Layouts
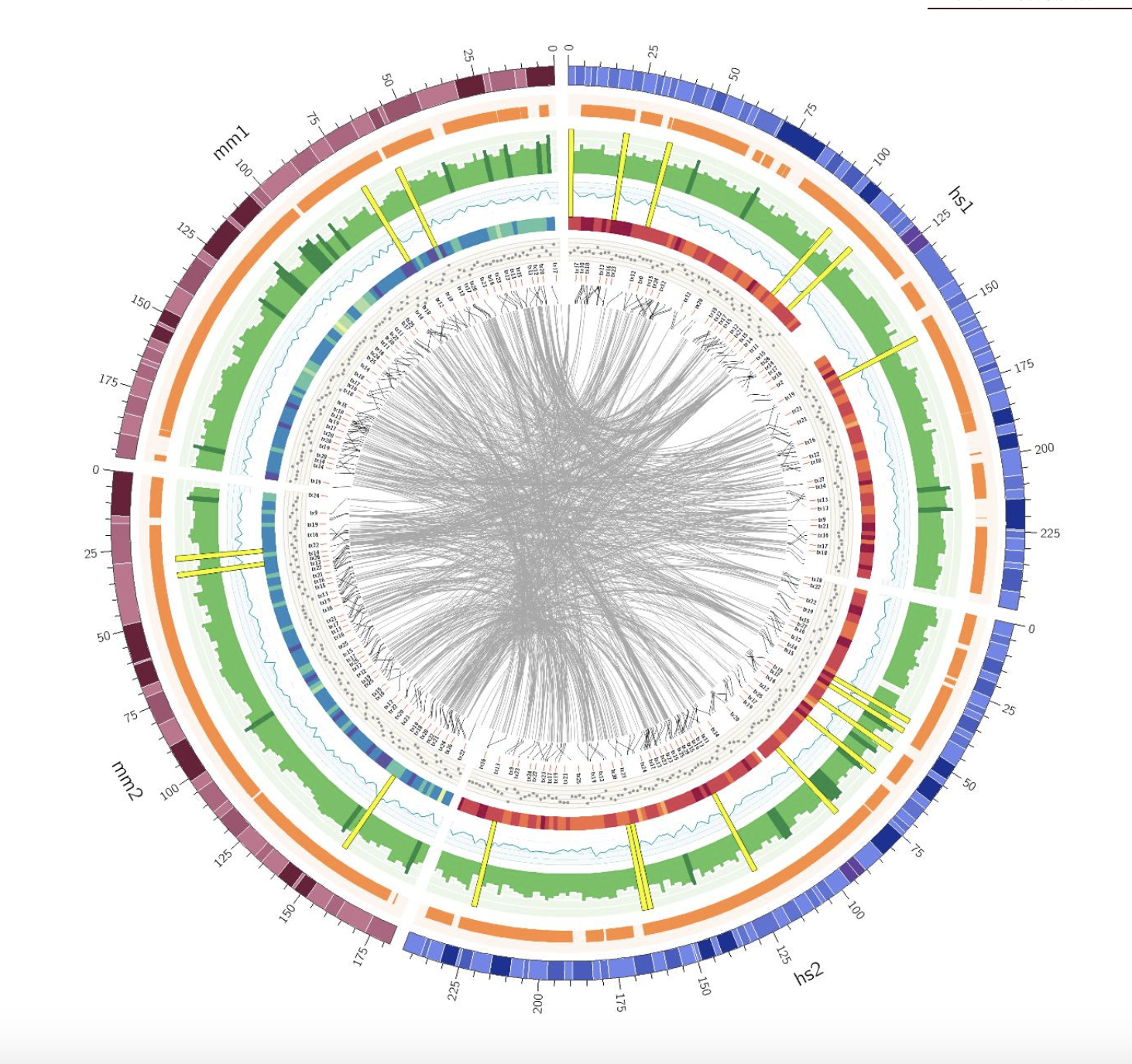
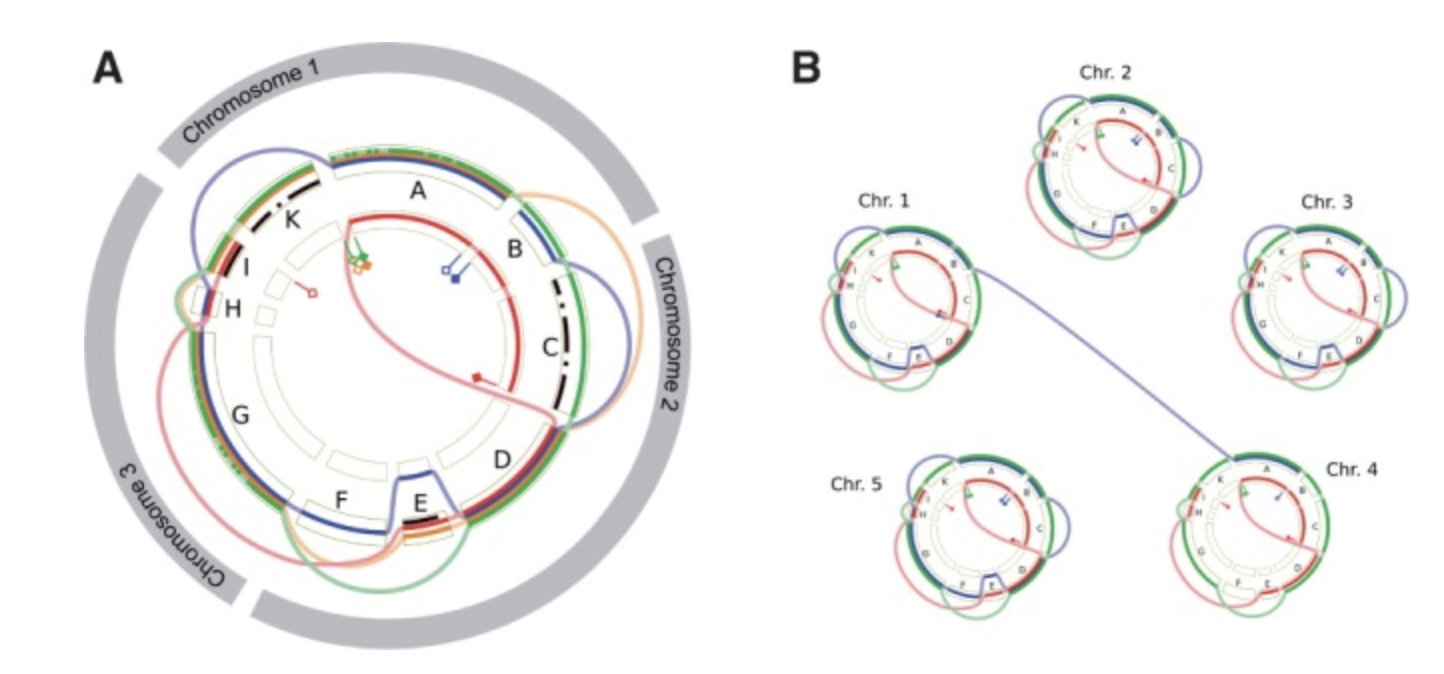
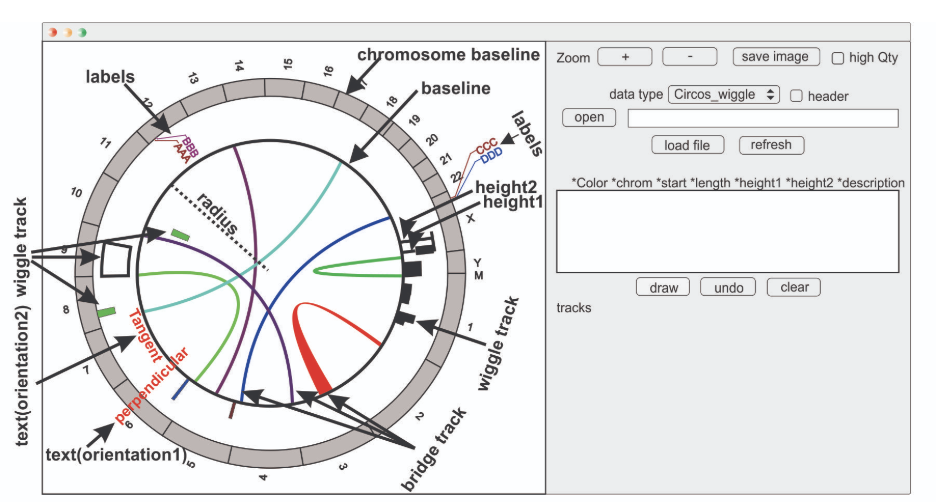
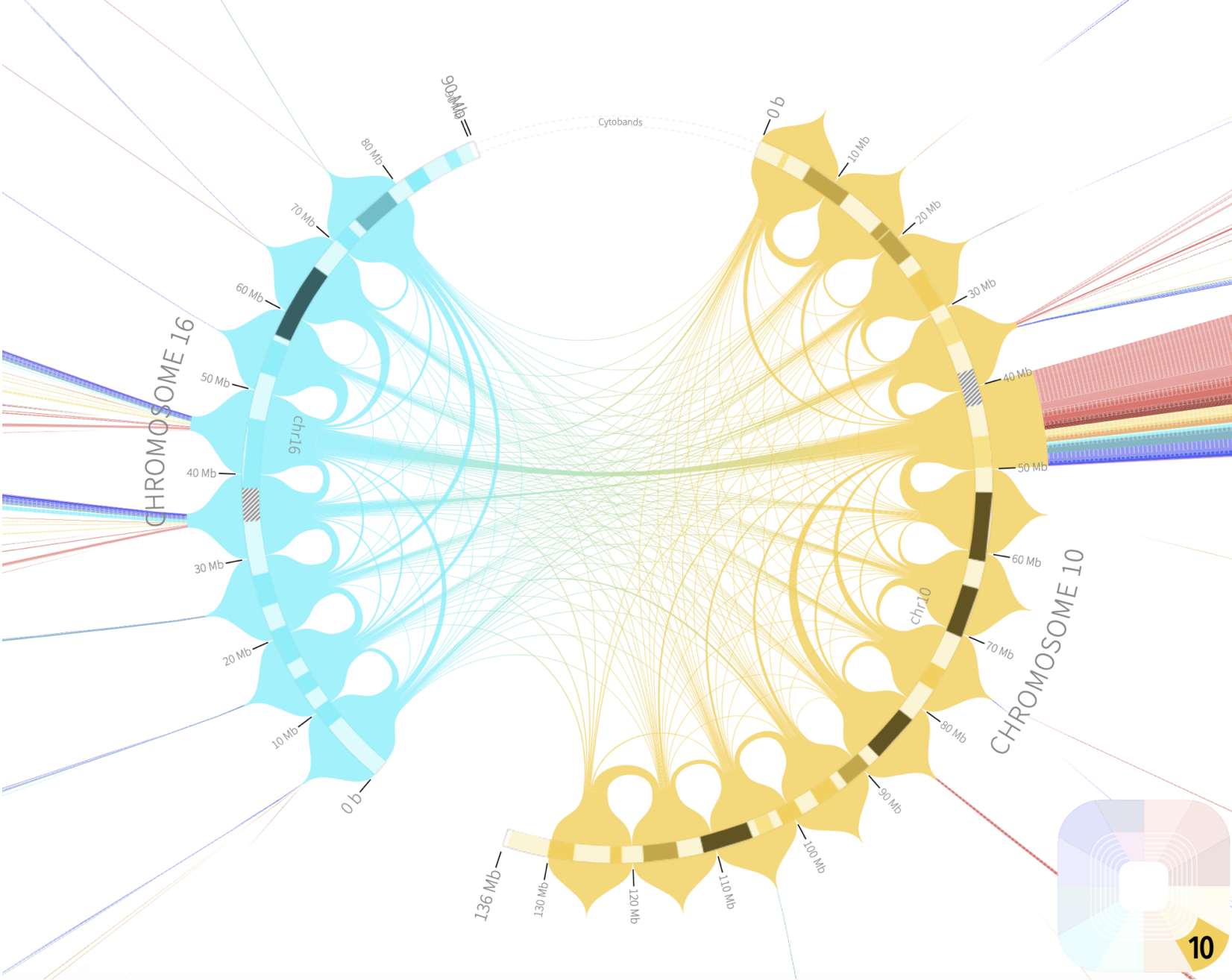
Circular
Circular layouts are mainly used (1) if the displayed sequence itself is circular, (2) to display a non-circular sequence in a space-saving way, and (3) to show interactions between different parts of the sequence(s) using a chord diagram.
