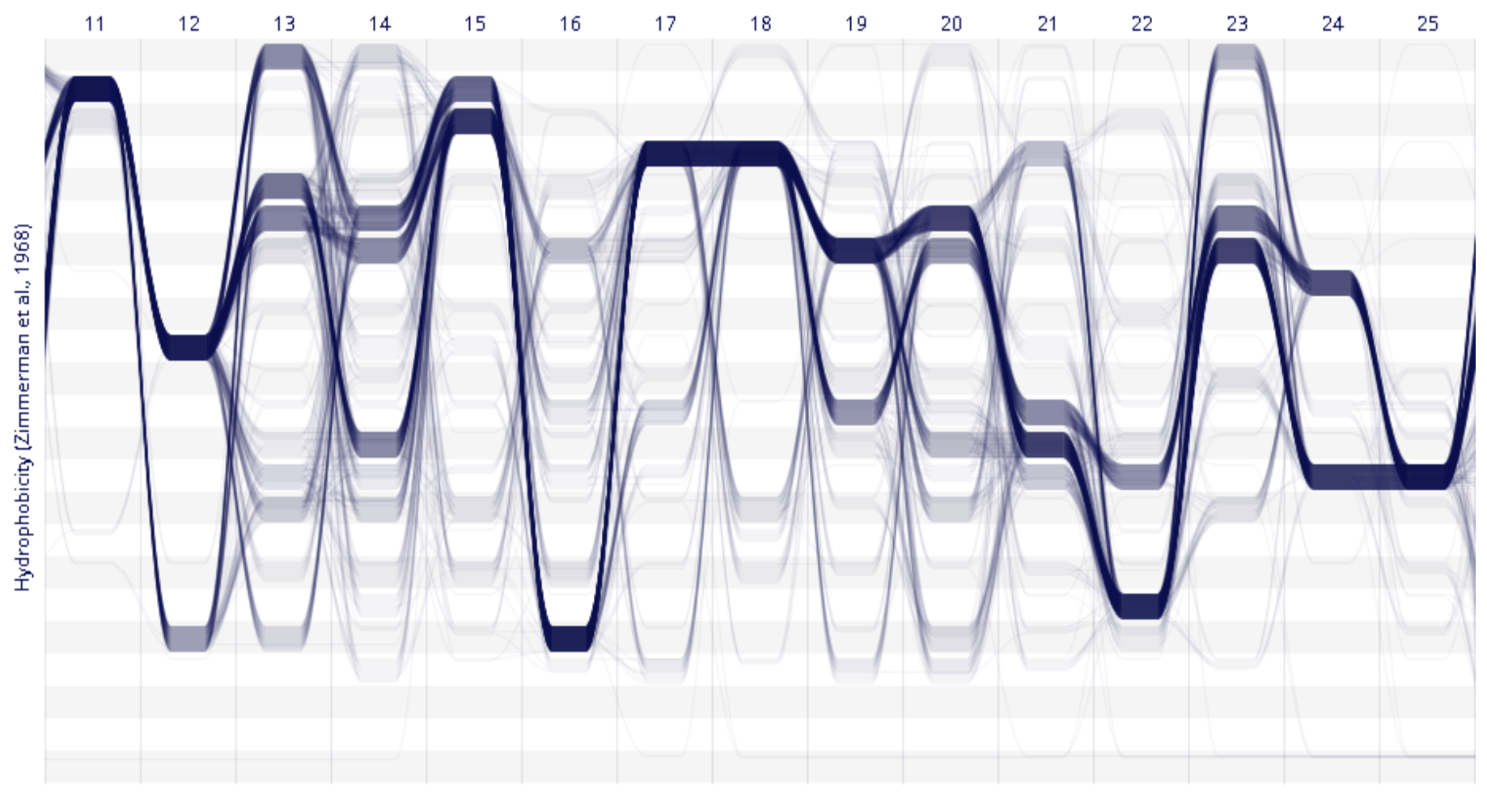 Sequence Surveyor
Sequence Surveyor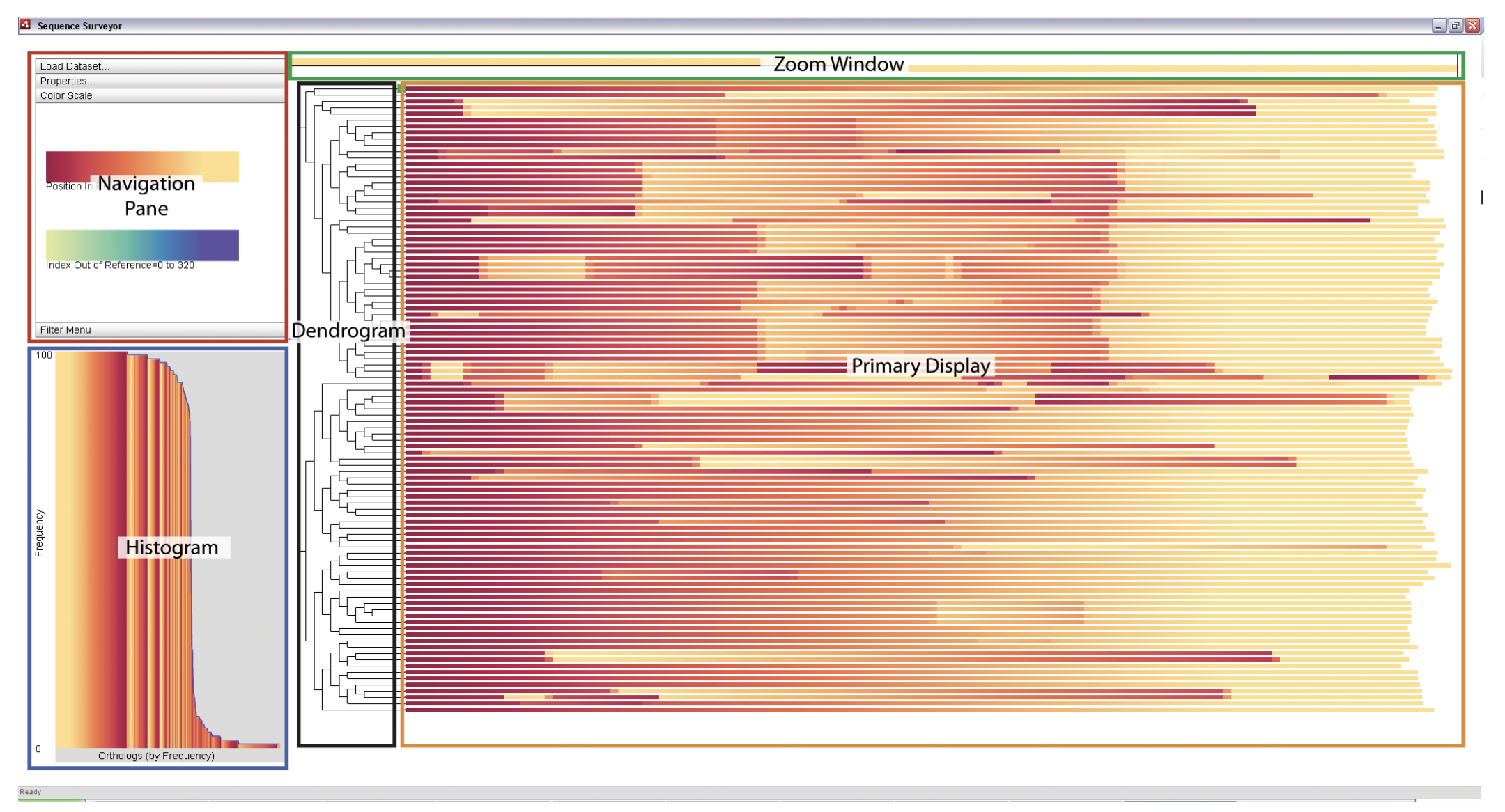 SilkDB 3.0
SilkDB 3.0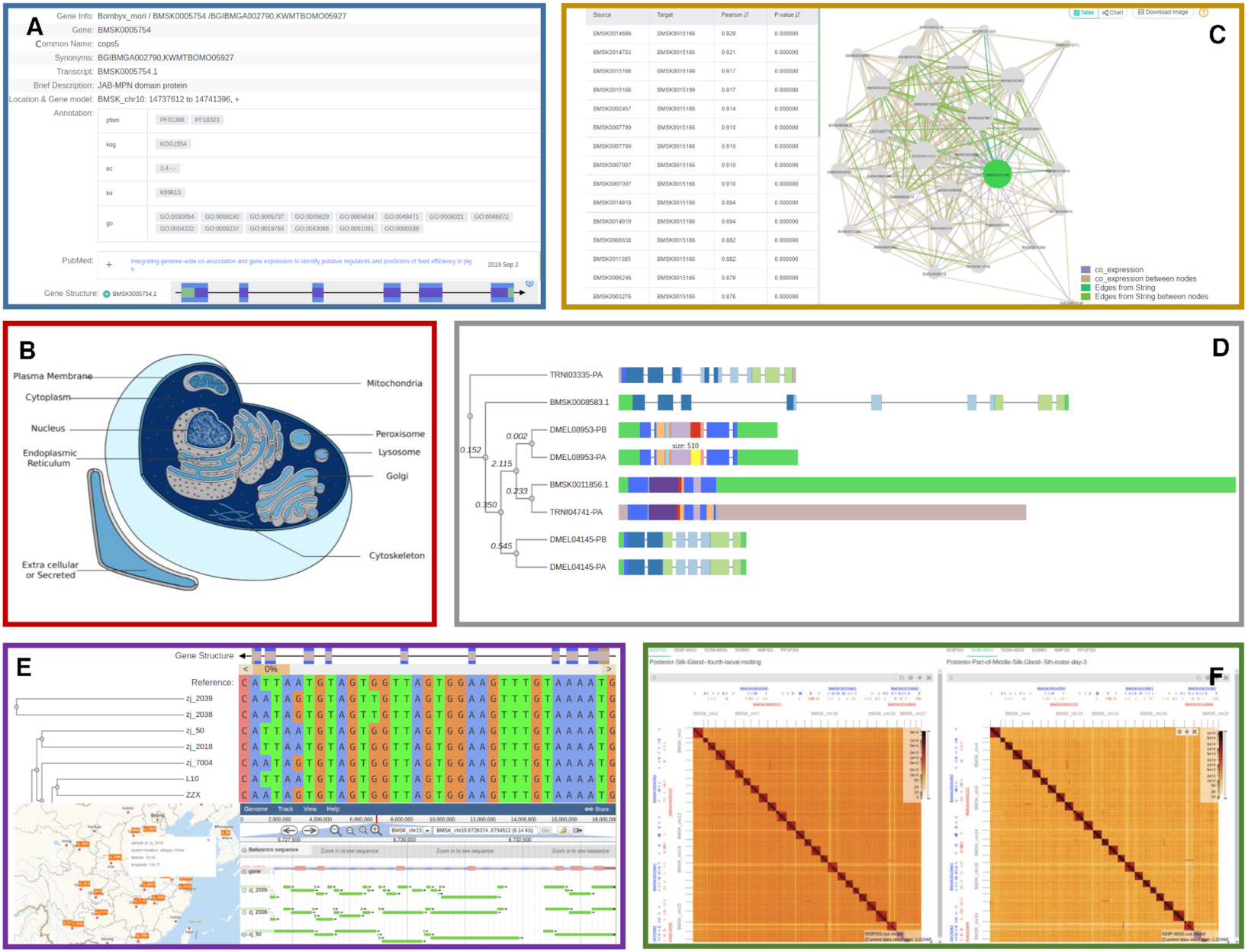 svist4get
svist4get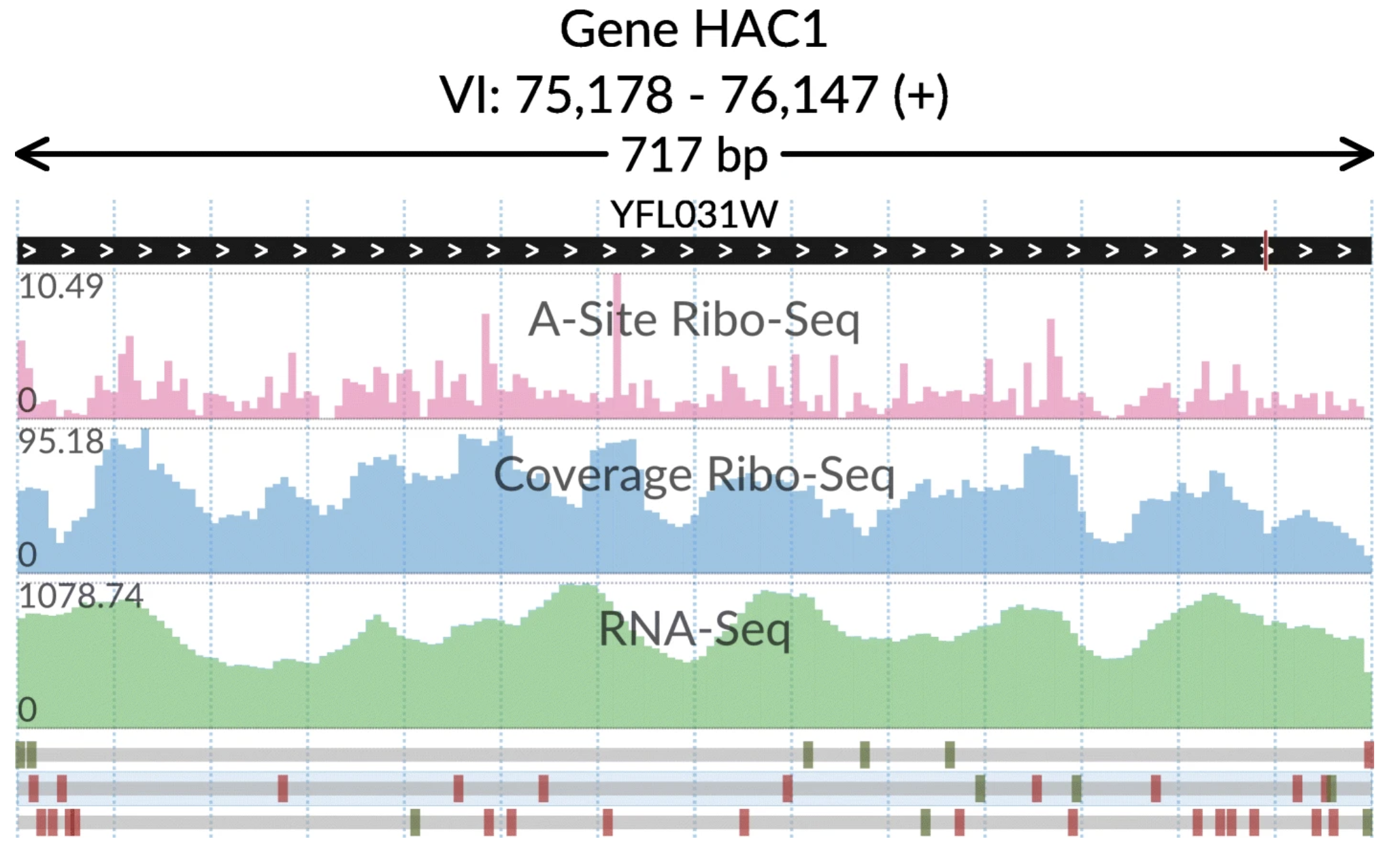 SWAV
SWAV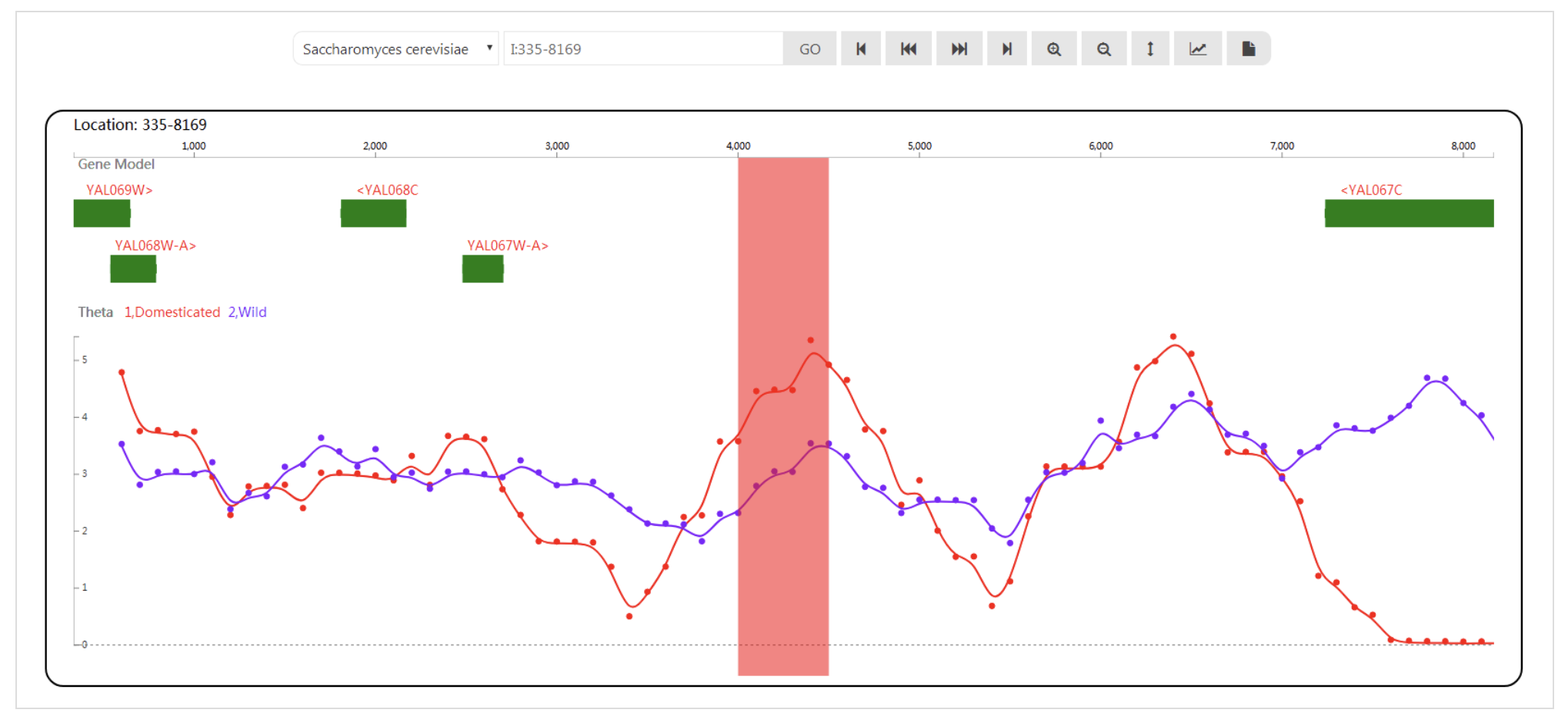 SynMap2
SynMap2 TFmotifView
TFmotifView Two Sample Logo
Two Sample Logo VCF Plotein
VCF Plotein Vials
Vials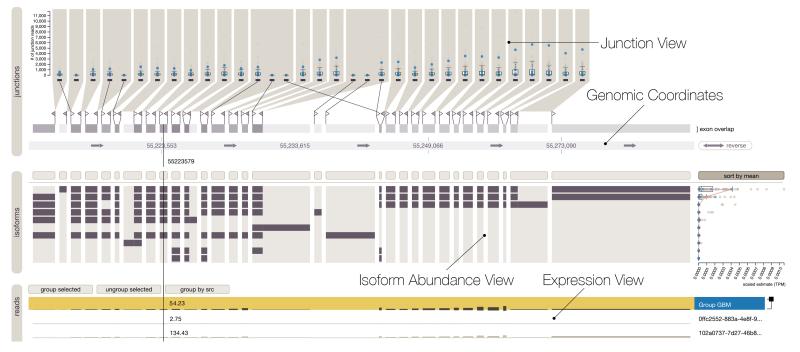 Vista Dot
Vista Dot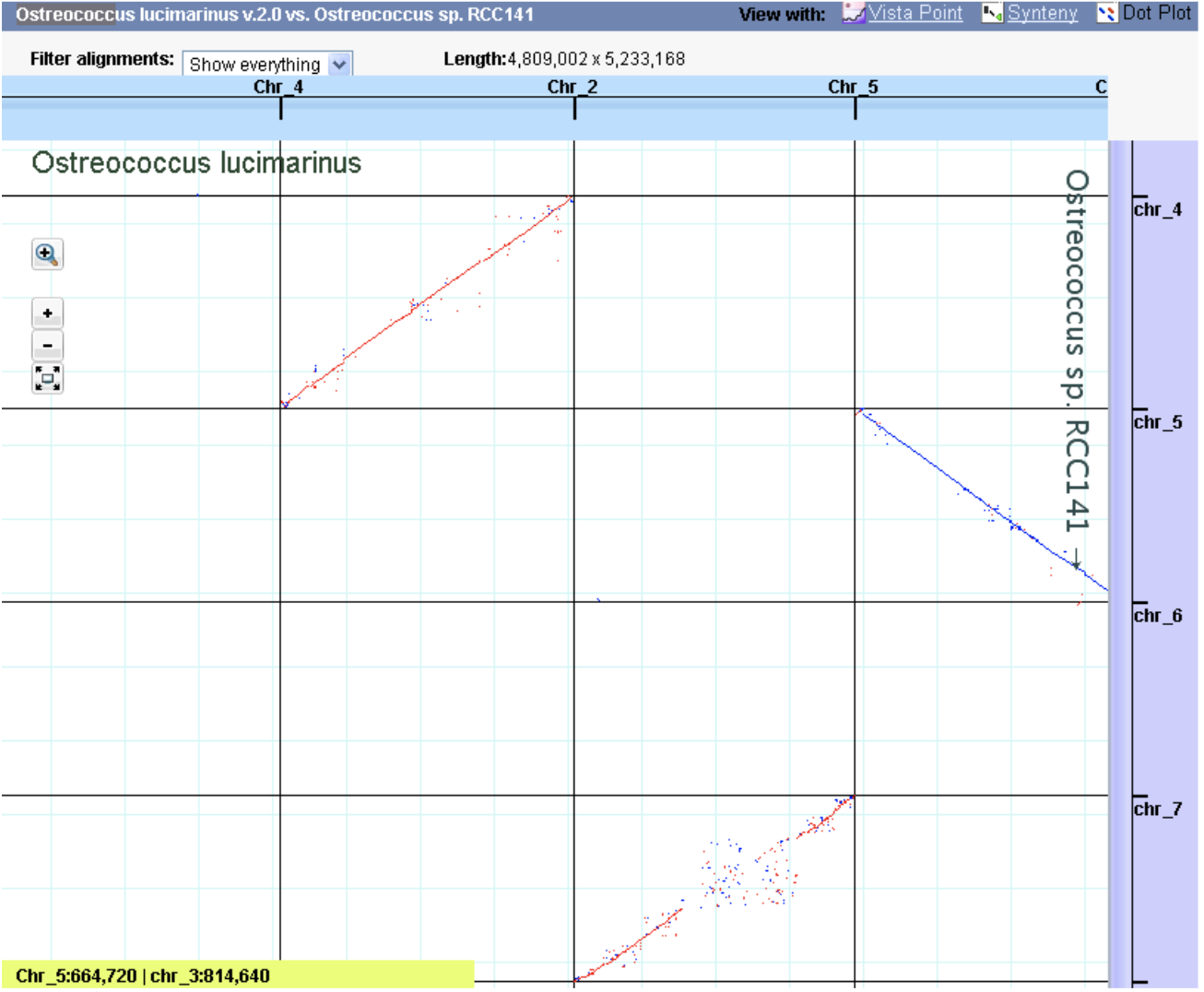 WashU Epigenome Browser
WashU Epigenome Browser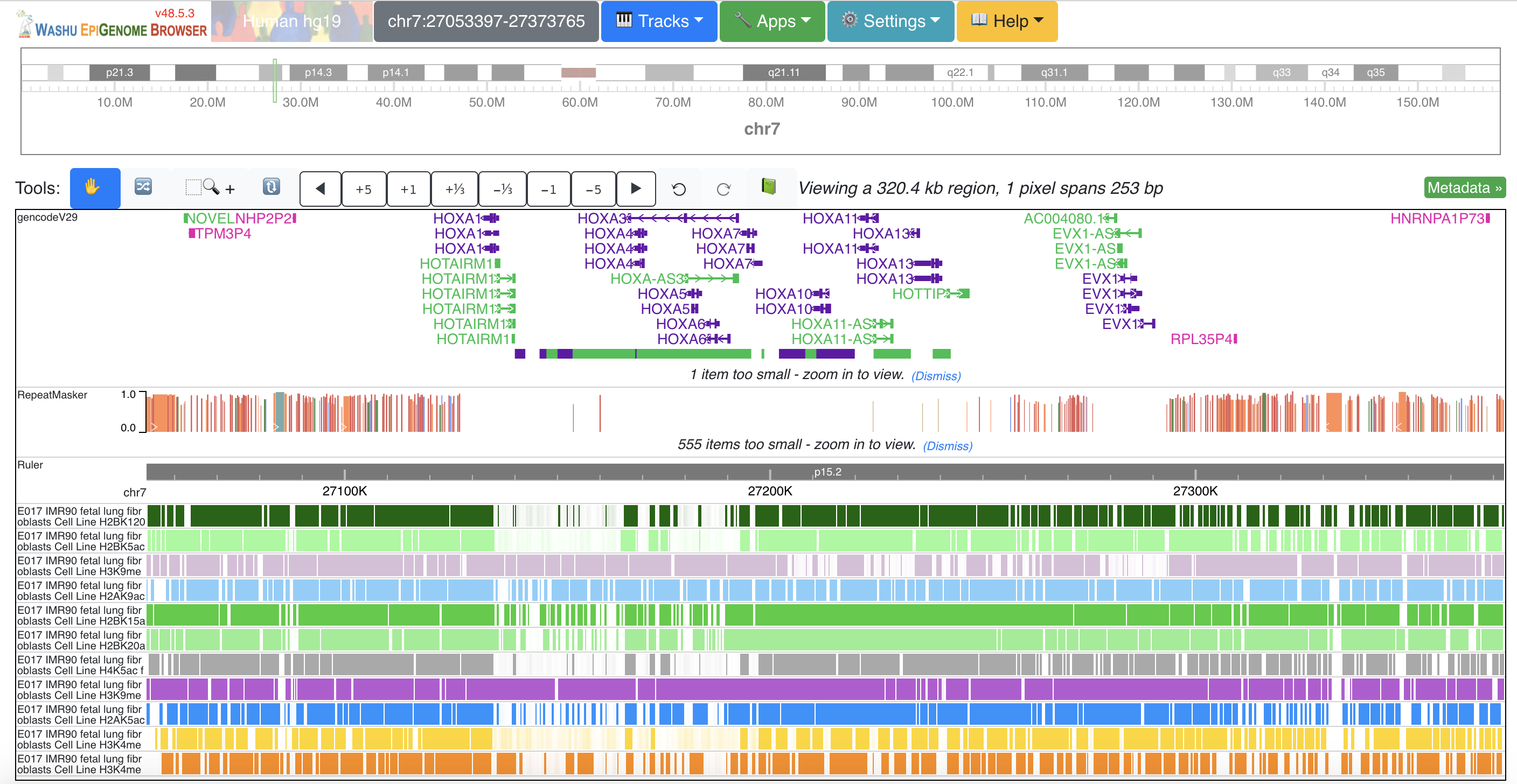 WebLogo
WebLogo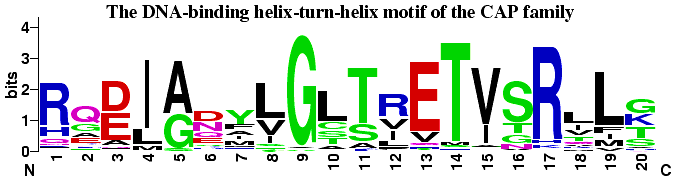
 Alvis
Alvis Apollo
Apollo BactoGenie
BactoGenie BedSect
BedSect Circos
Circos Civi