17 tools
Linear
Linear layouts are more intuitive and easy to read, but may be extremely long and require zooming and panning.
95 tools
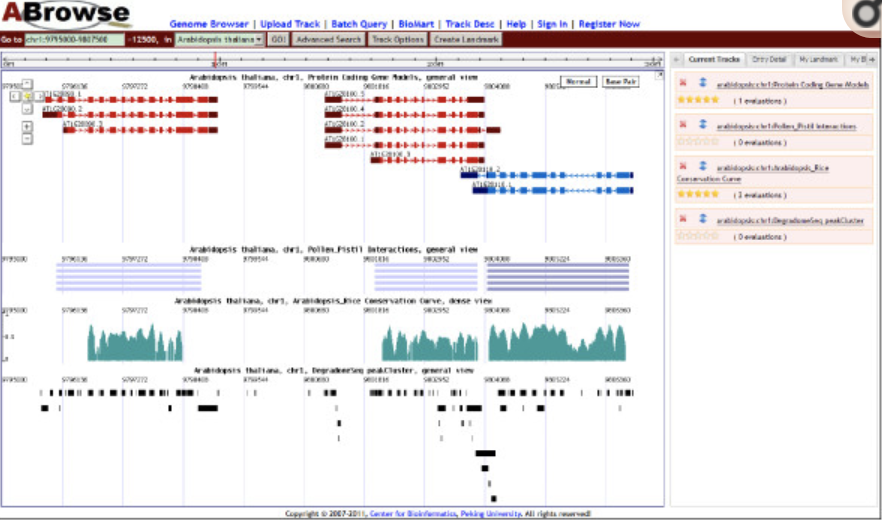
ABrowse
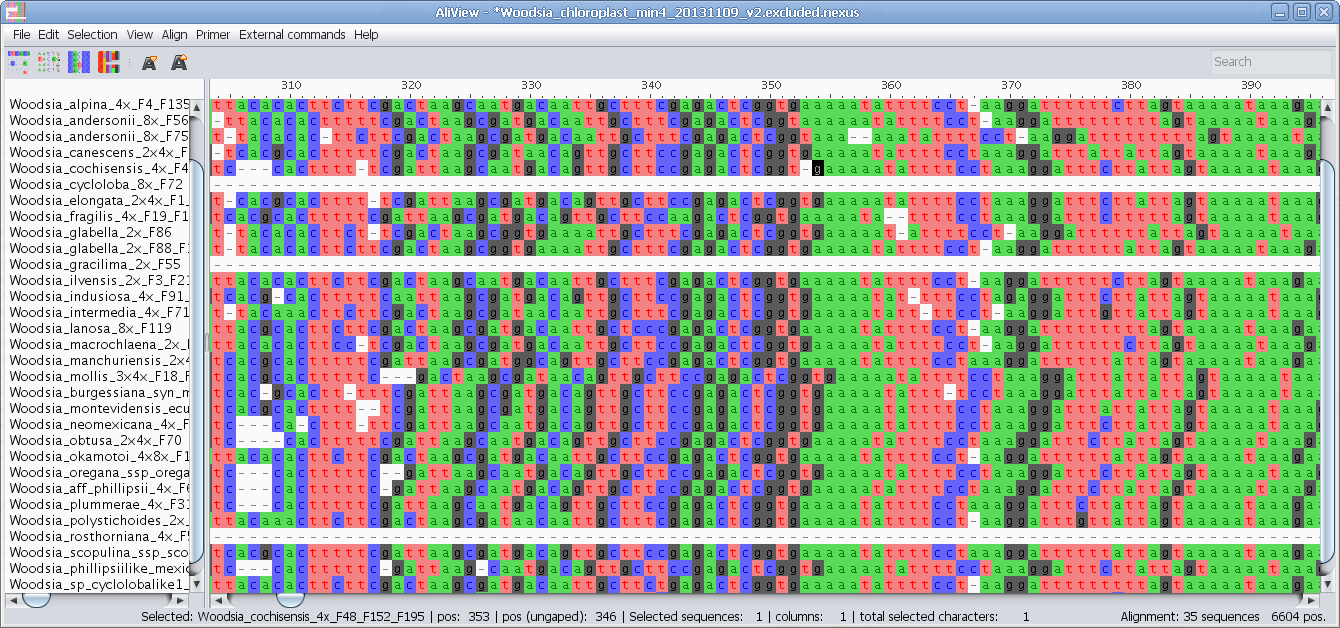
AliView
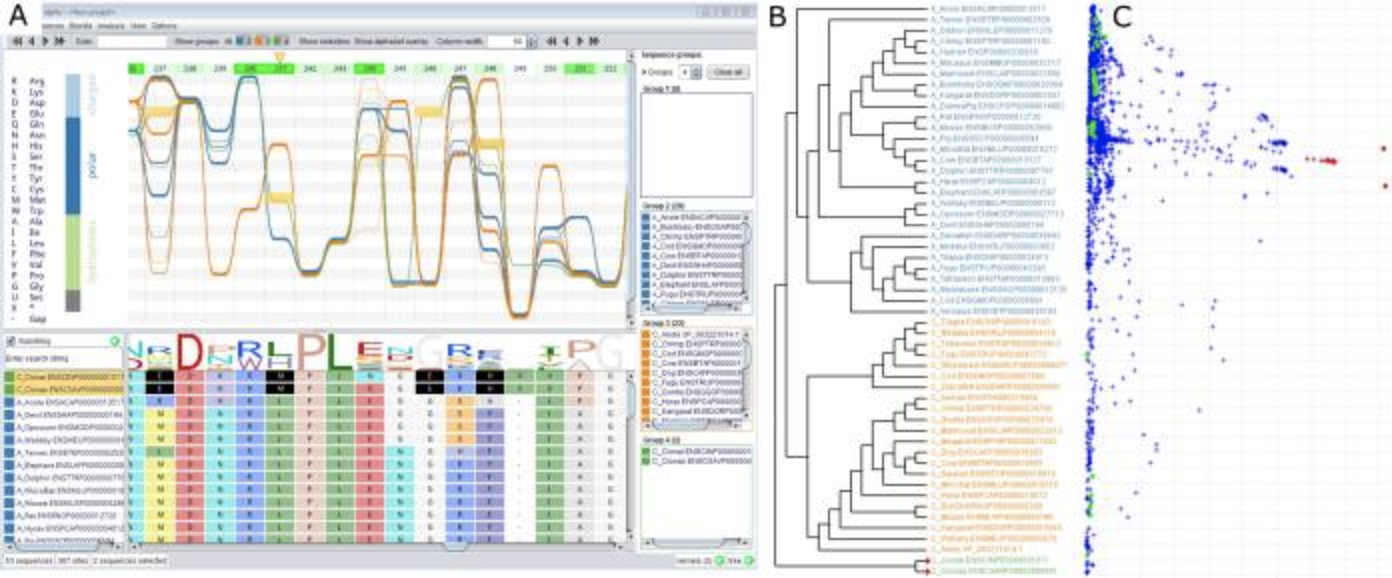
Alvis
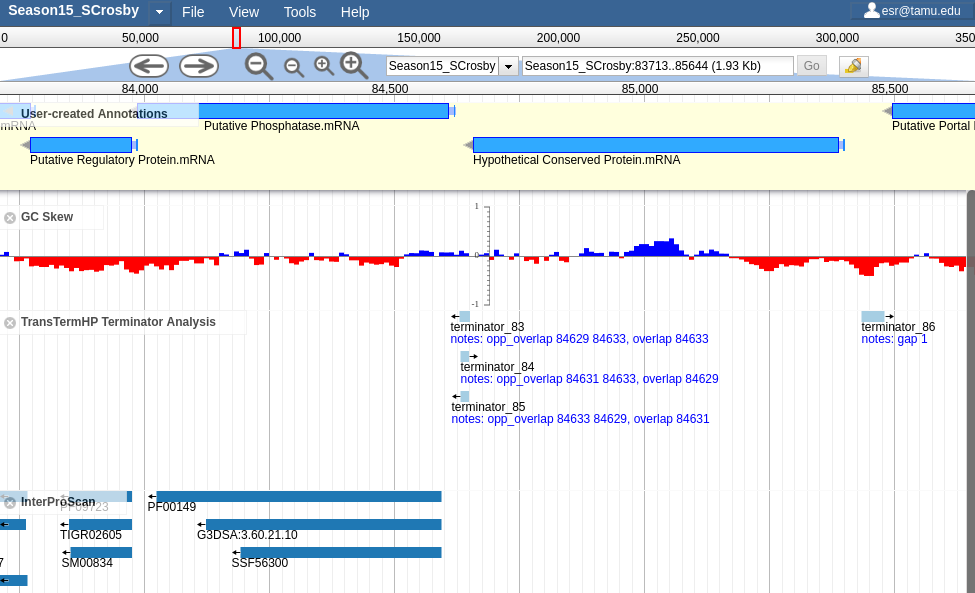
Apollo
BactoGenie
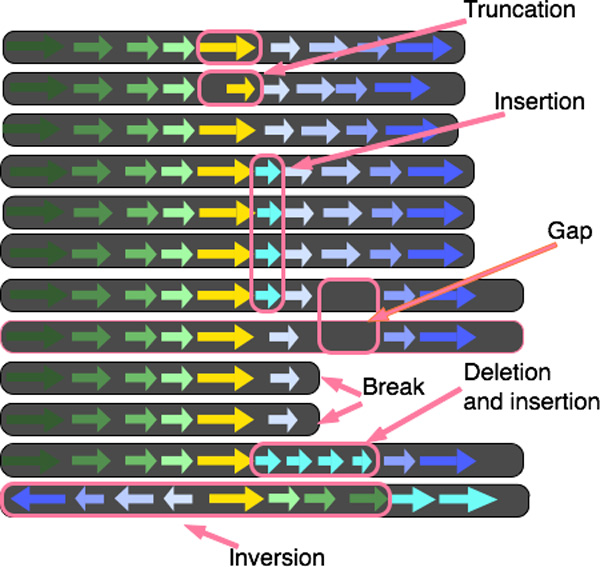
BedSect
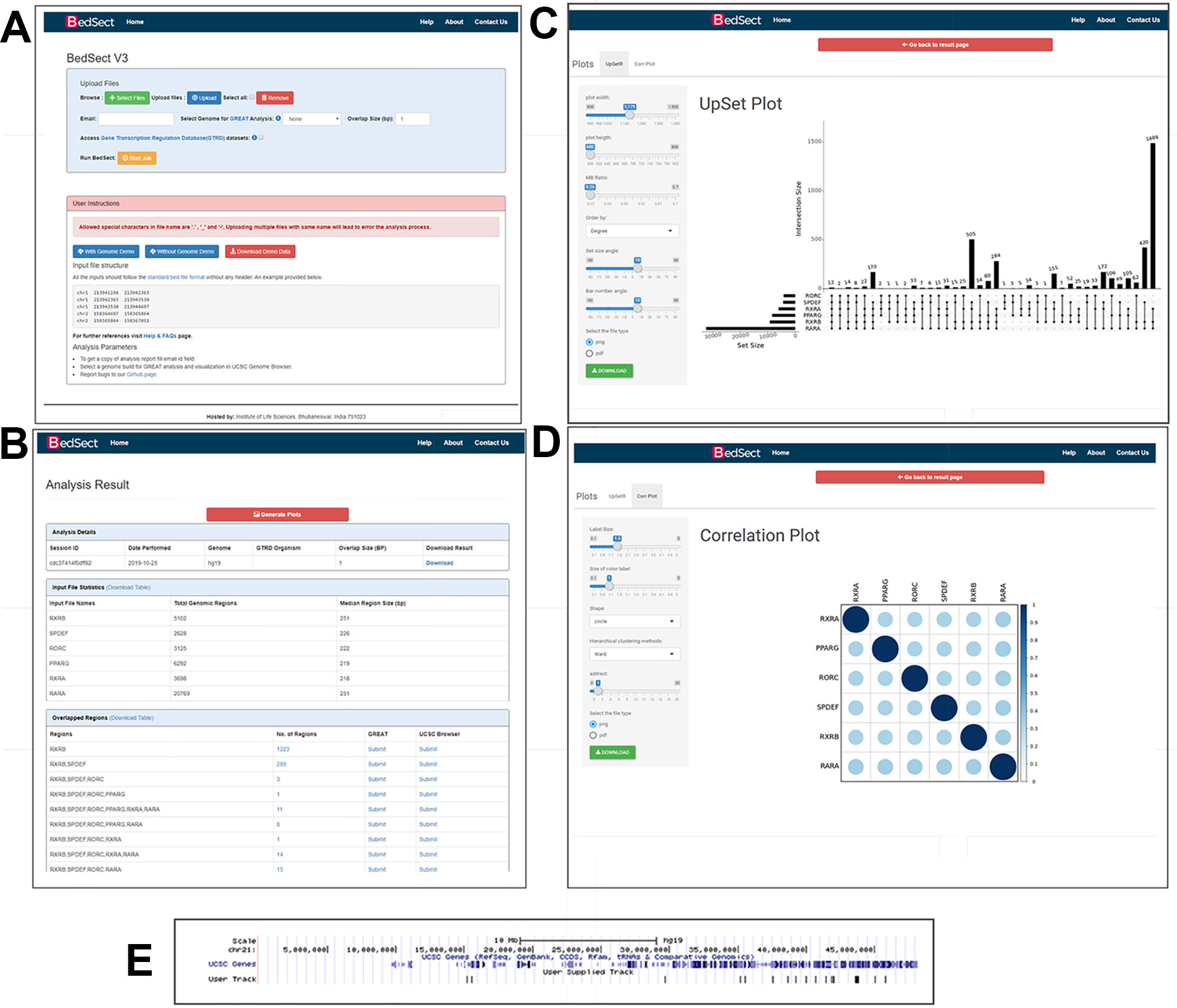
CEpBrowser