Civi ClicO Free Service
ClicO Free Service CNVkit
CNVkit Cooler
Cooler CRAMER
CRAMER CRISPResso2
CRISPResso2 Deep Motif Dashboard
Deep Motif Dashboard DNAPlotter
DNAPlotter Edgar Genome Browser
Edgar Genome Browser Edgar Synteny Plots
Edgar Synteny Plots Galaxy HiCExplorer
Galaxy HiCExplorer GenomeRing
GenomeRing Gepard
Gepard ggBio
ggBio Gremlin
Gremlin HiGlass
HiGlass HilbertCurve
HilbertCurve HilbertVis
HilbertVis HiPiler
HiPiler IGB
IGB Integrative Genomics Viewer
Integrative Genomics Viewer J-Circos
J-Circos JuiceBox
JuiceBox Juiceboxjs
Juiceboxjs Lollipop Plot cBio
Lollipop Plot cBio MEME
MEME MEXPRESS
MEXPRESS MGcV
MGcV MicroScope
MicroScope MizBee
MizBee MSAViewer
MSAViewer my5c
my5c ngs.plot
ngs.plot Oviz-Bio
Oviz-Bio pLogo
pLogo Rondo
Rondo Sashimi Plot
Sashimi Plot SCGV
SCGV Sequence Bundles
Sequence Bundles Sequence Surveyor
Sequence Surveyor SilkDB 3.0
SilkDB 3.0 svist4get
svist4get SWAV
SWAV SynMap2
SynMap2 TFmotifView
TFmotifView Two Sample Logo
Two Sample Logo VCF Plotein
VCF Plotein Vials
Vials Vista Dot
Vista Dot WashU Epigenome Browser
WashU Epigenome Browser WebLogo
WebLogo
Segregated

Segments, typically individual chromosomes, of the genome are displayed separately.
3D Genome Browser AliView
AliView CEpBrowser
CEpBrowser CGView
CGView CGView Server
CGView Server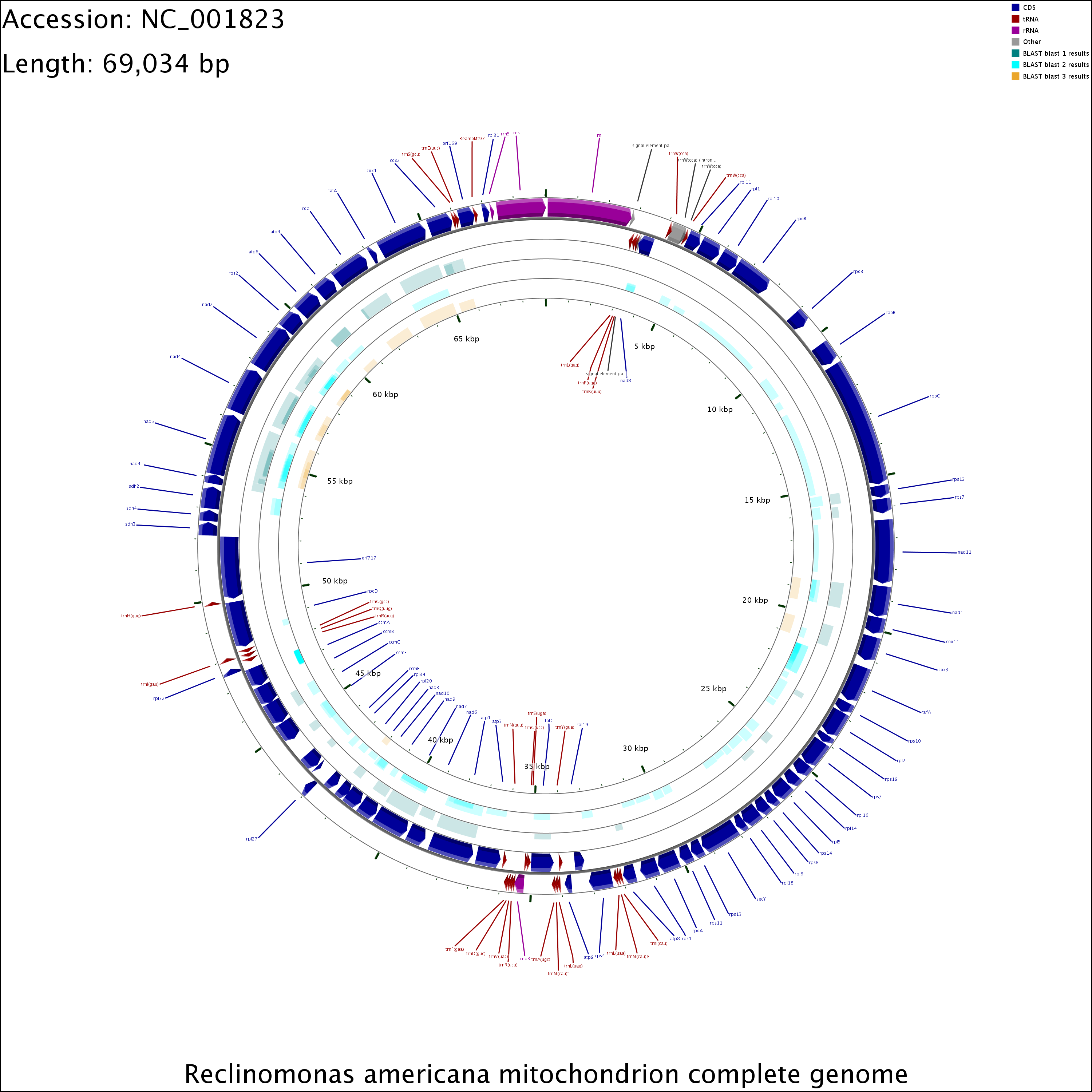 Cinteny
Cinteny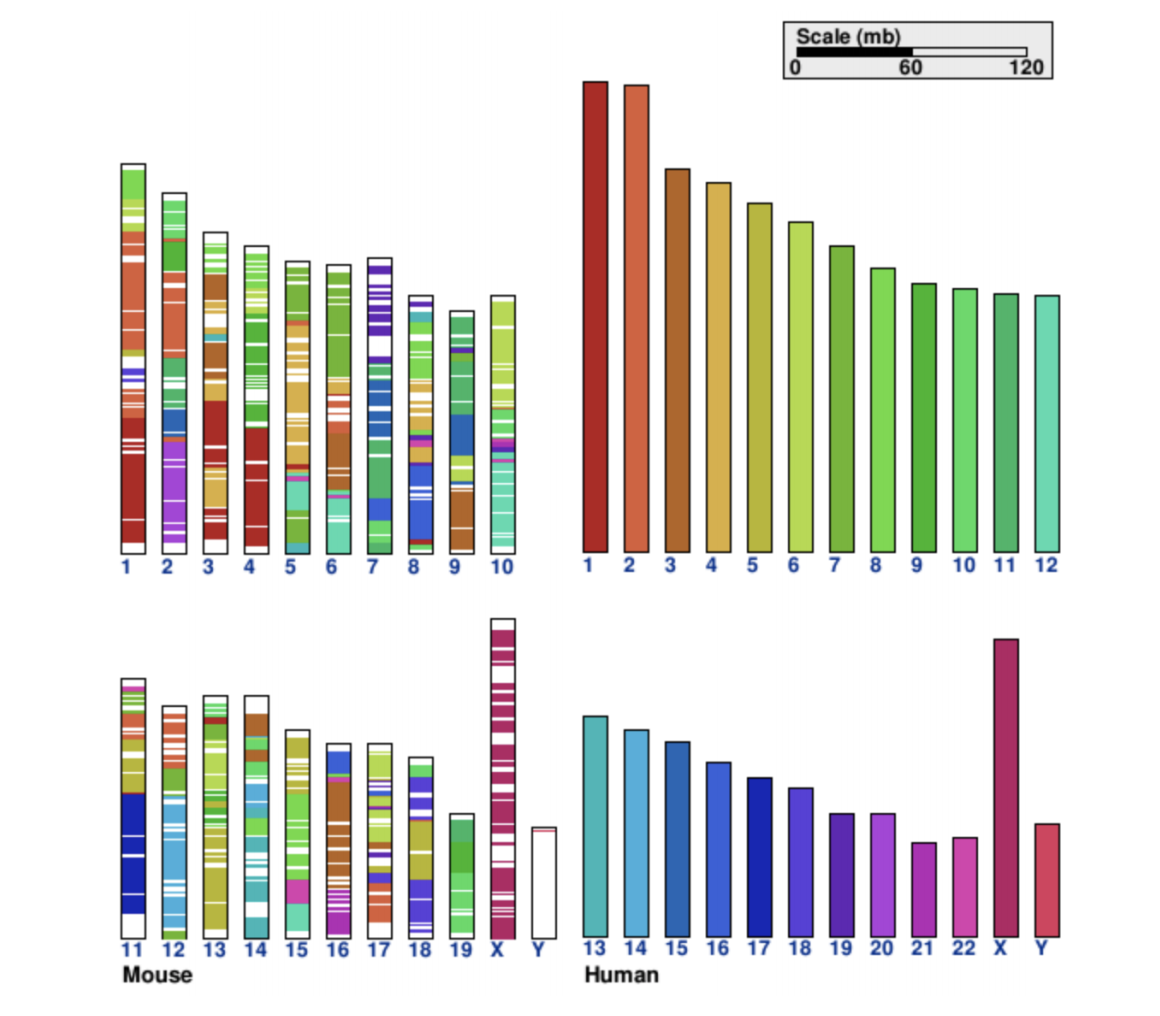 Circos
Circos ClicO Free Service