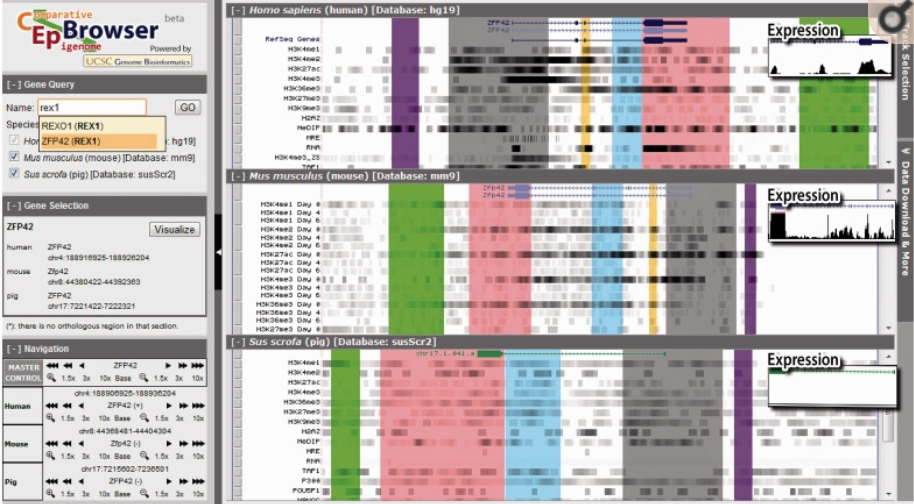
Cinteny
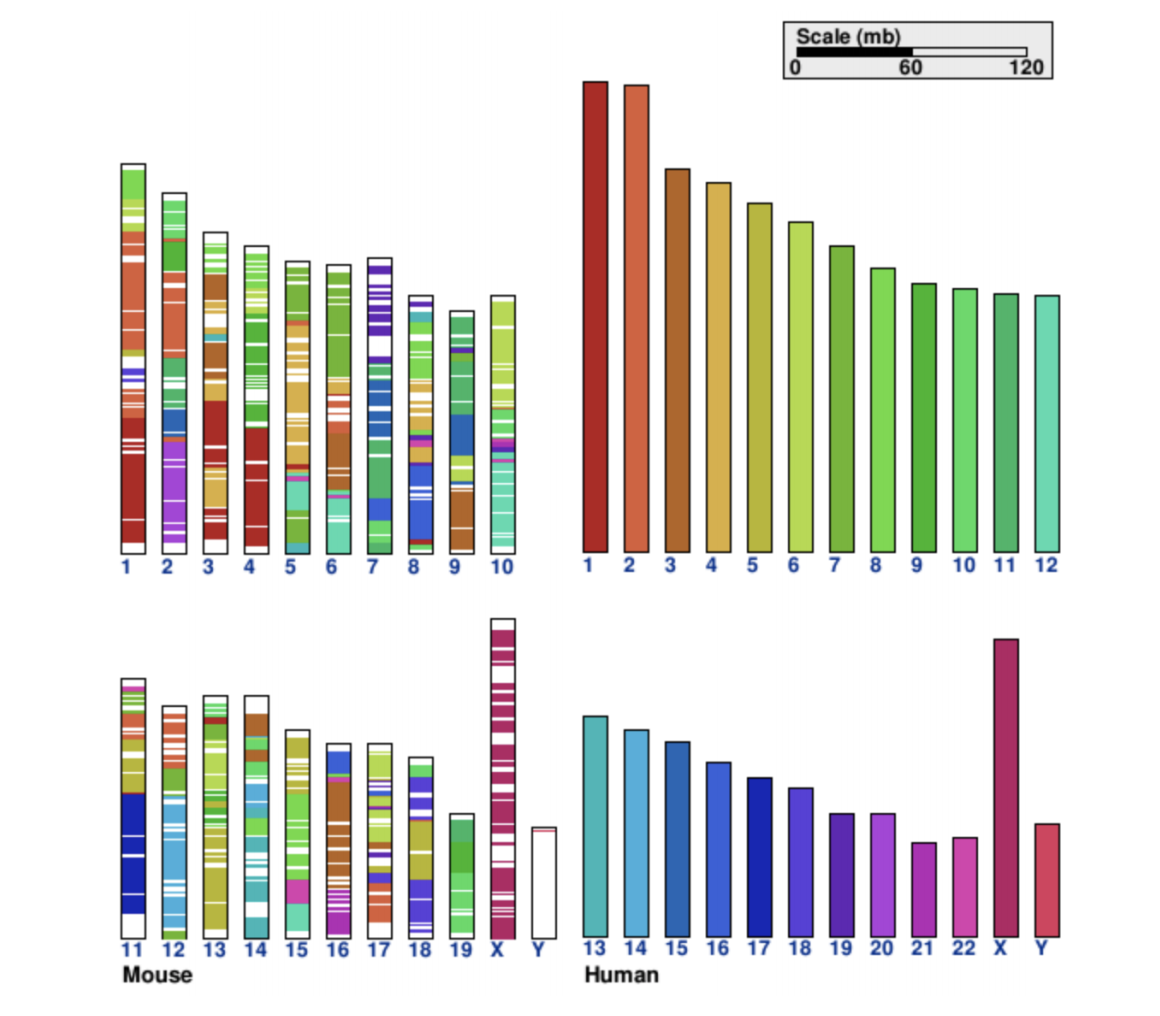
CNVkit
Combo
Cooler
CRAMER
CRISPResso2
Dalliance
Deep Motif Dashboard
deepTools Heatmap
DNAPlotter
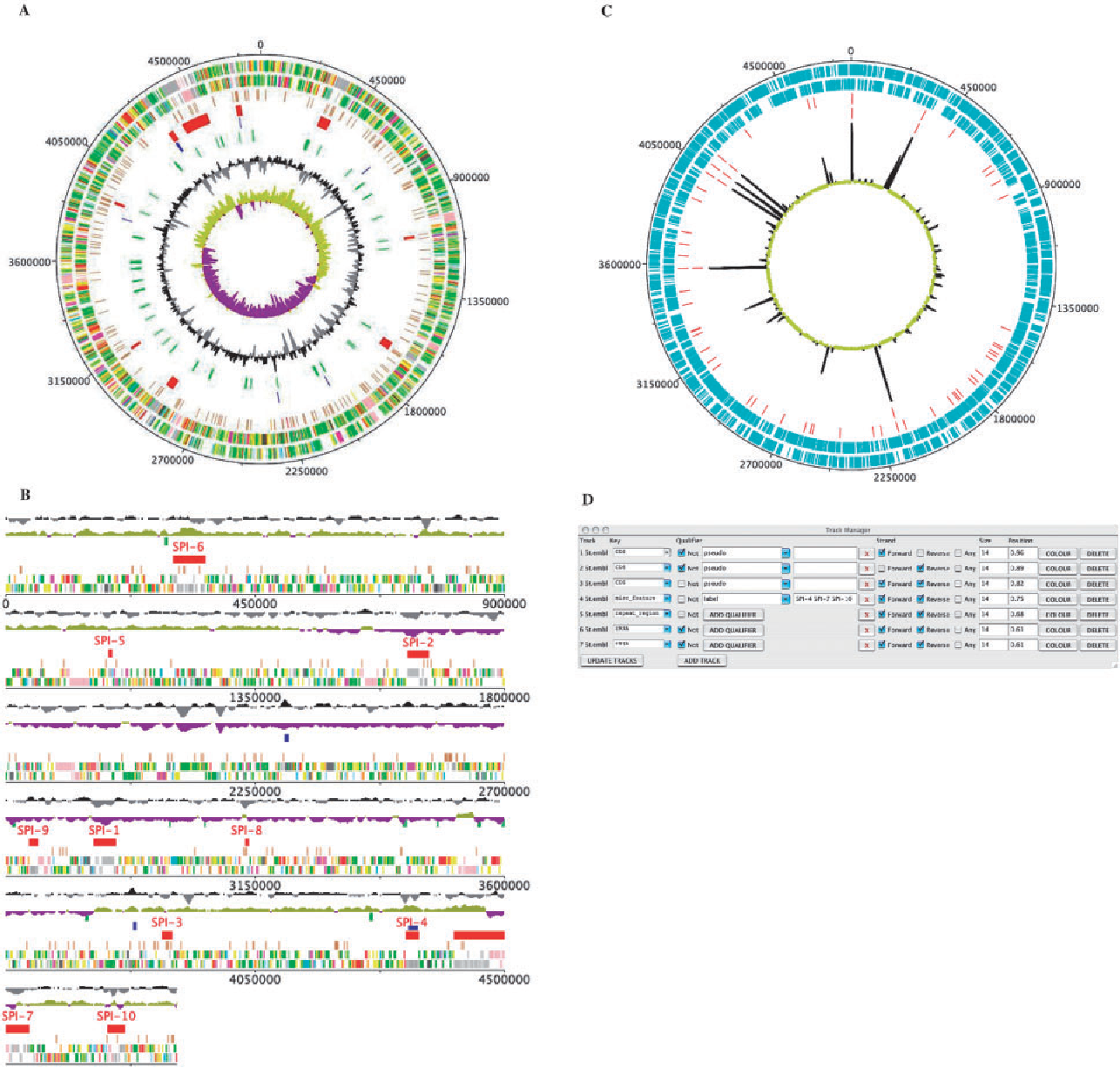
EaSeq
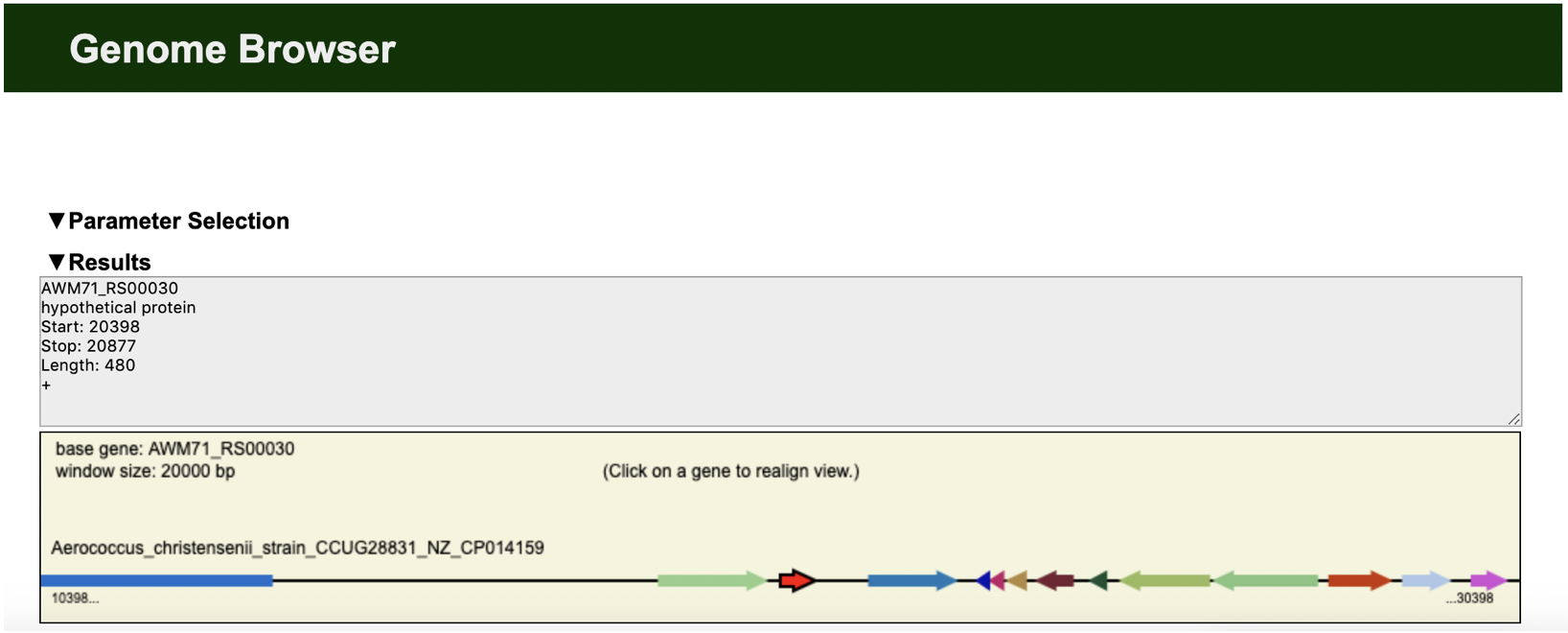
Edgar Genome Browser
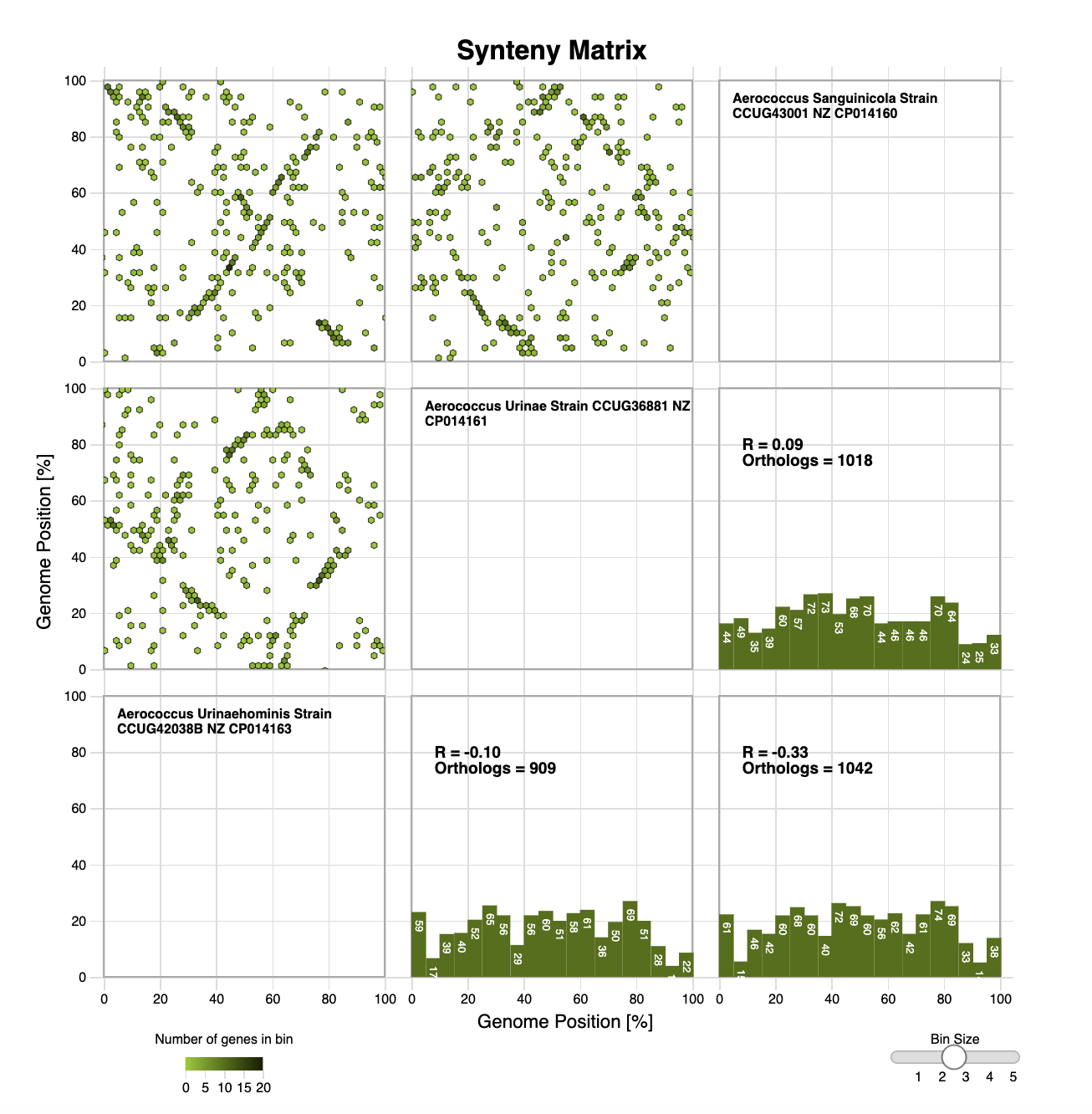
Edgar Synteny Plots
EnrichedHeatmap
Ensembl
EpiViz
Galaxy HiCExplorer
GBrowse