ClicO Free Service CNVkit
CNVkit Dalliance
Dalliance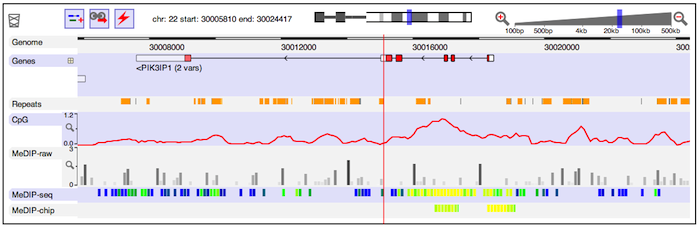 deepTools Heatmap
deepTools Heatmap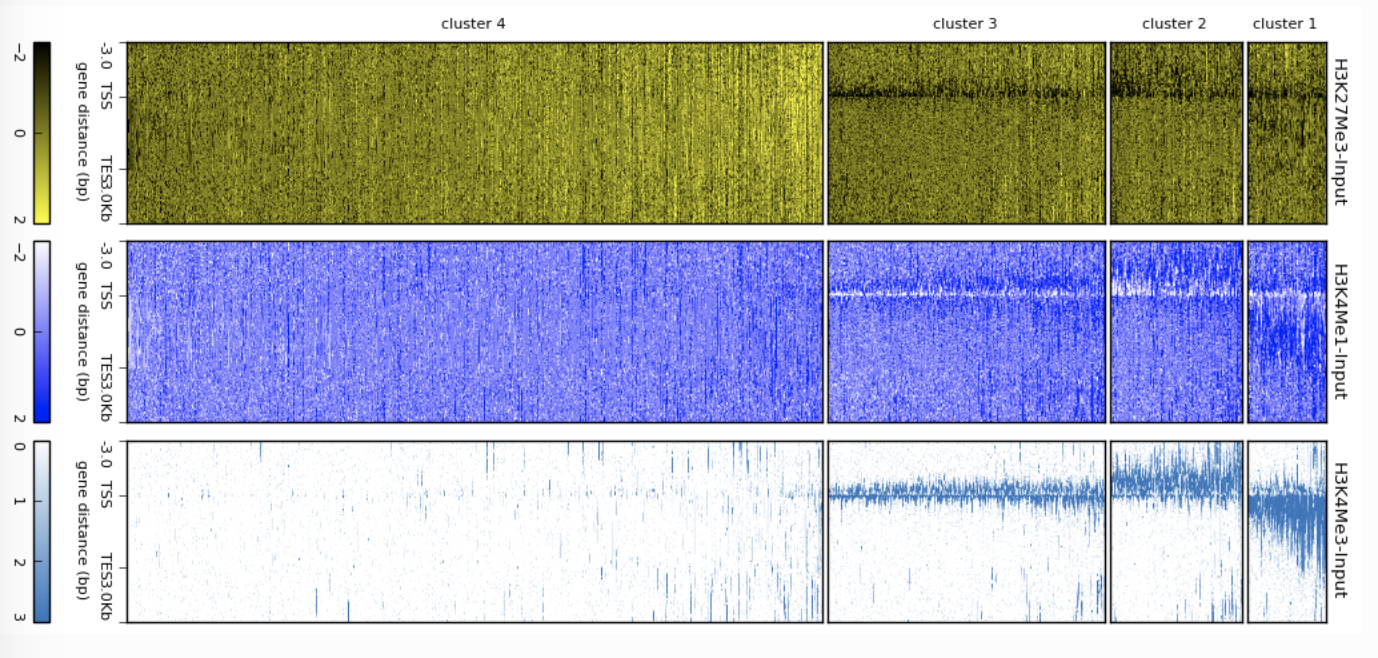 Edgar Genome Browser
Edgar Genome Browser EnrichedHeatmap
EnrichedHeatmap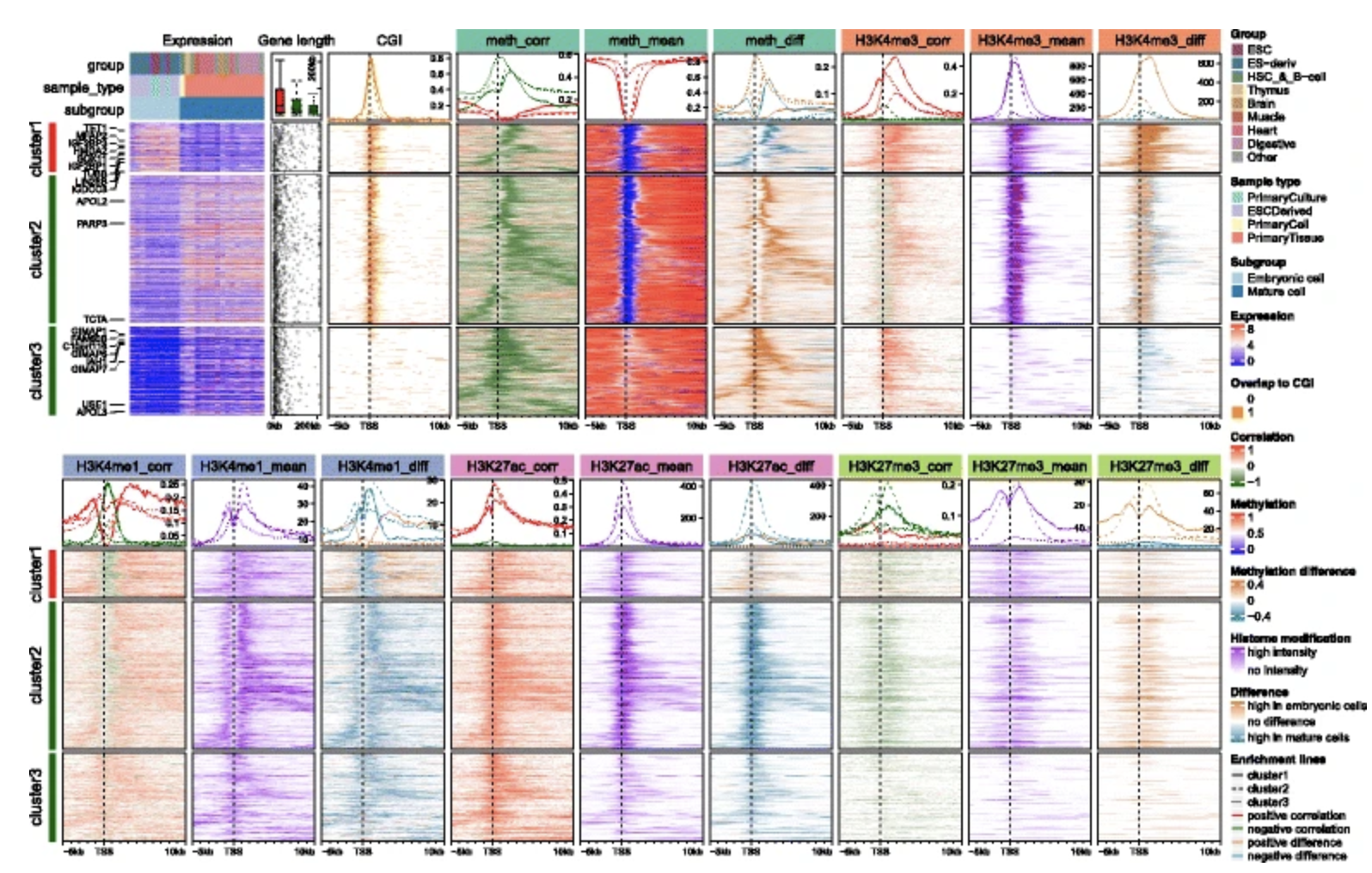 Ensembl
Ensembl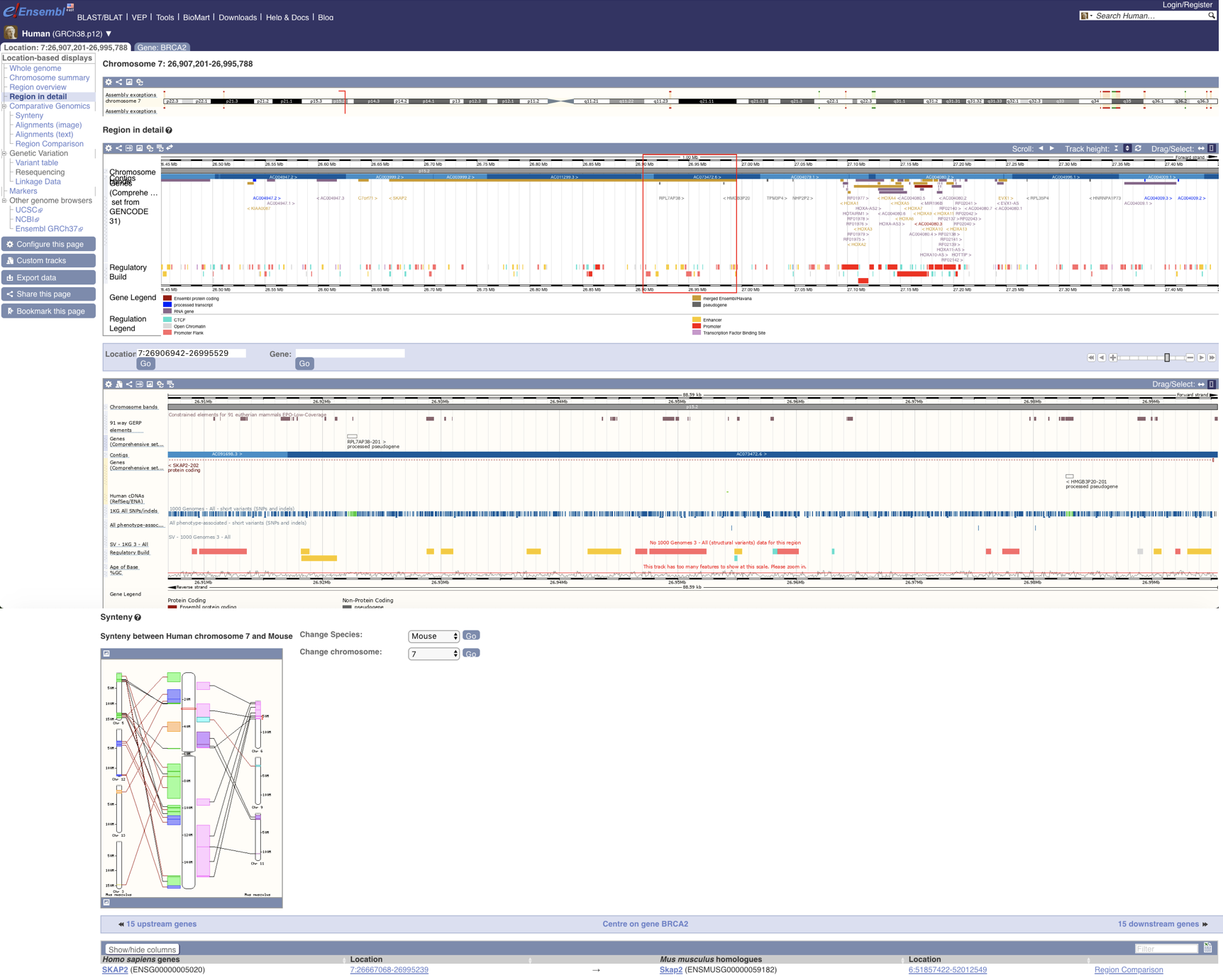 EpiViz
EpiViz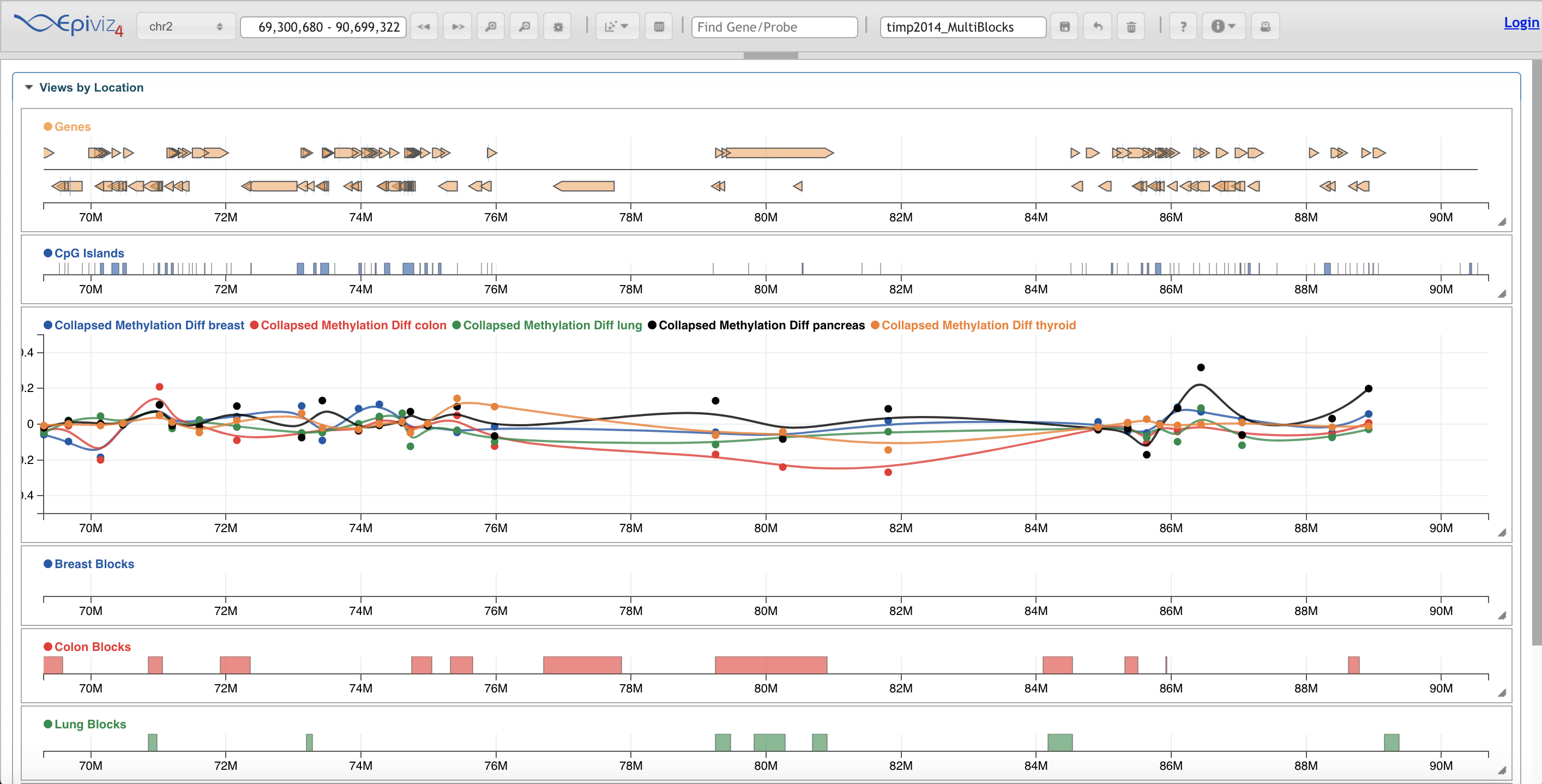 GBrowse
GBrowse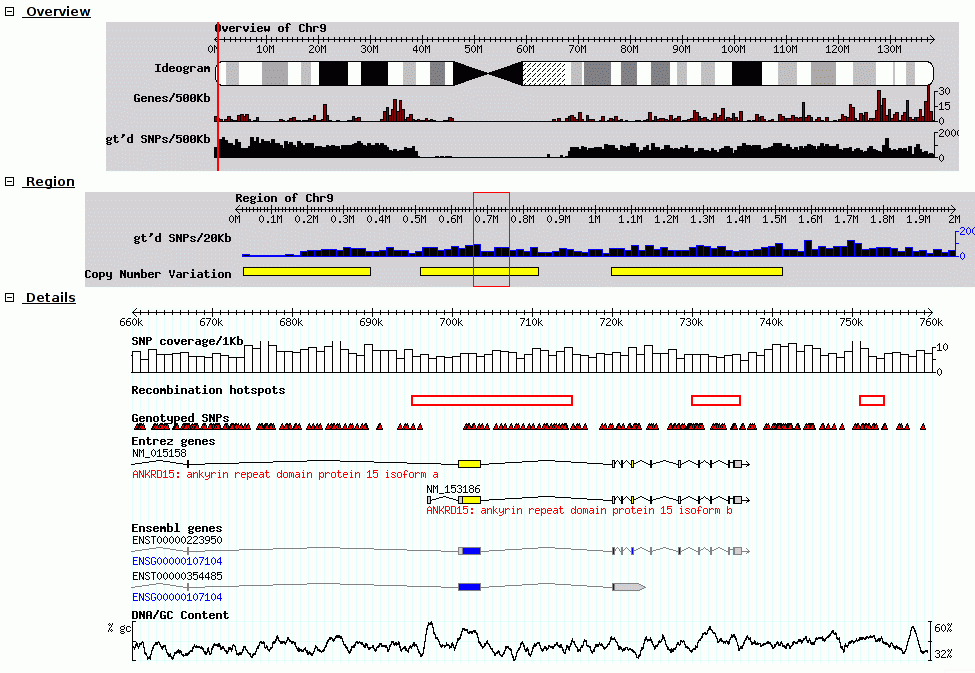 GBrowse_syn
GBrowse_syn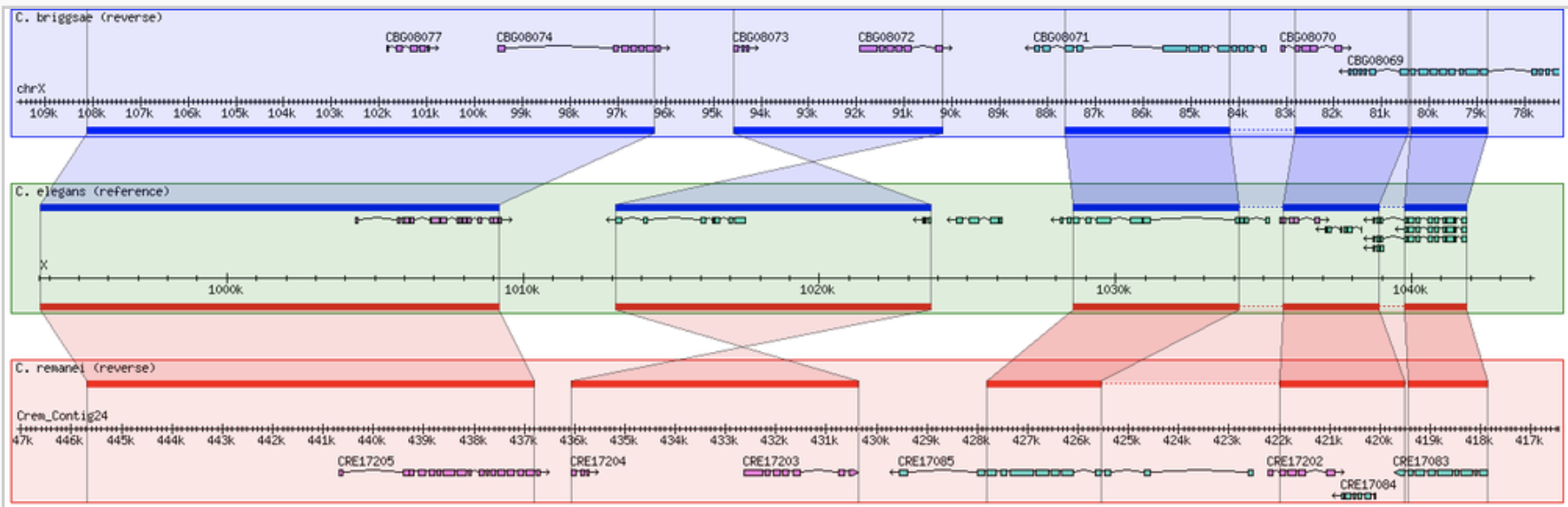 GenomeRing
GenomeRing GenomeView
GenomeView genoPlotR
genoPlotR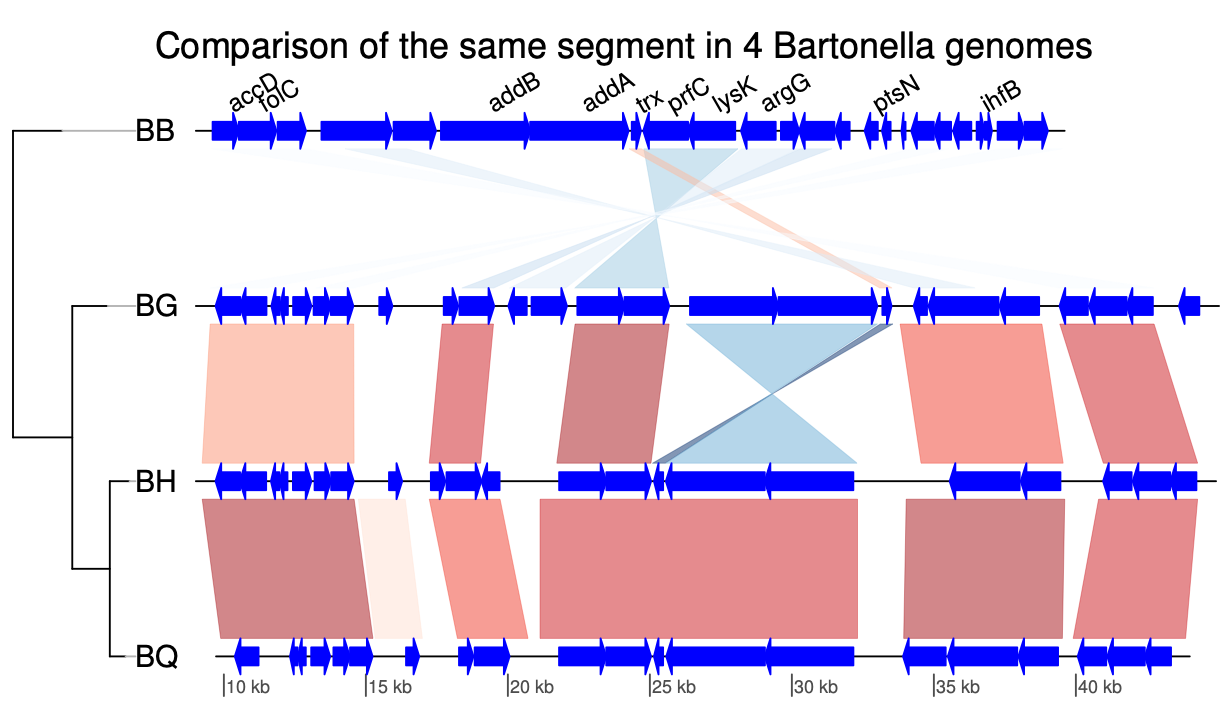 GenPlay
GenPlay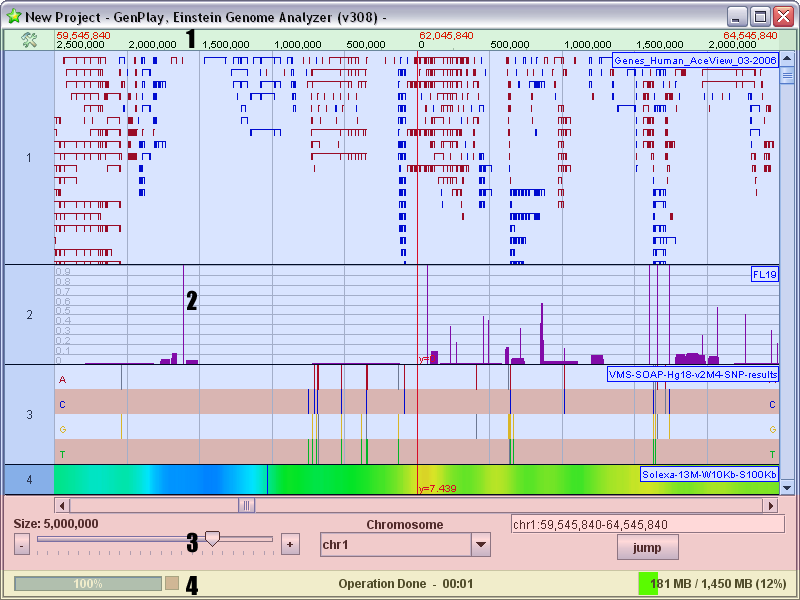 ggBio
ggBio GIVE
GIVE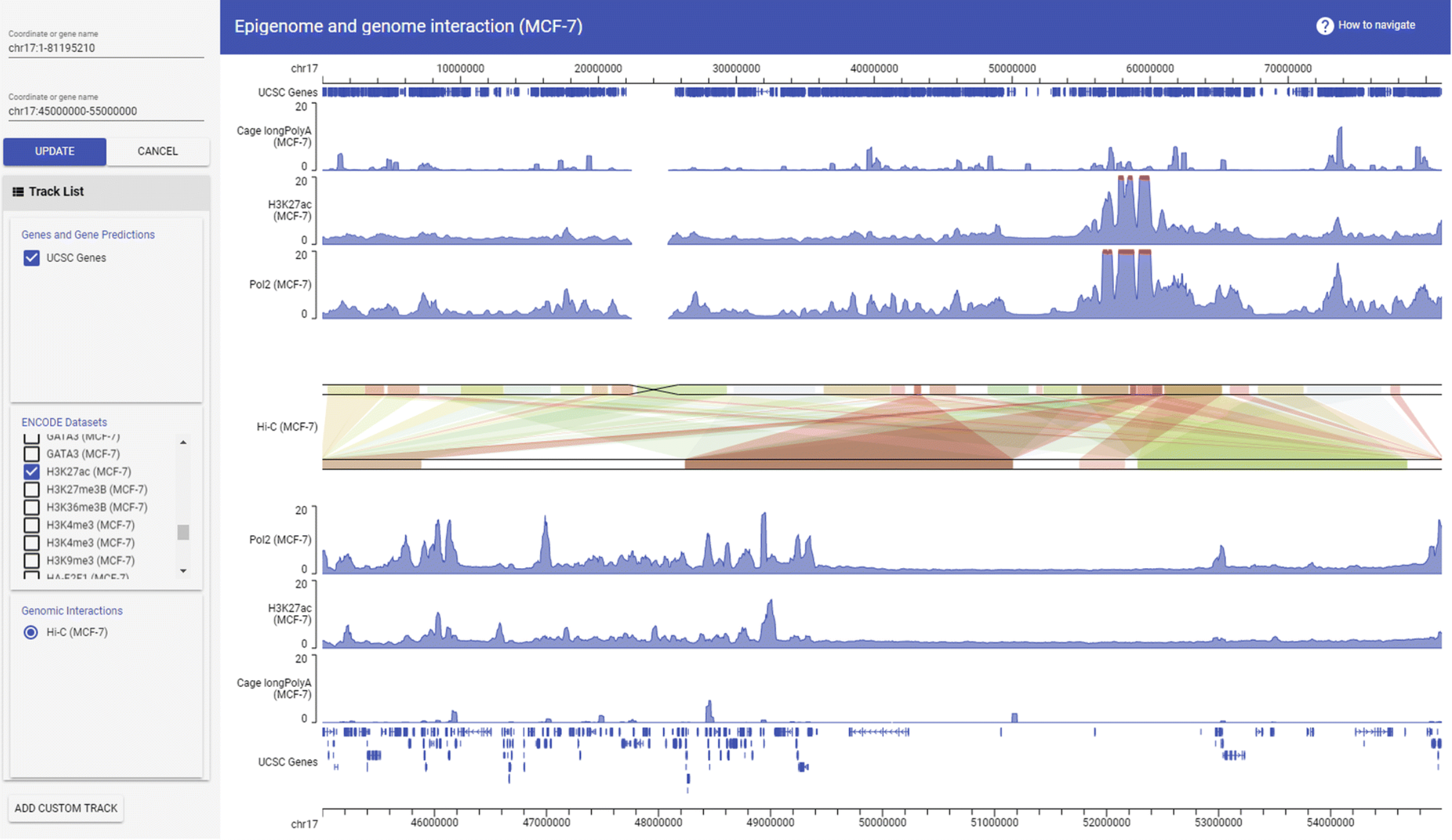 HUGIn