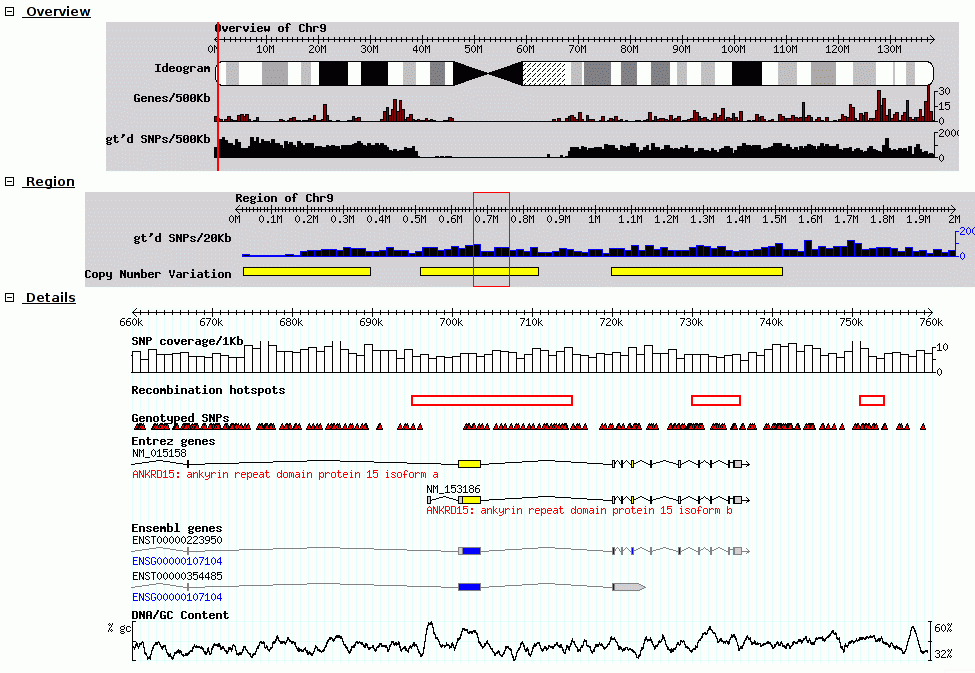
GBrowse_syn
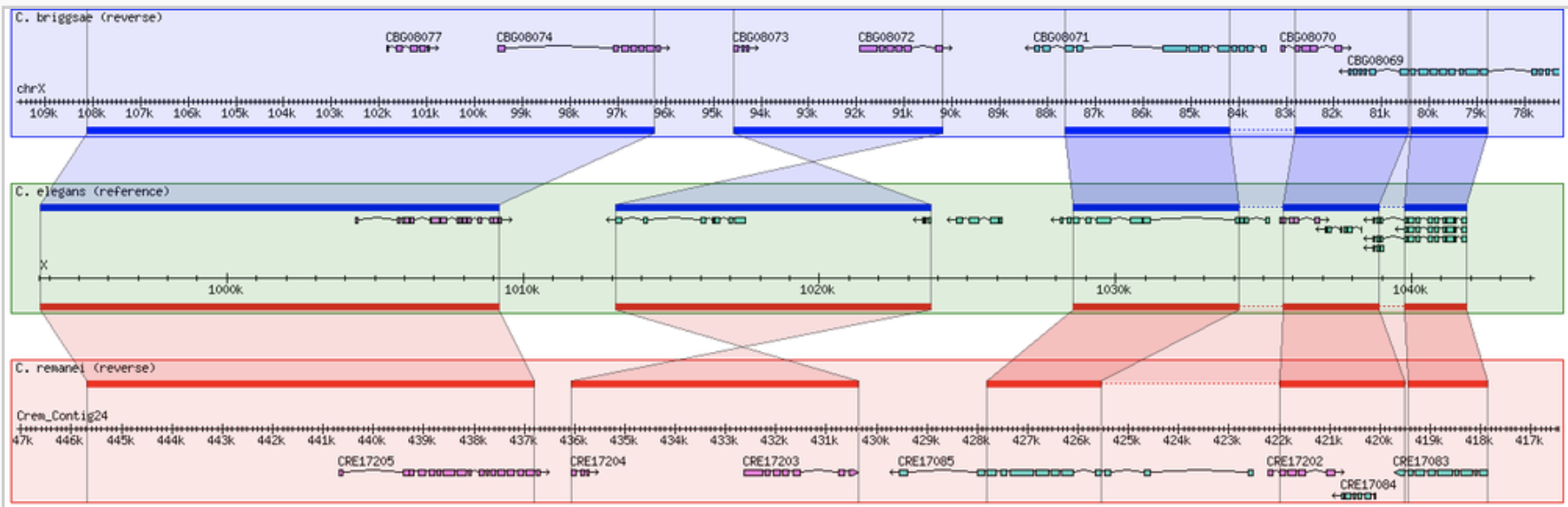
Geneious
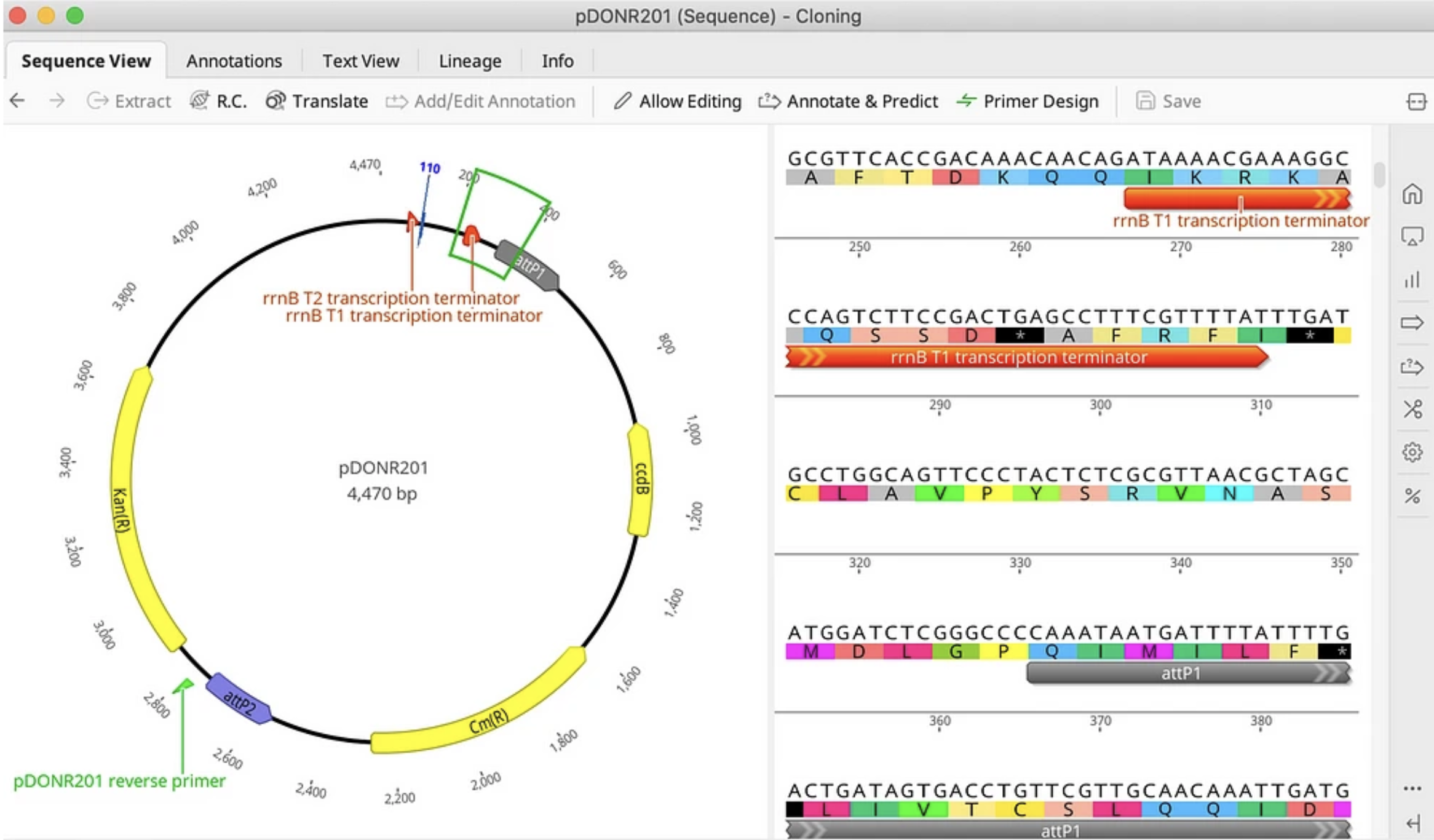
Genome Annotator Light (GAL)
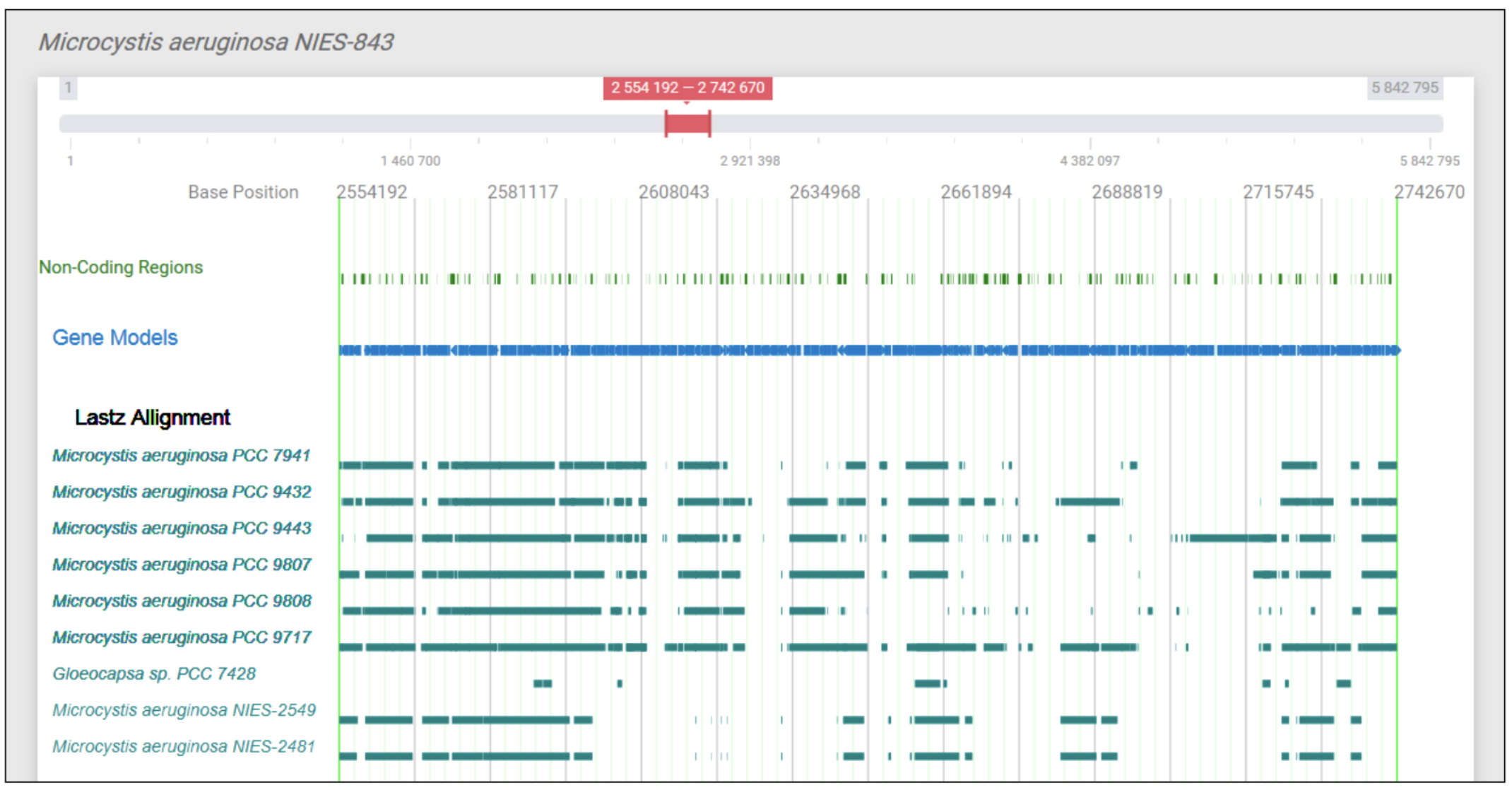
GenomeView
genoPlotR
GenPlay
Gepard
ggBio
GIVE
Gosling
Gremlin
GView
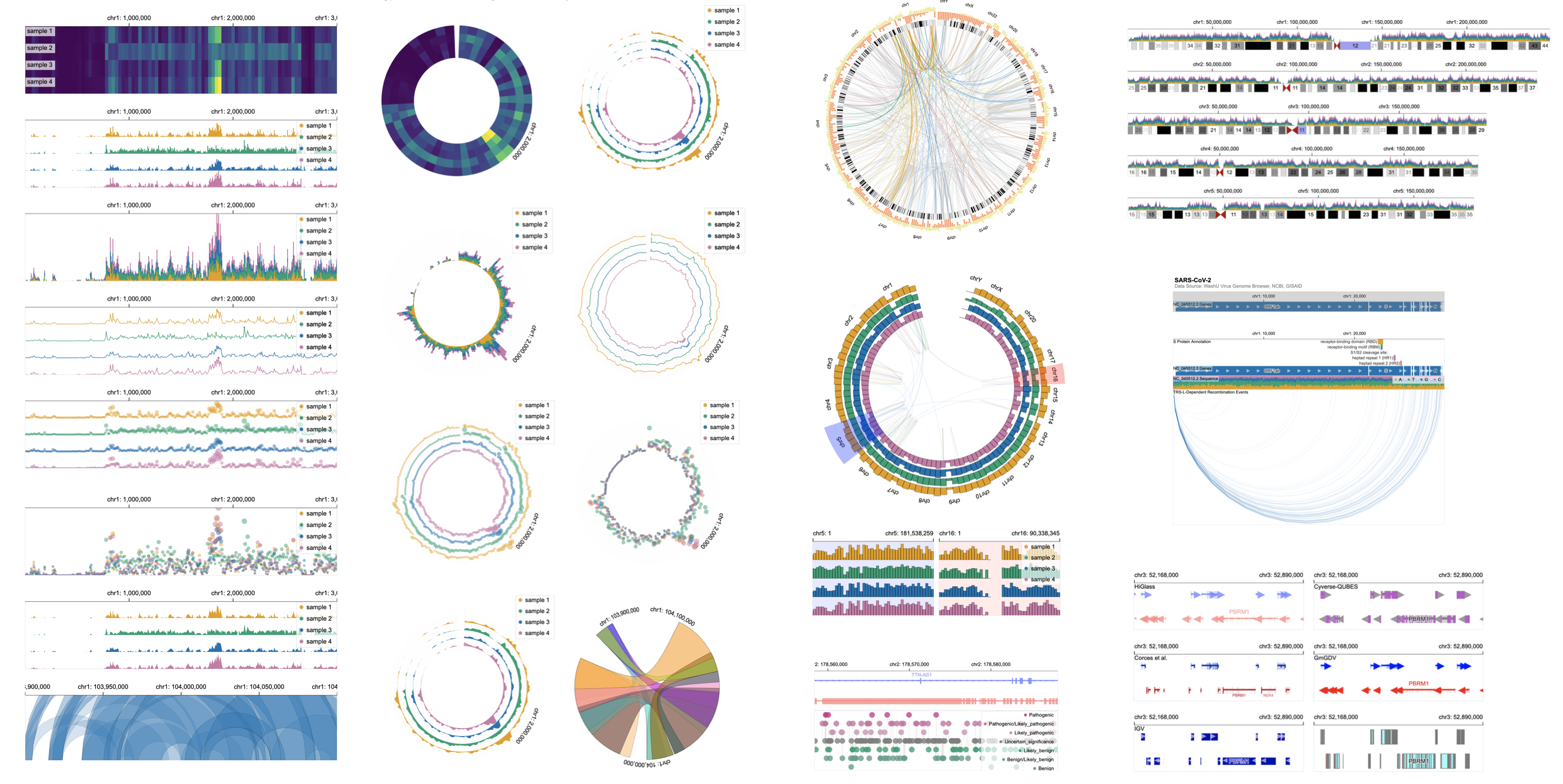
HiGlass
HiPiler

HUGIn
IGB
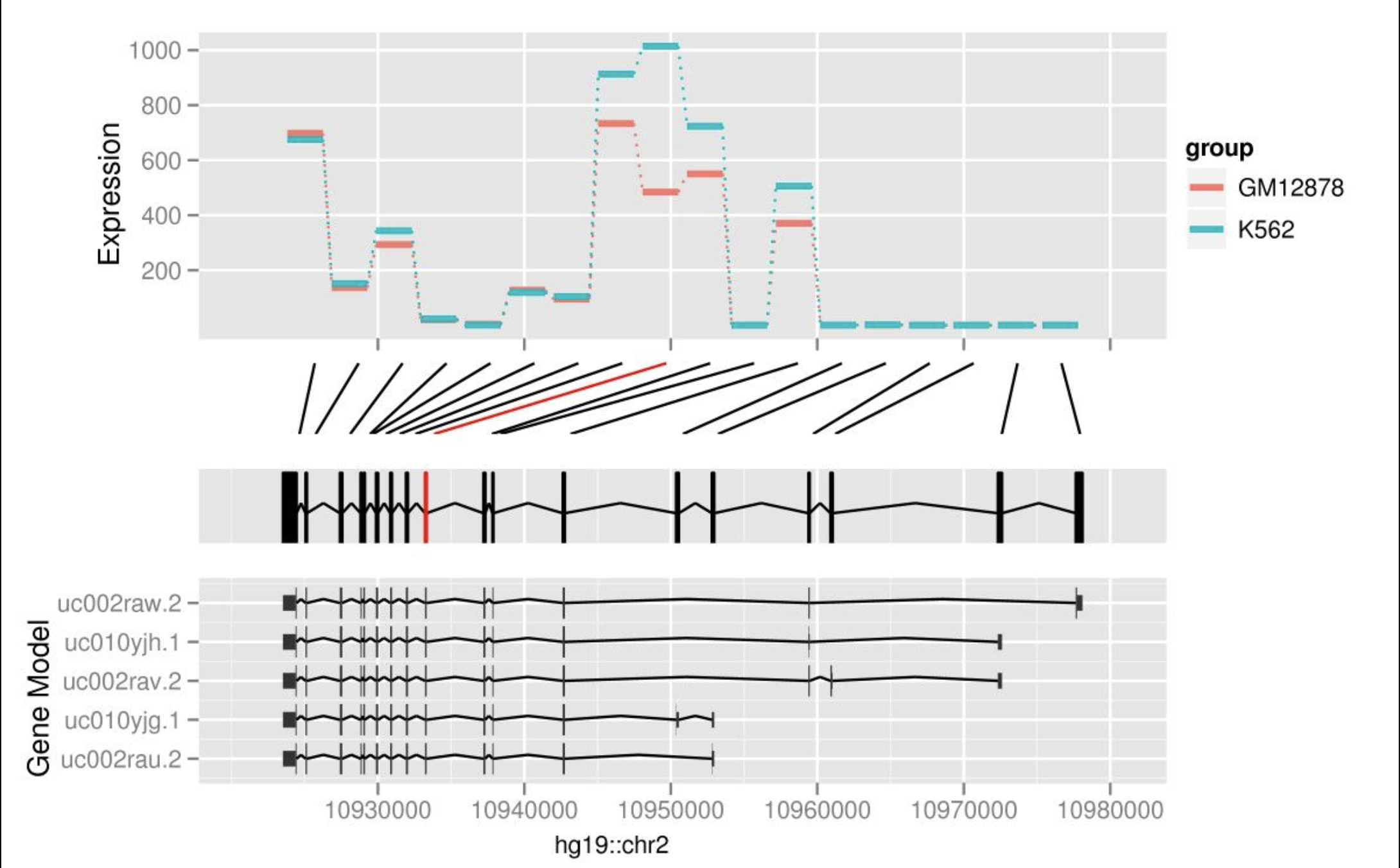
Integrative Genomics Viewer
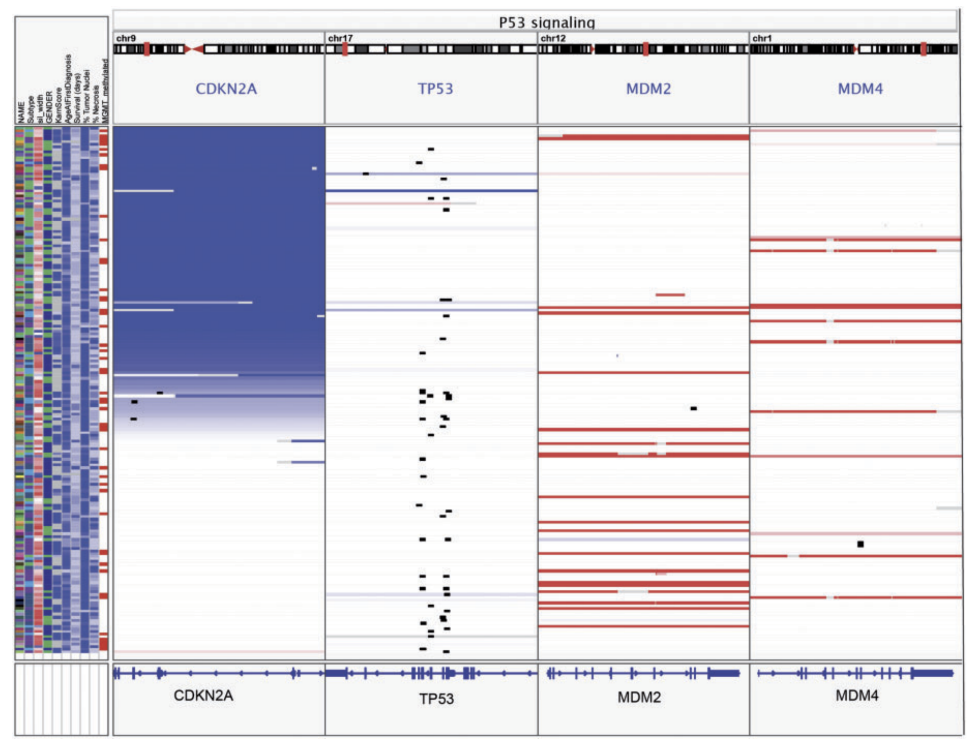