HUGIn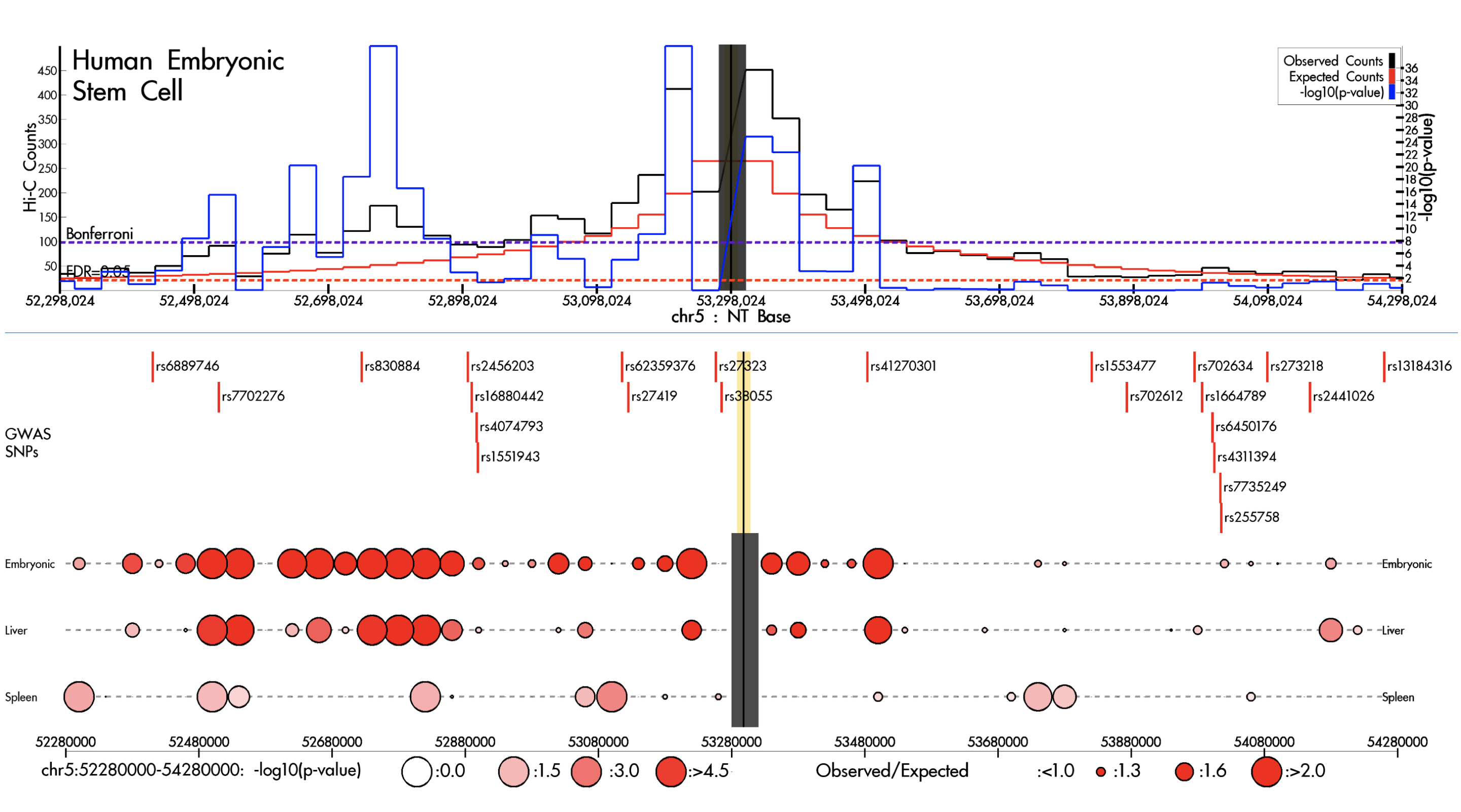 IRScope
IRScope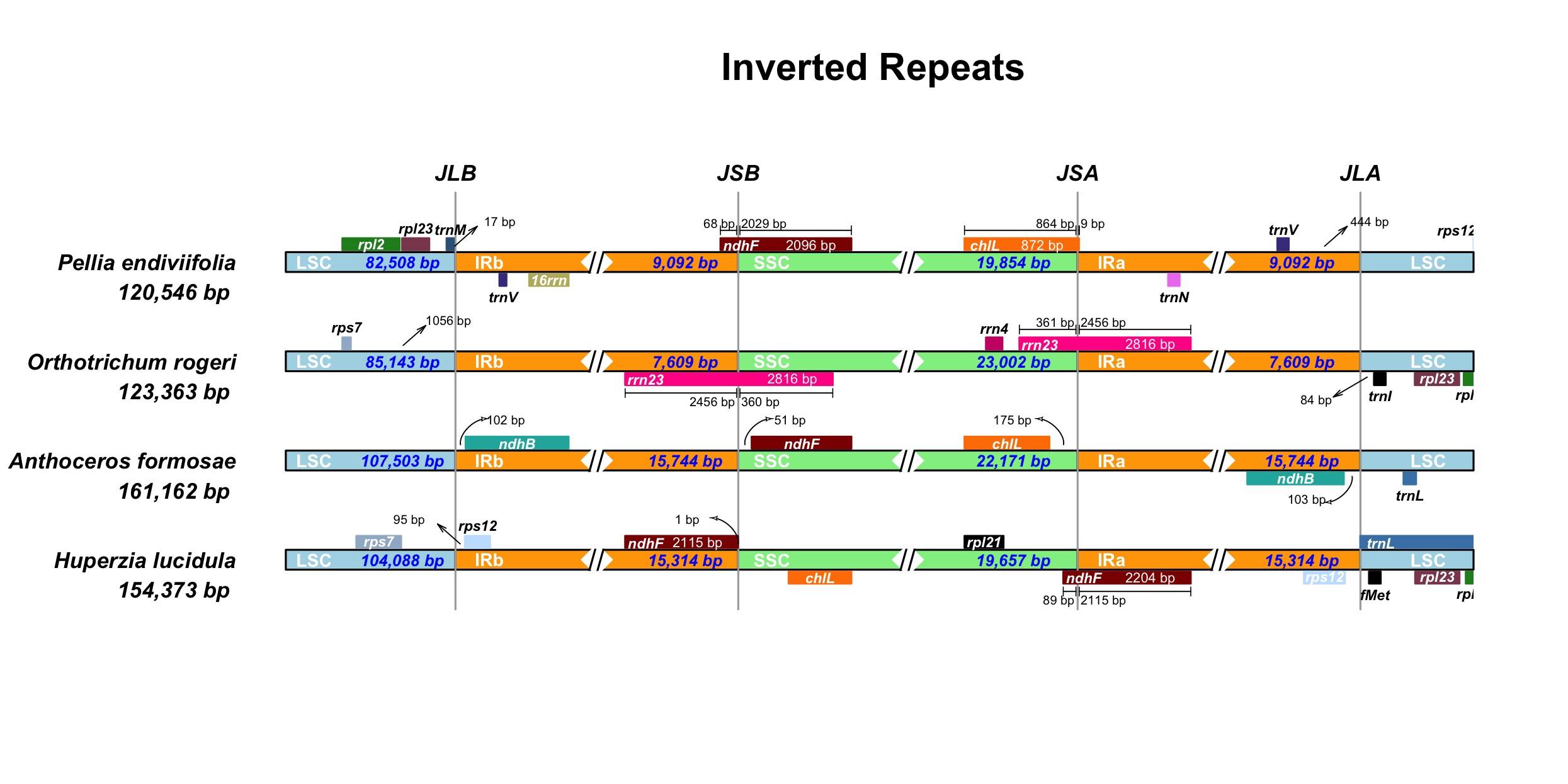 Island Viewer
Island Viewer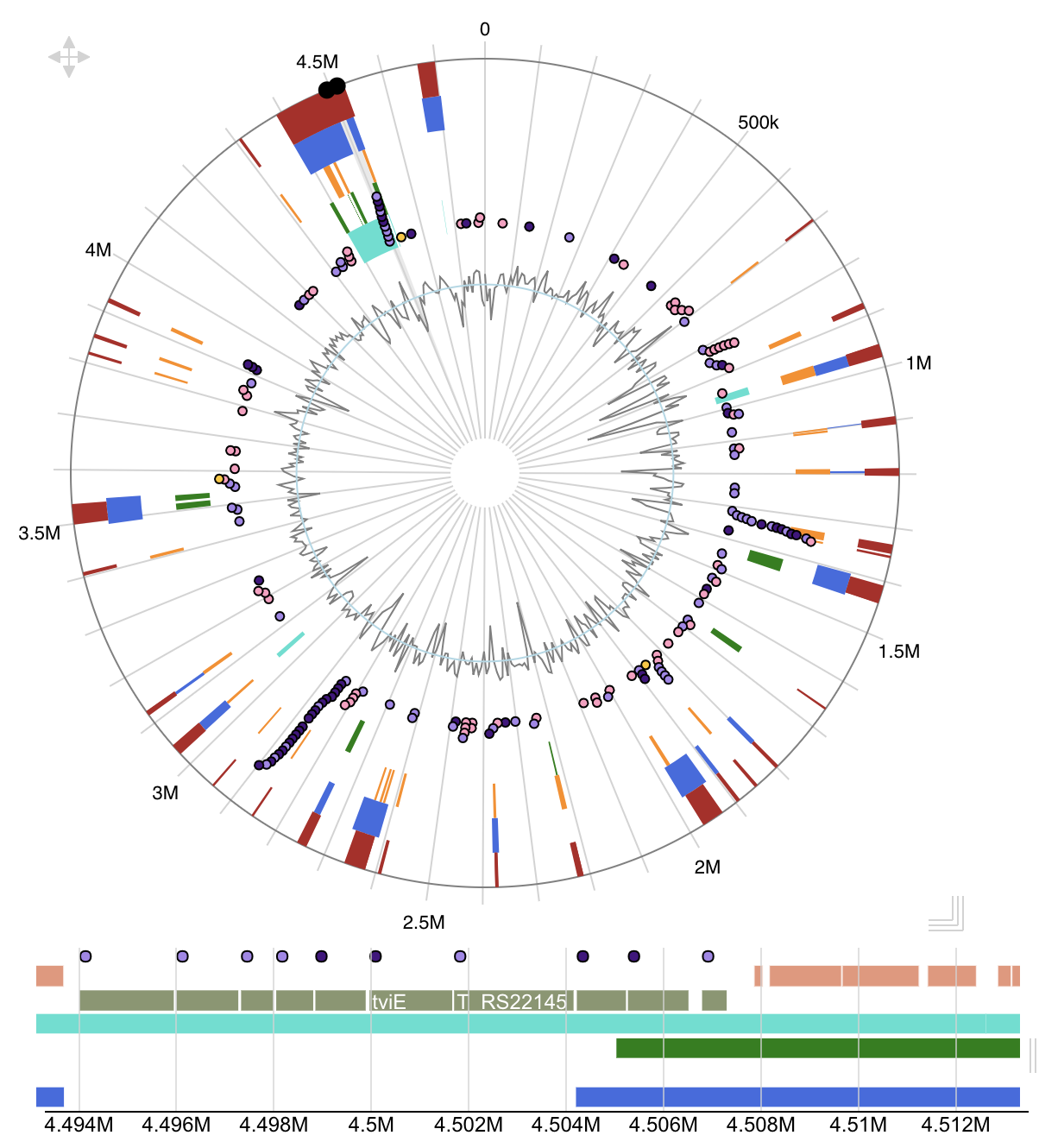 JalView
JalView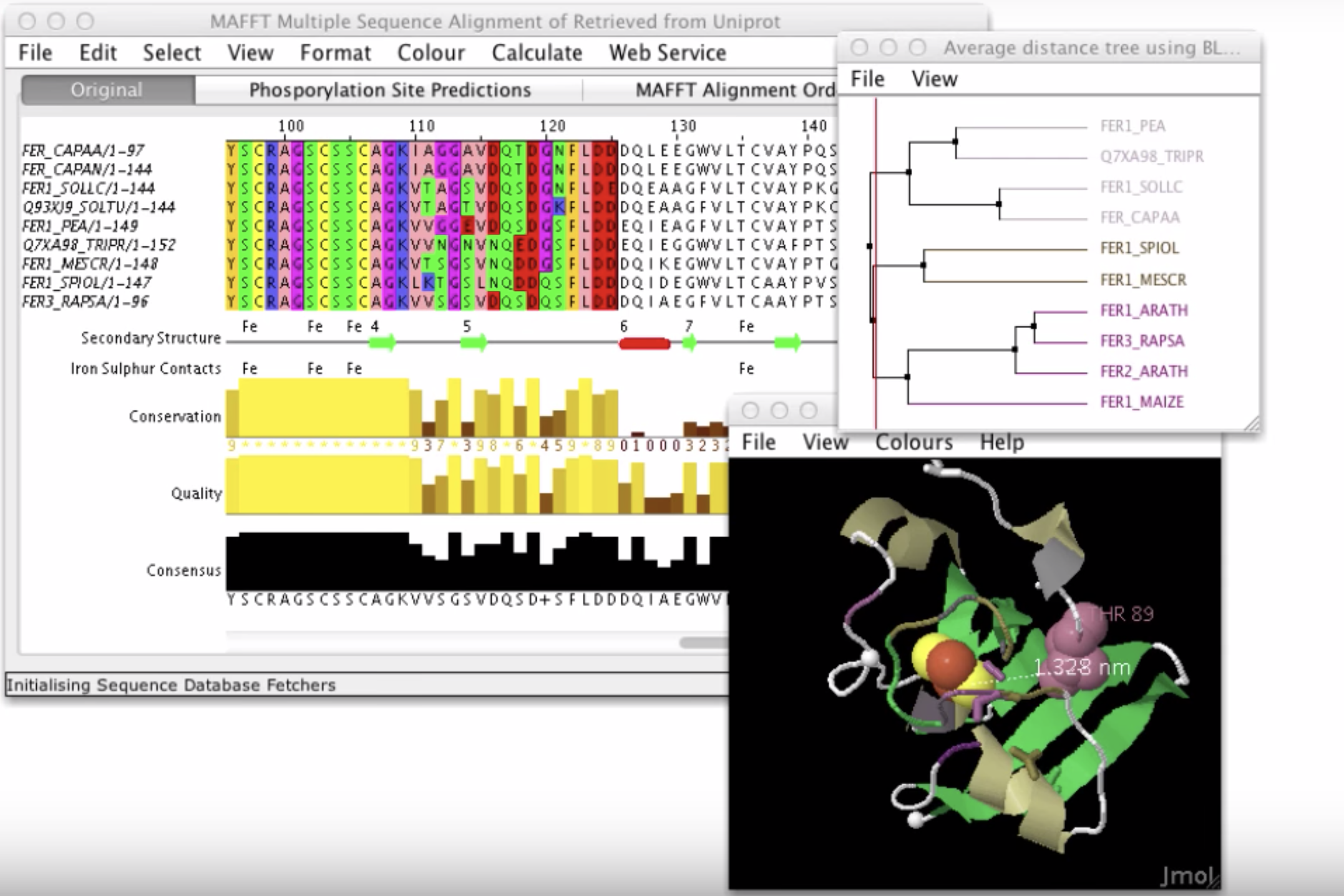 JBrowse
JBrowse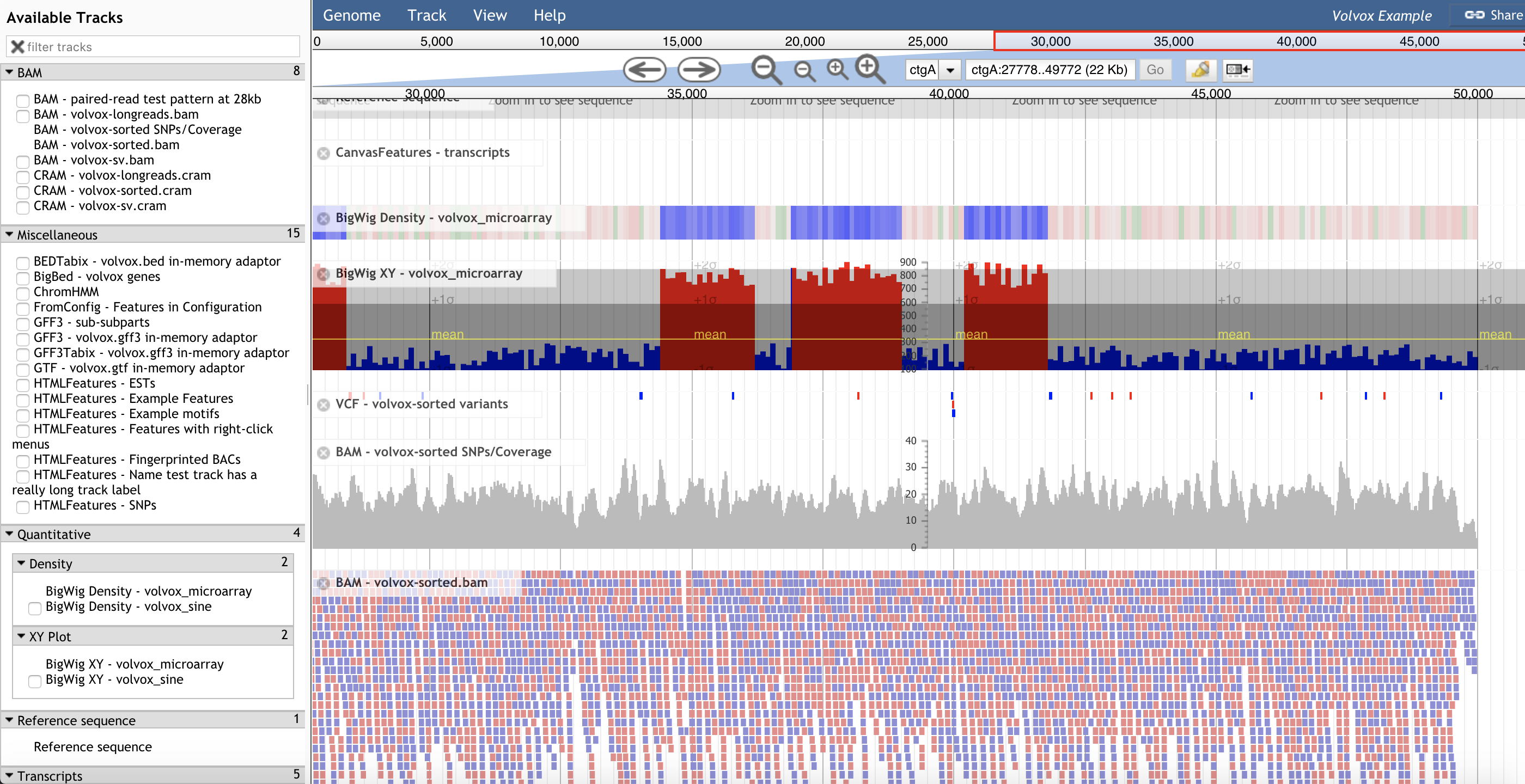 MAGI
MAGI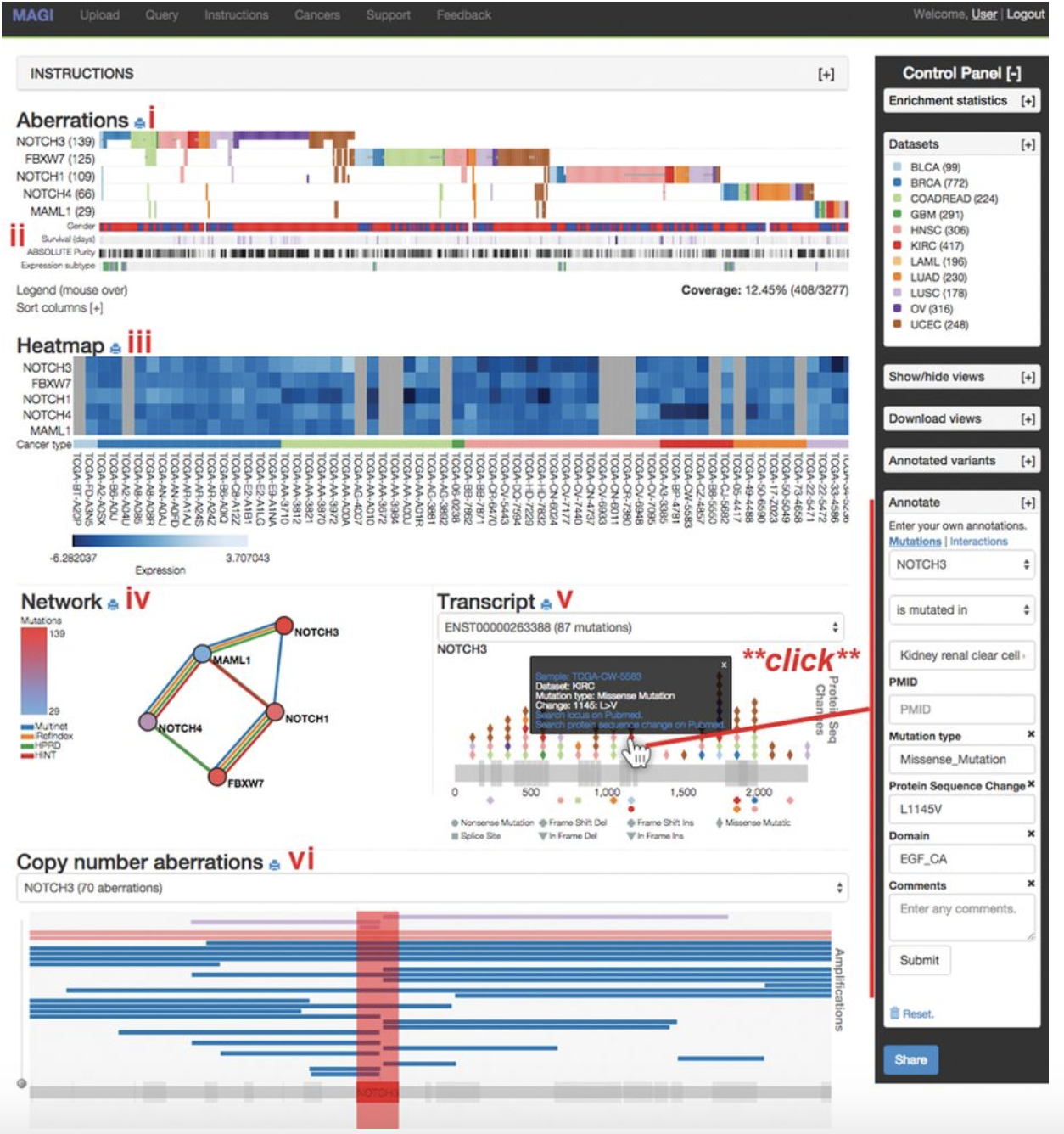 MochiView
MochiView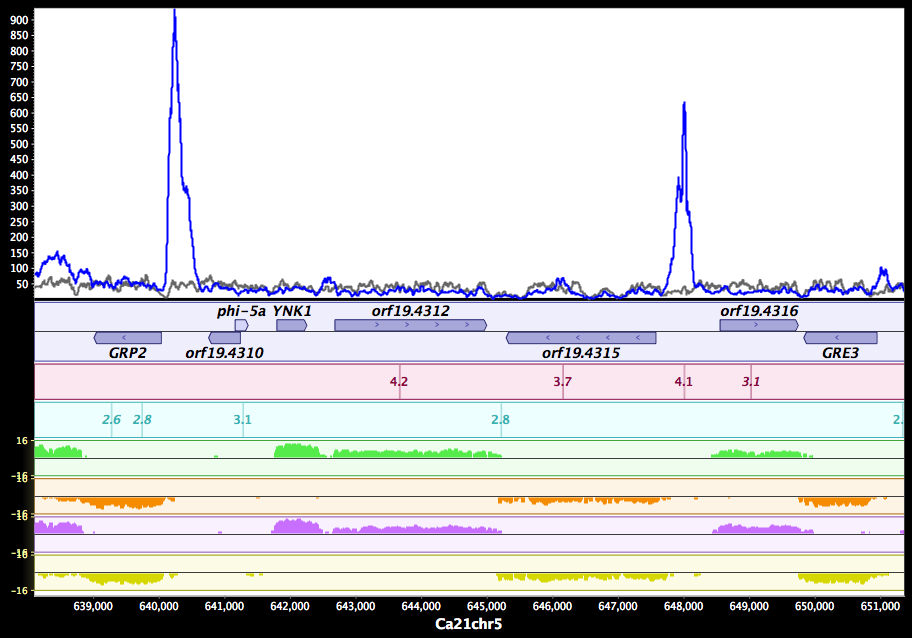 NCBI Genome Viewer
NCBI Genome Viewer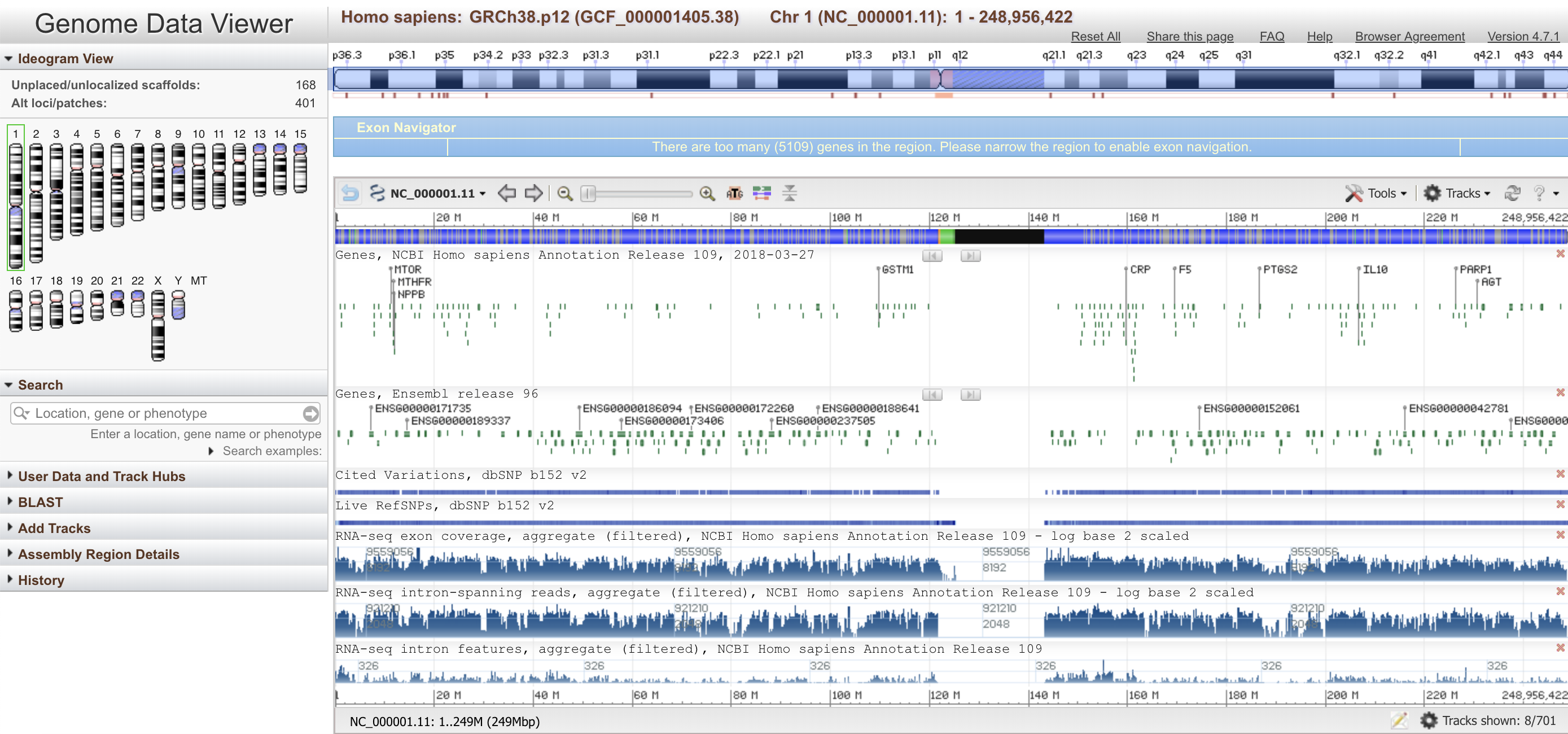 NCBI Sequence Viewer
NCBI Sequence Viewer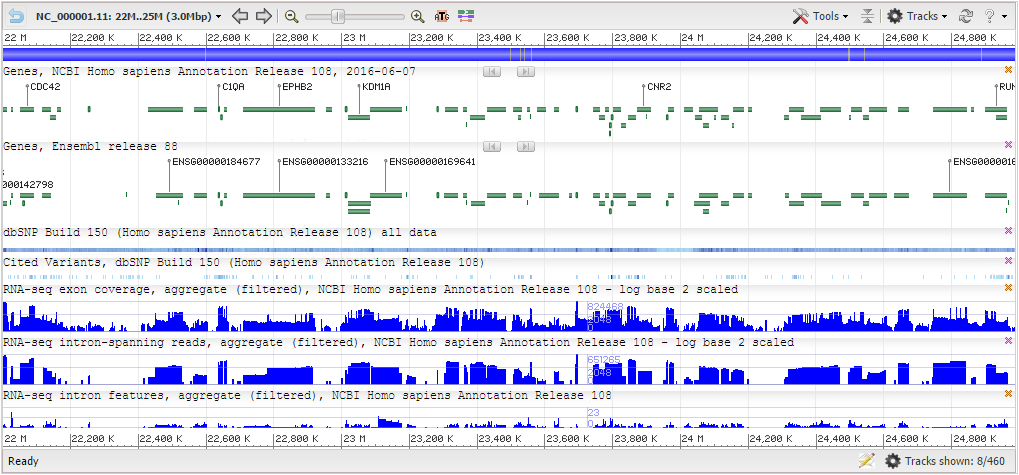 Persephone
Persephone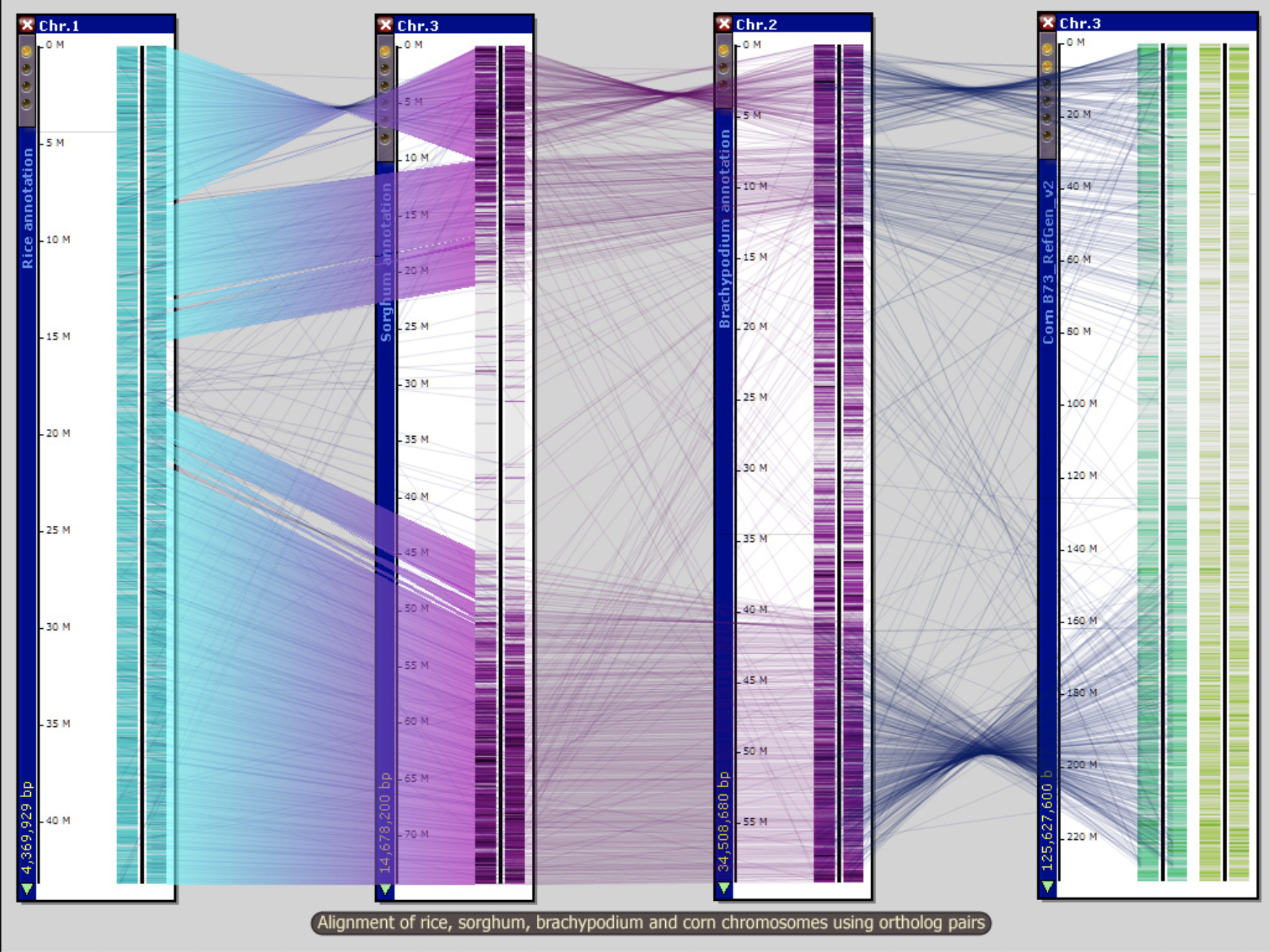 PSU 3D Genome Browser
PSU 3D Genome Browser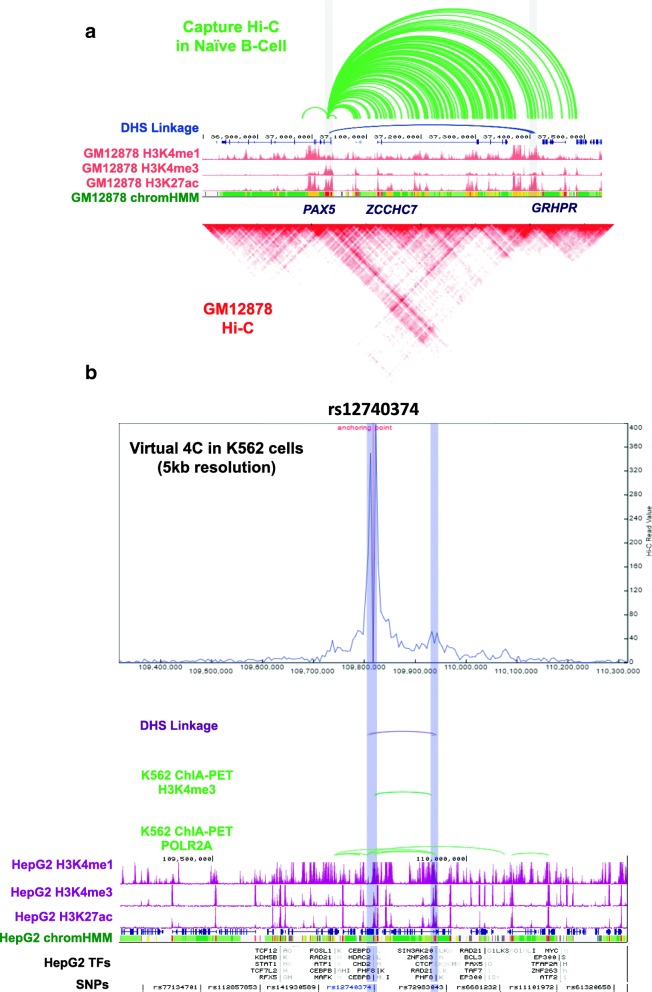 ReadXplorer
ReadXplorer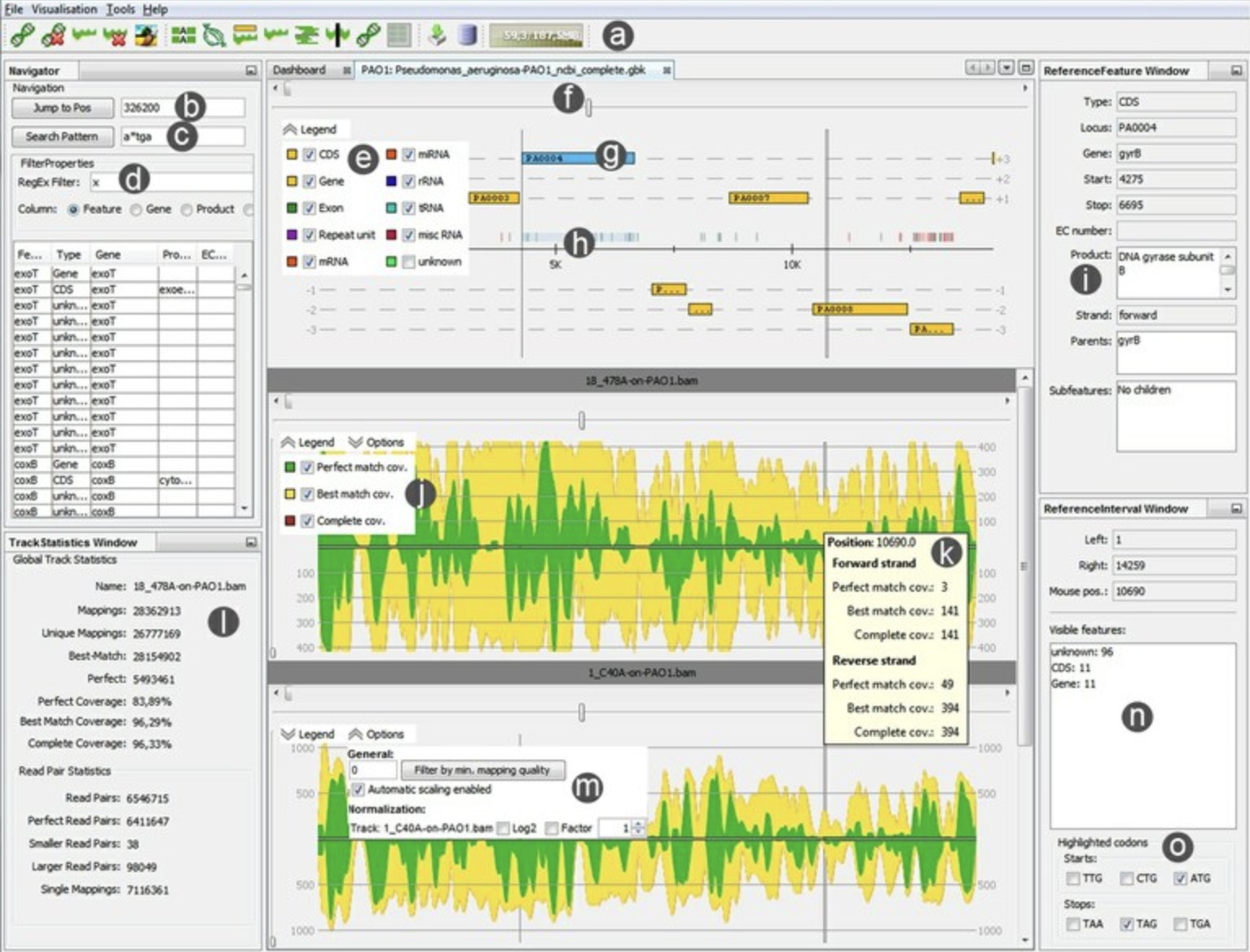 RIdeogram
RIdeogram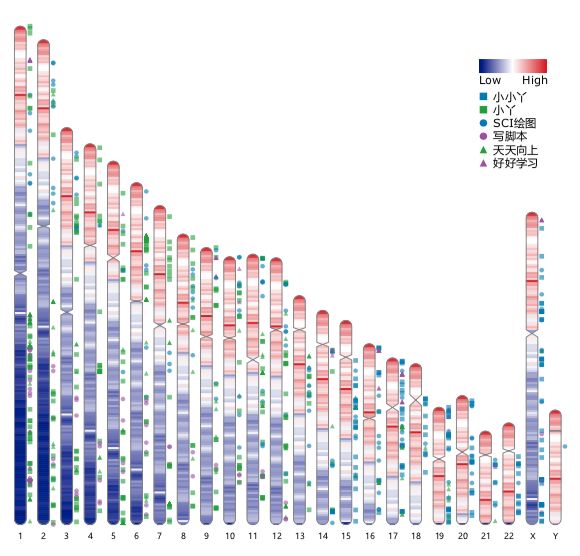 Savant Genome Browser 2
Savant Genome Browser 2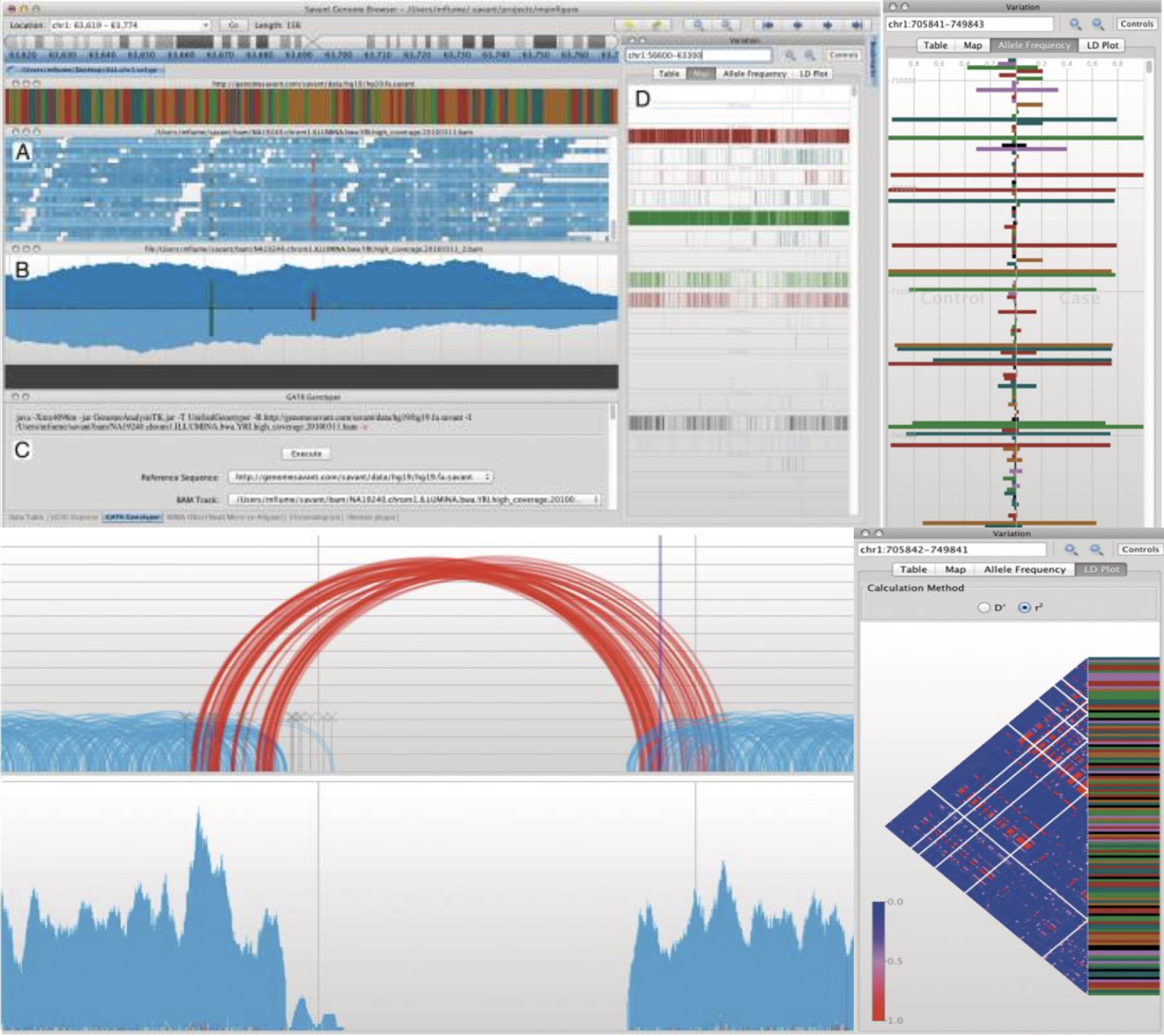 Spatial DB
Spatial DB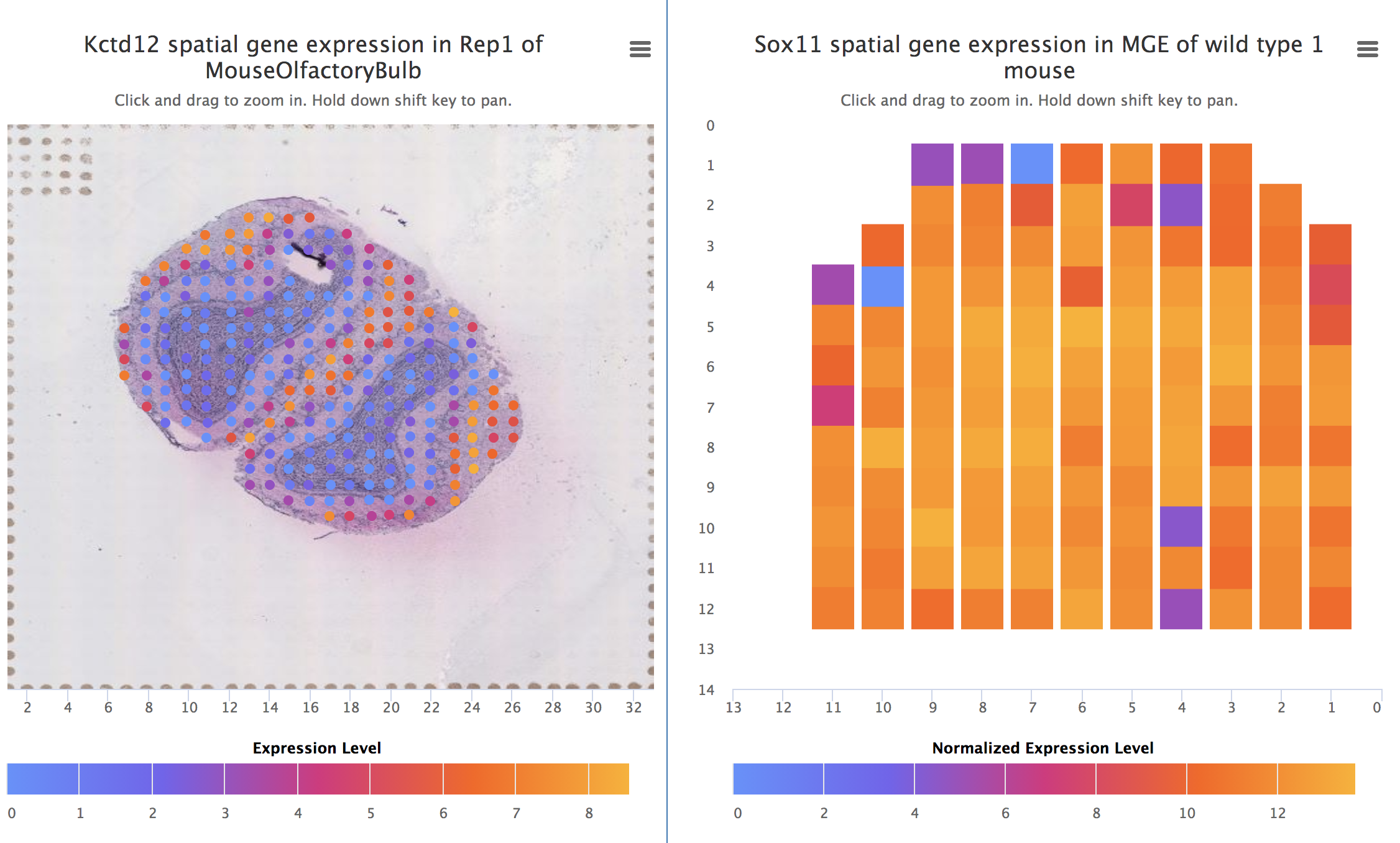 SpliceGrapher
SpliceGrapher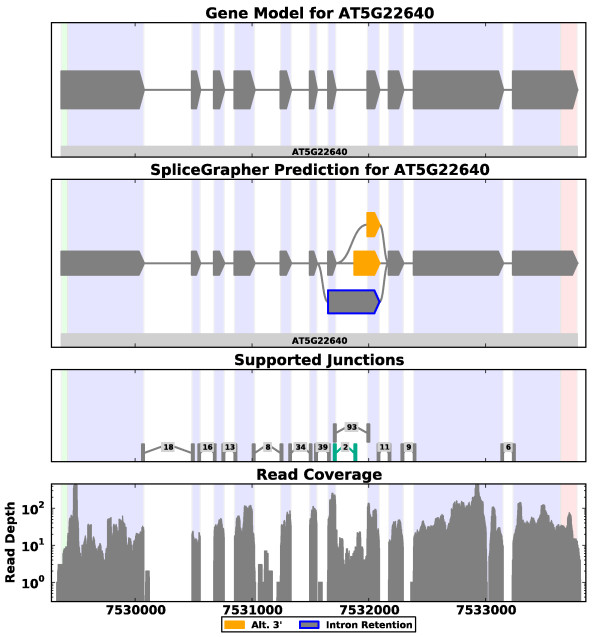 SplicePlot
SplicePlot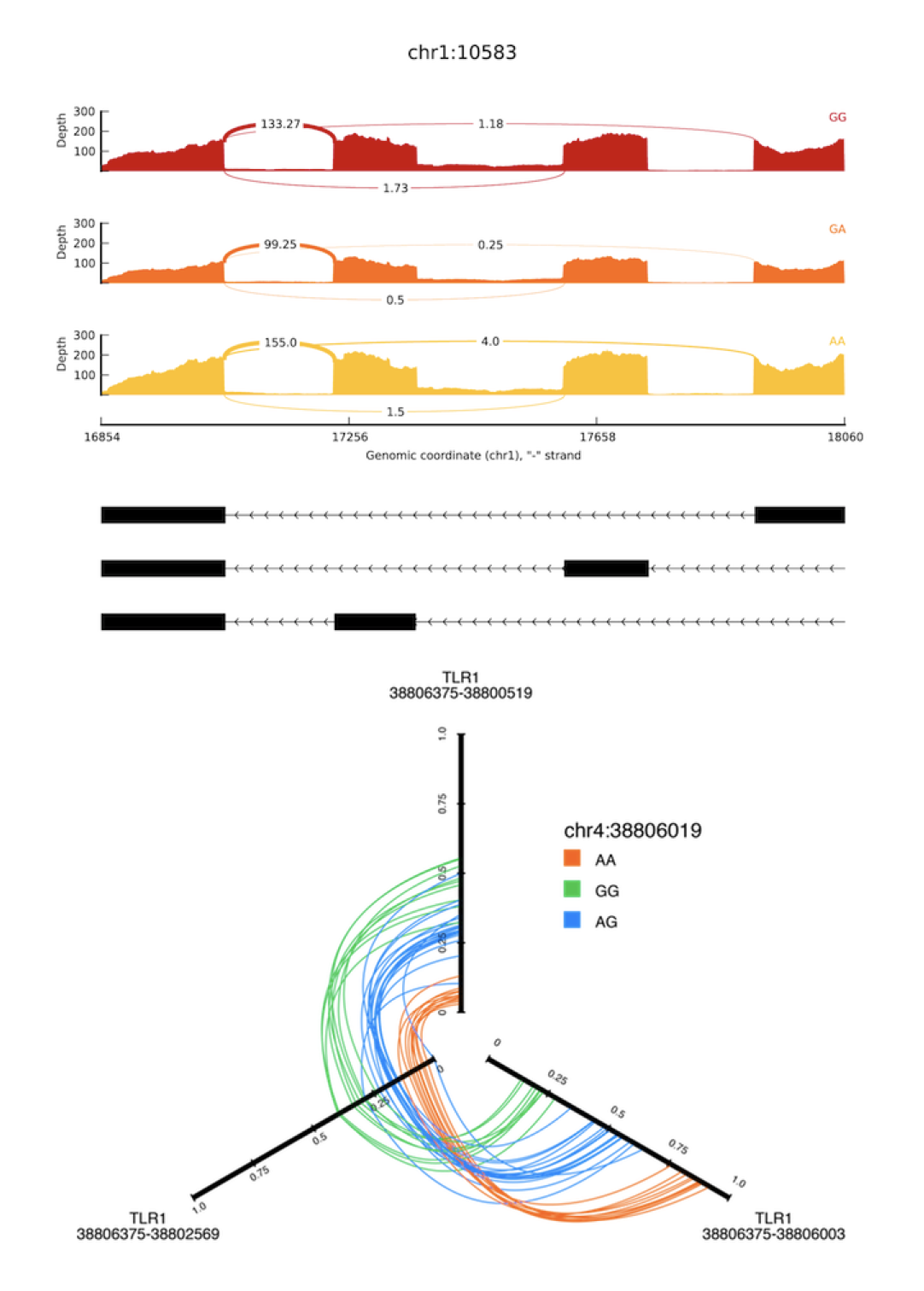 SpliceSeq
SpliceSeq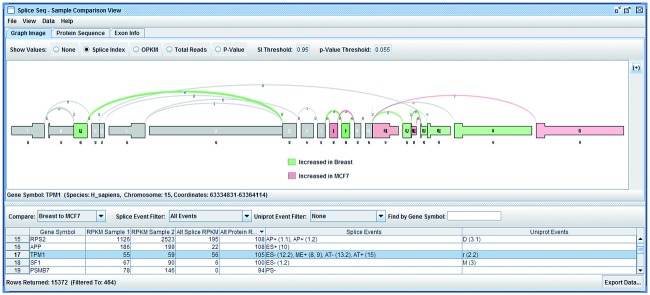 SynteBase and SynteView
SynteBase and SynteView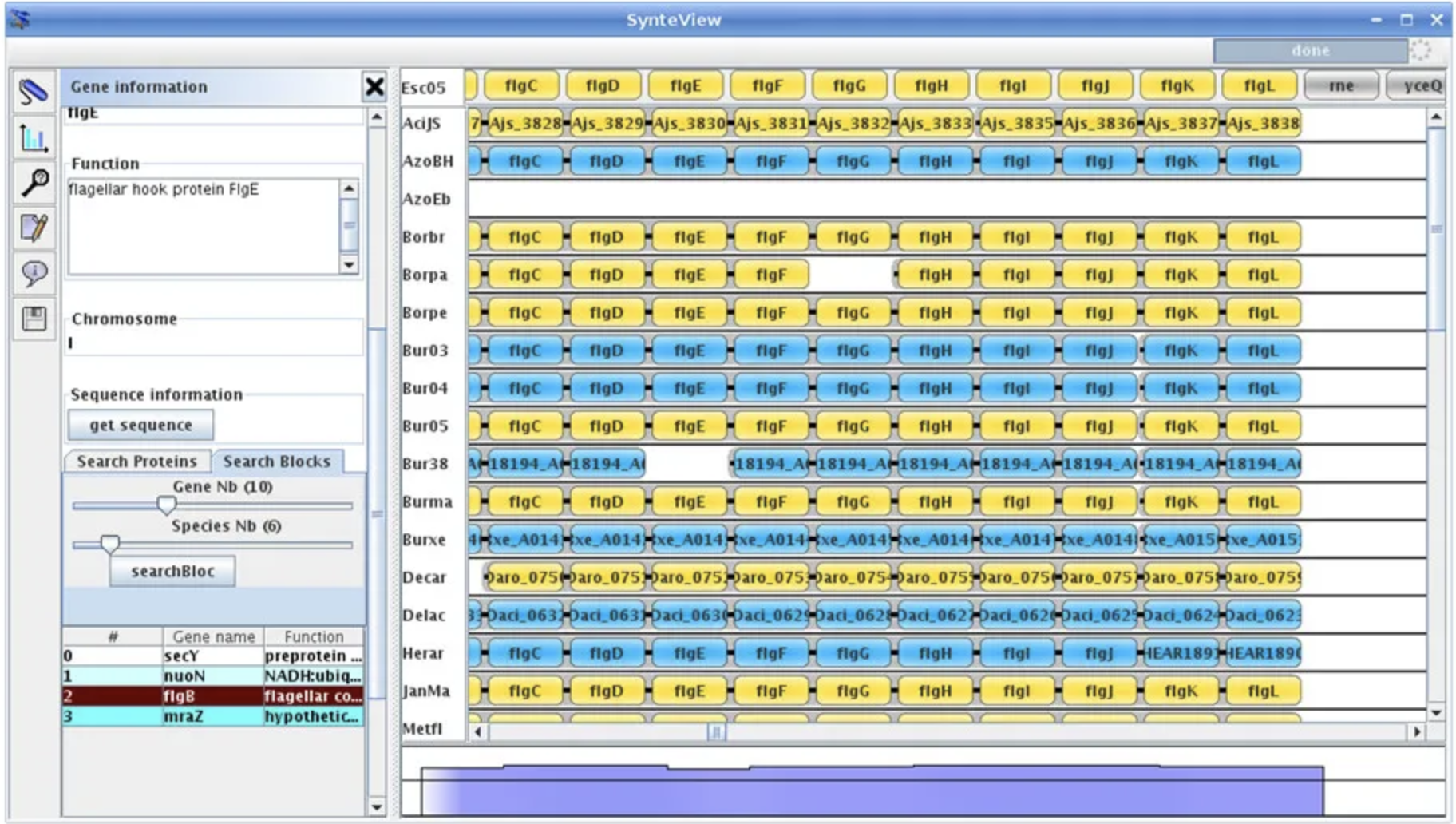 Synteny Explorer
Synteny Explorer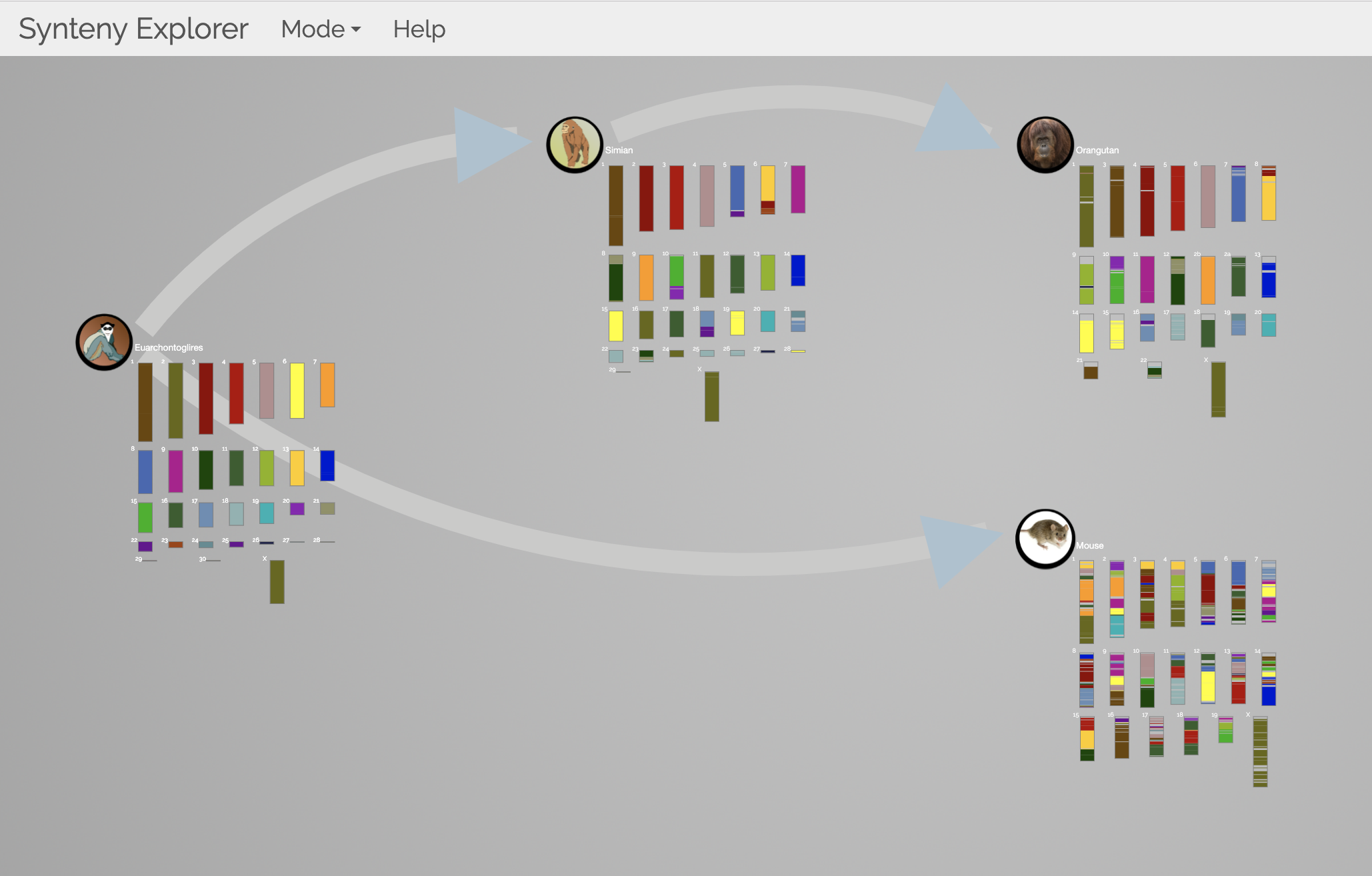 trackViewer
trackViewer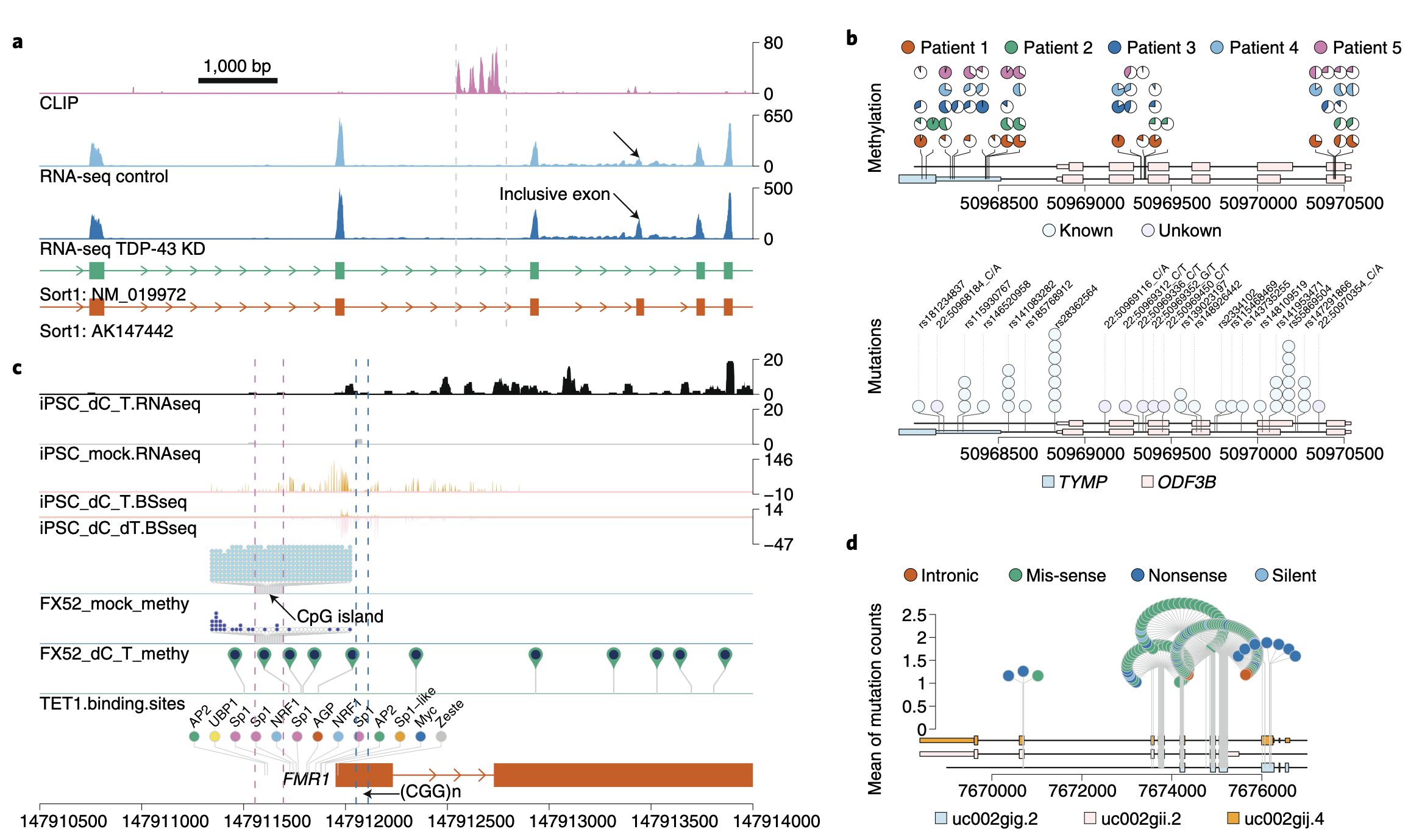 UCSC Genome Browser
UCSC Genome Browser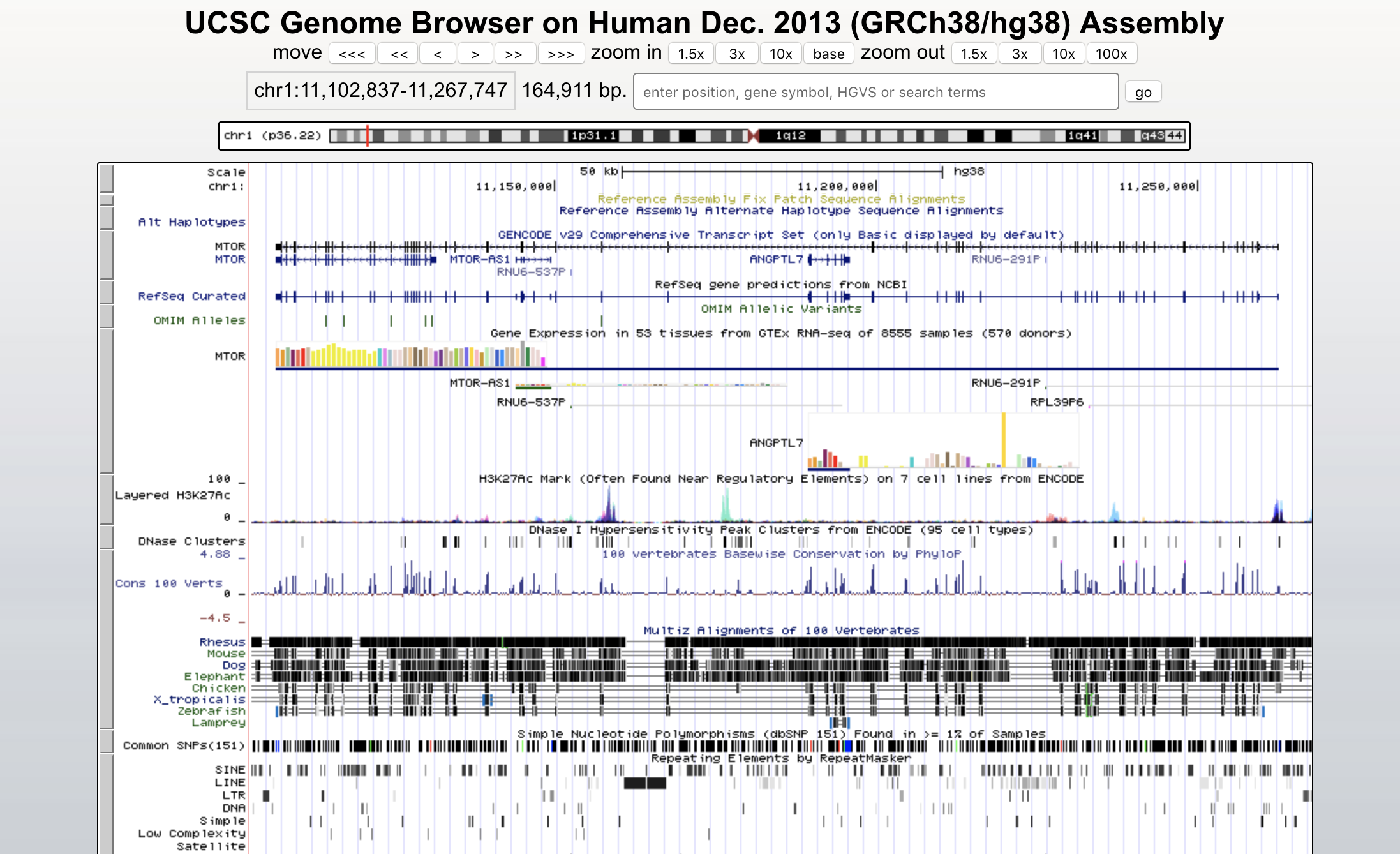 Variant View
Variant View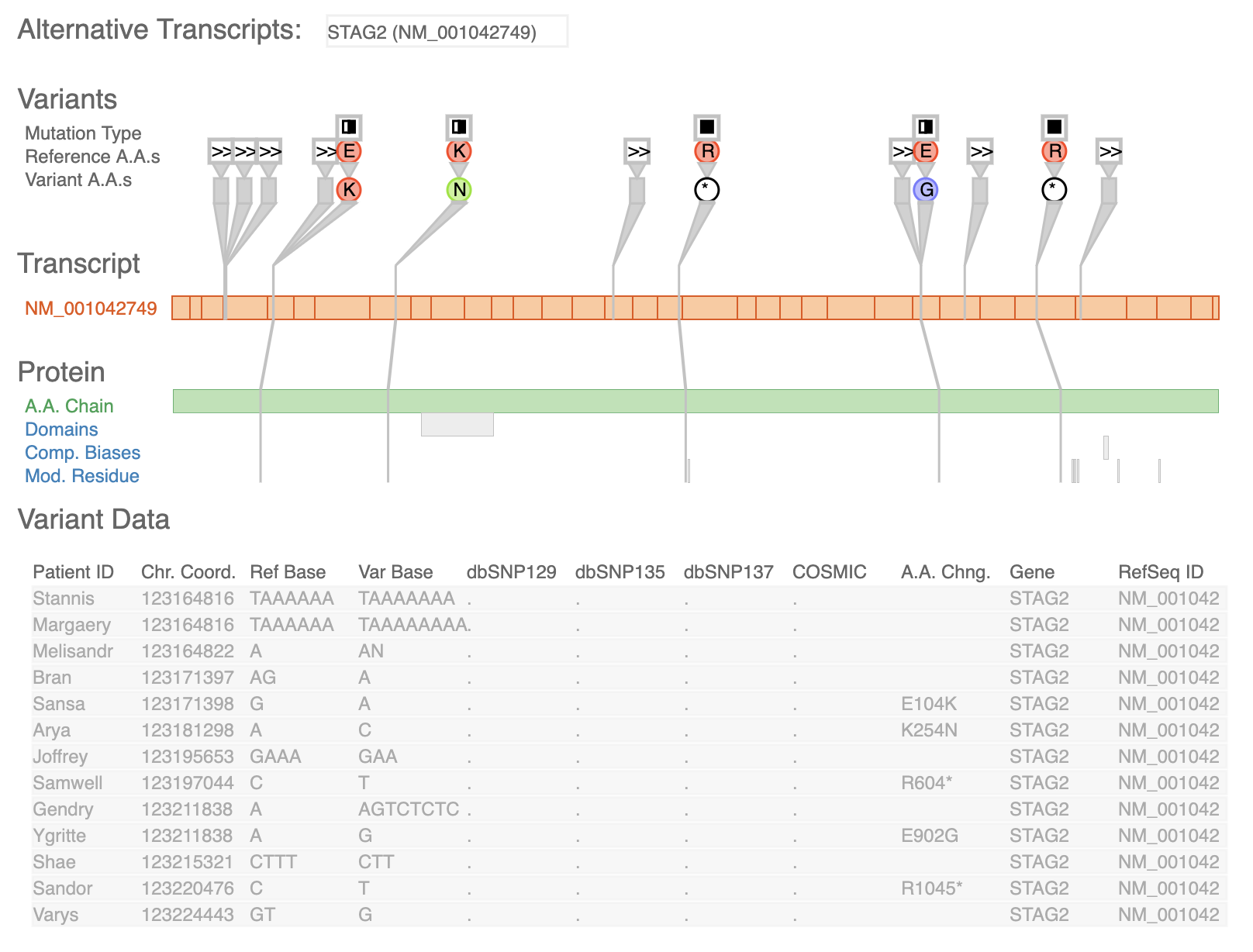 Vista Synteny
Vista Synteny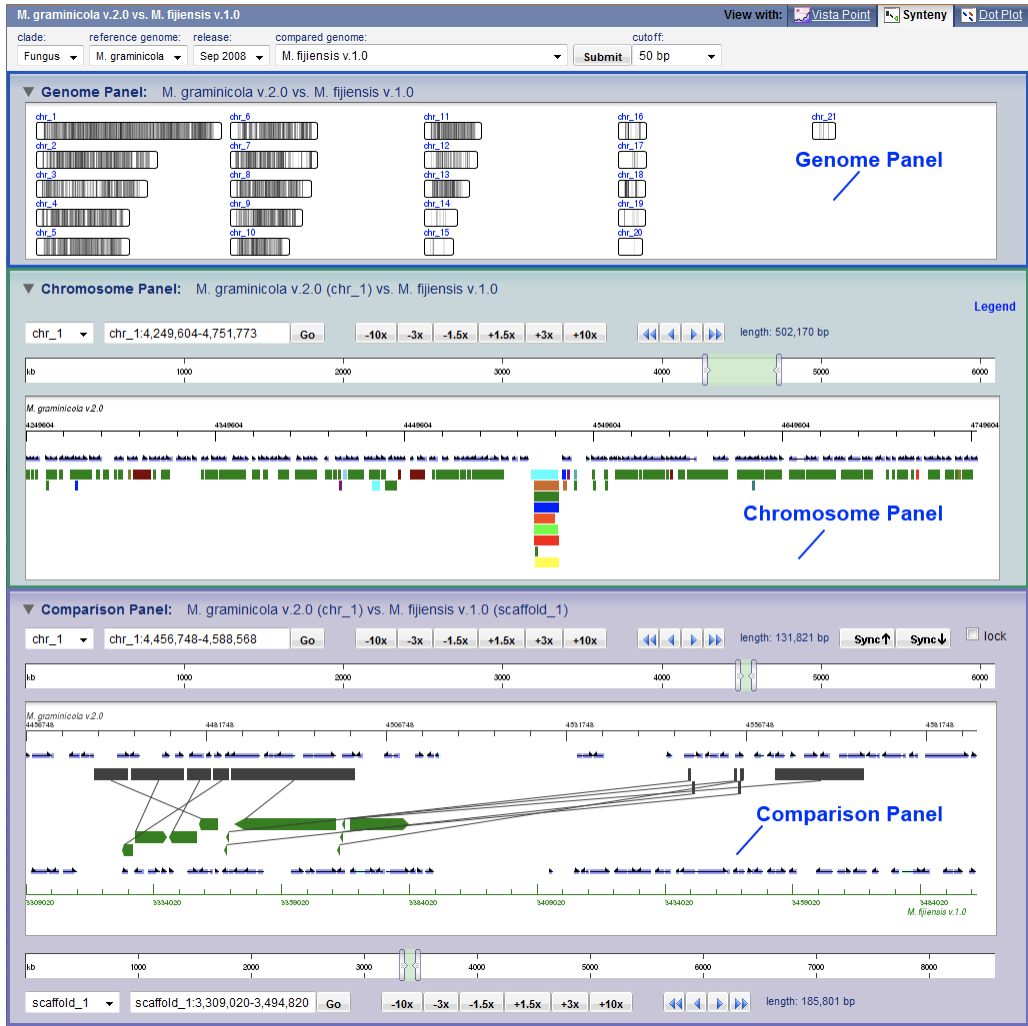 VistaPoint
VistaPoint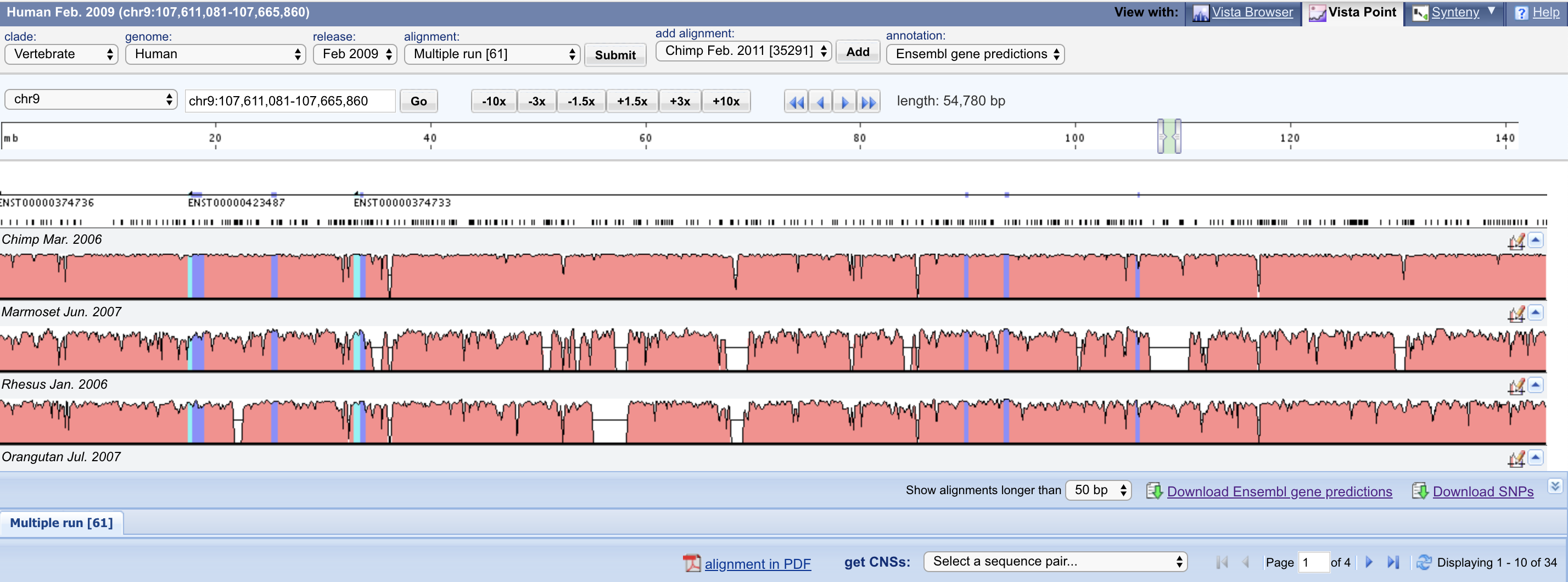 Xena
Xena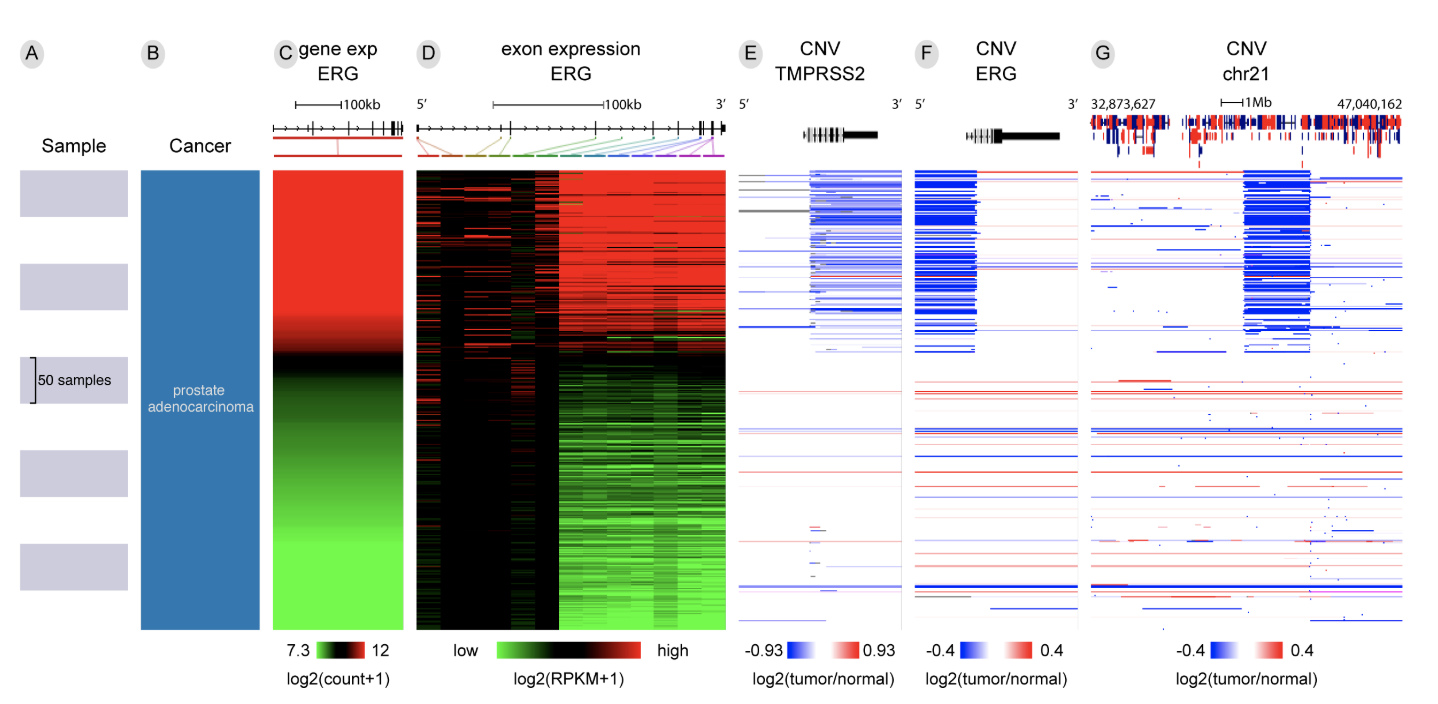
 AliView
AliView CEpBrowser
CEpBrowser CGView
CGView CGView Server
CGView Server Cinteny
Cinteny Circos
Circos ClicO Free Service
ClicO Free Service CNVkit
CNVkit Dalliance
Dalliance deepTools Heatmap
deepTools Heatmap Edgar Genome Browser
Edgar Genome Browser EnrichedHeatmap
EnrichedHeatmap Ensembl
Ensembl EpiViz
EpiViz GBrowse
GBrowse GBrowse_syn
GBrowse_syn GenomeRing
GenomeRing GenomeView
GenomeView genoPlotR
genoPlotR GenPlay
GenPlay ggBio
ggBio GIVE
GIVE HUGIn
HUGIn IRScope
IRScope Island Viewer
Island Viewer JalView
JalView JBrowse
JBrowse MAGI
MAGI MochiView
MochiView NCBI Genome Viewer
NCBI Genome Viewer NCBI Sequence Viewer
NCBI Sequence Viewer Persephone
Persephone PSU 3D Genome Browser
PSU 3D Genome Browser ReadXplorer
ReadXplorer RIdeogram
RIdeogram Savant Genome Browser 2
Savant Genome Browser 2 Spatial DB
Spatial DB SpliceGrapher
SpliceGrapher SplicePlot
SplicePlot SpliceSeq
SpliceSeq SynteBase and SynteView
SynteBase and SynteView Synteny Explorer
Synteny Explorer trackViewer
trackViewer UCSC Genome Browser
UCSC Genome Browser Variant View
Variant View Vista Synteny
Vista Synteny VistaPoint
VistaPoint Xena
Xena