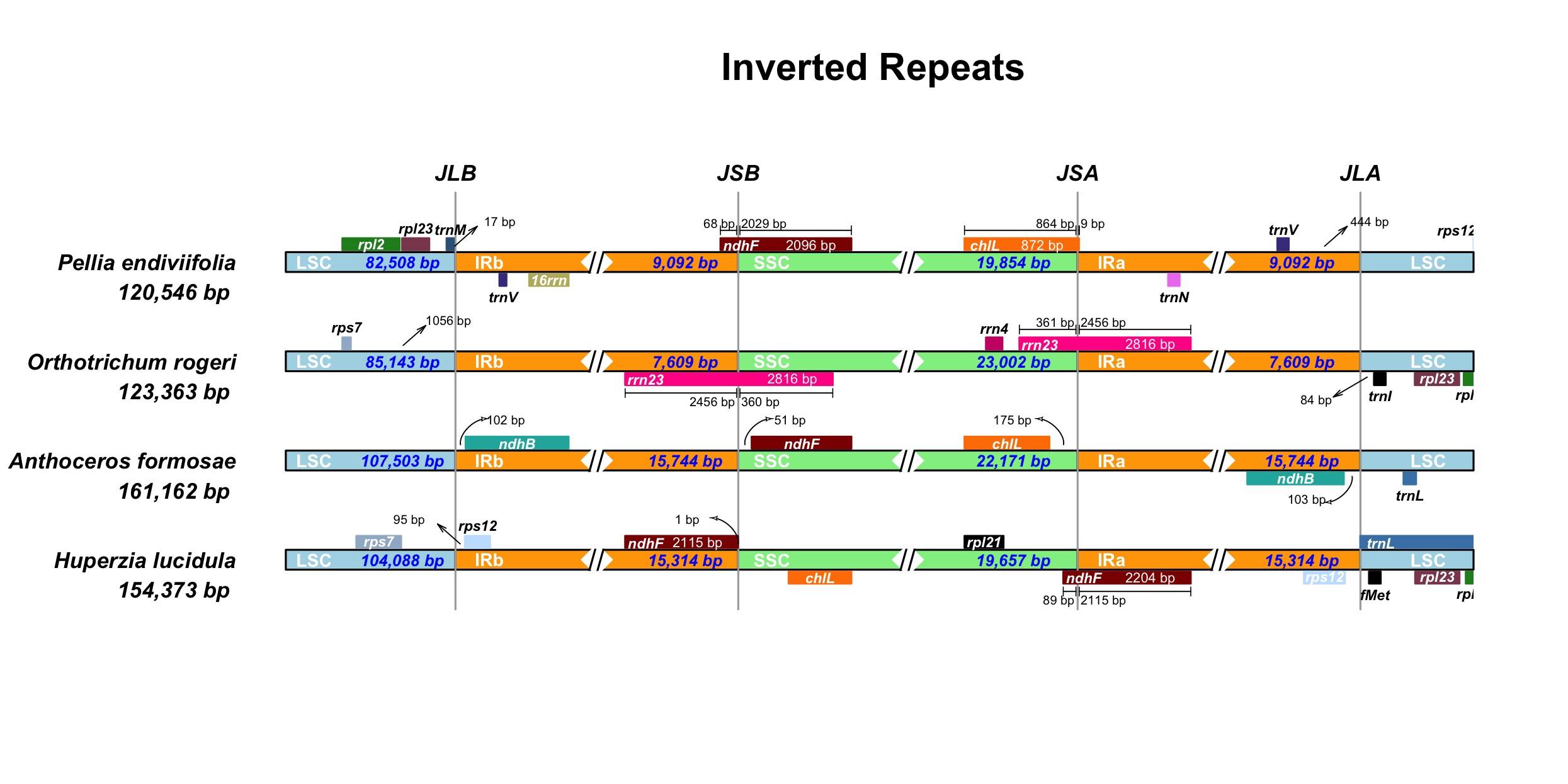
IRScope
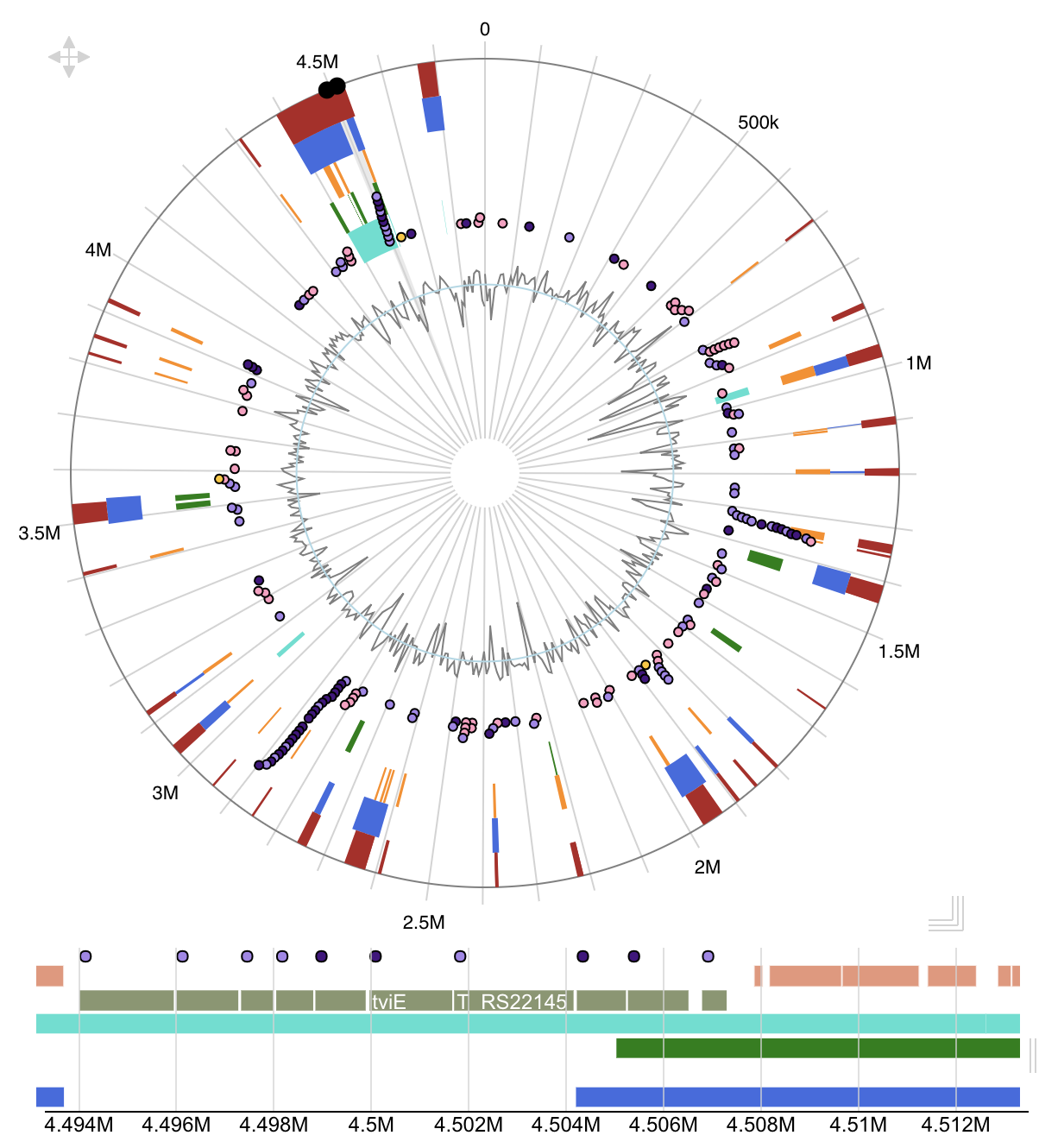
Island Viewer
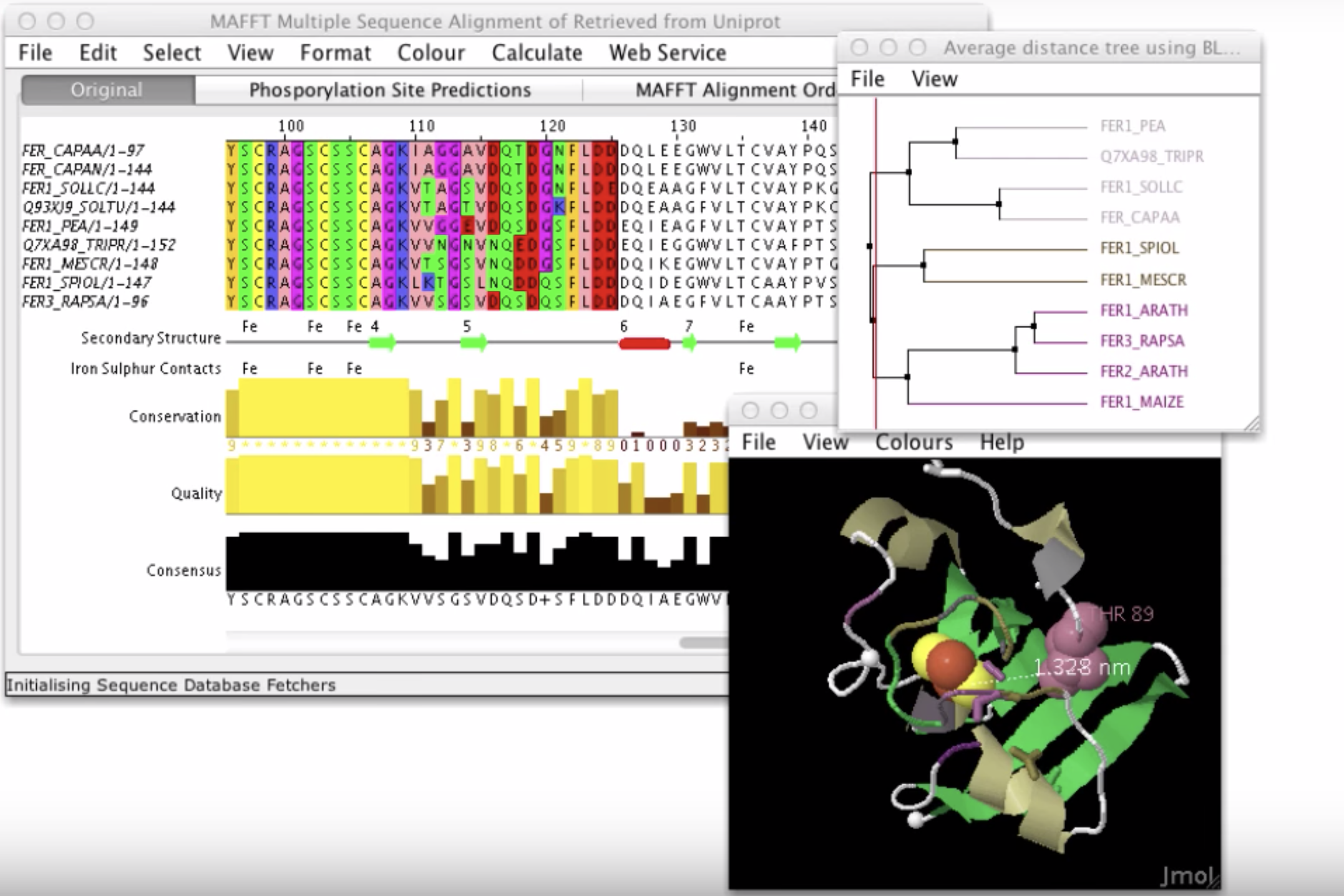
JalView
JBrowse
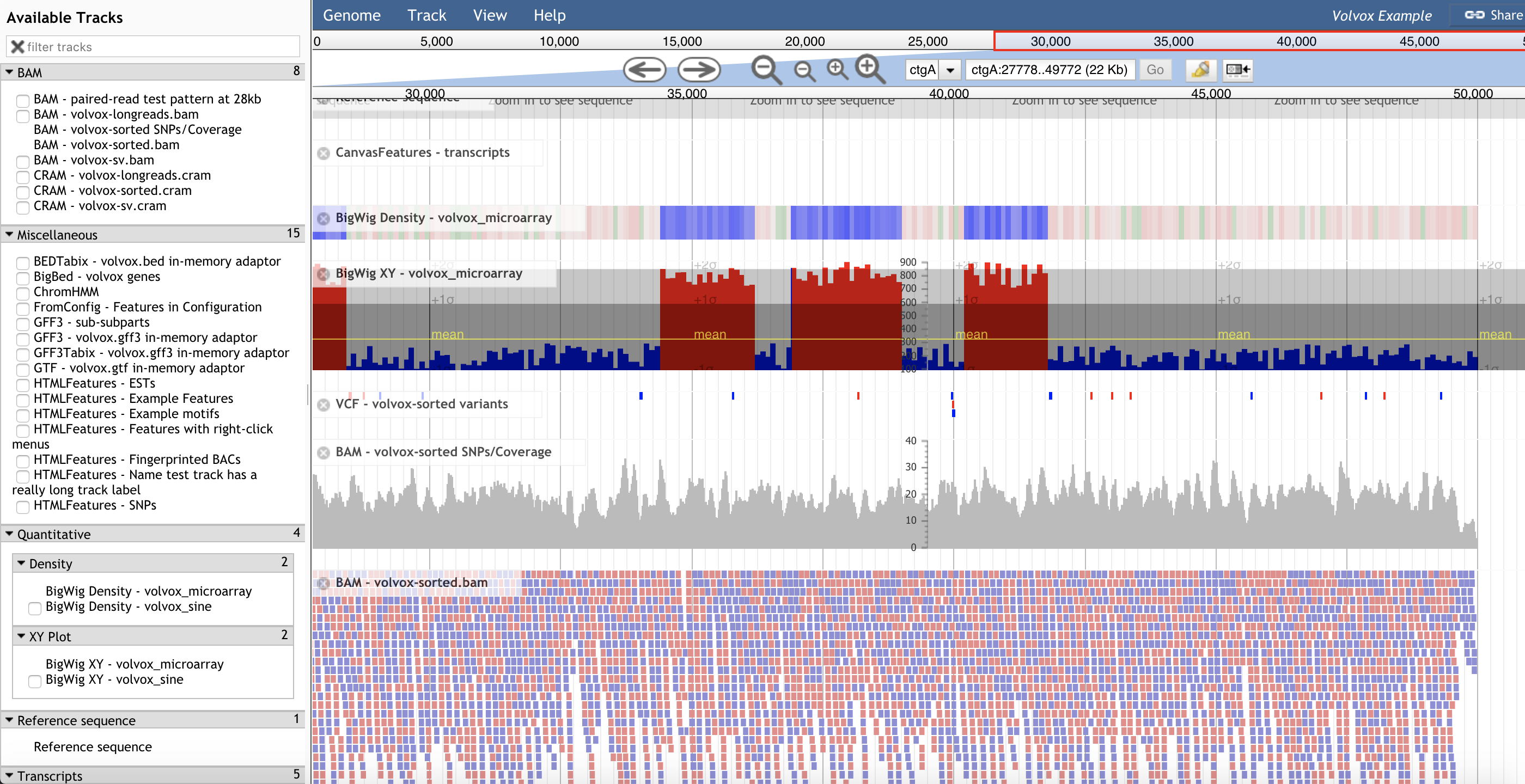
JuiceBox
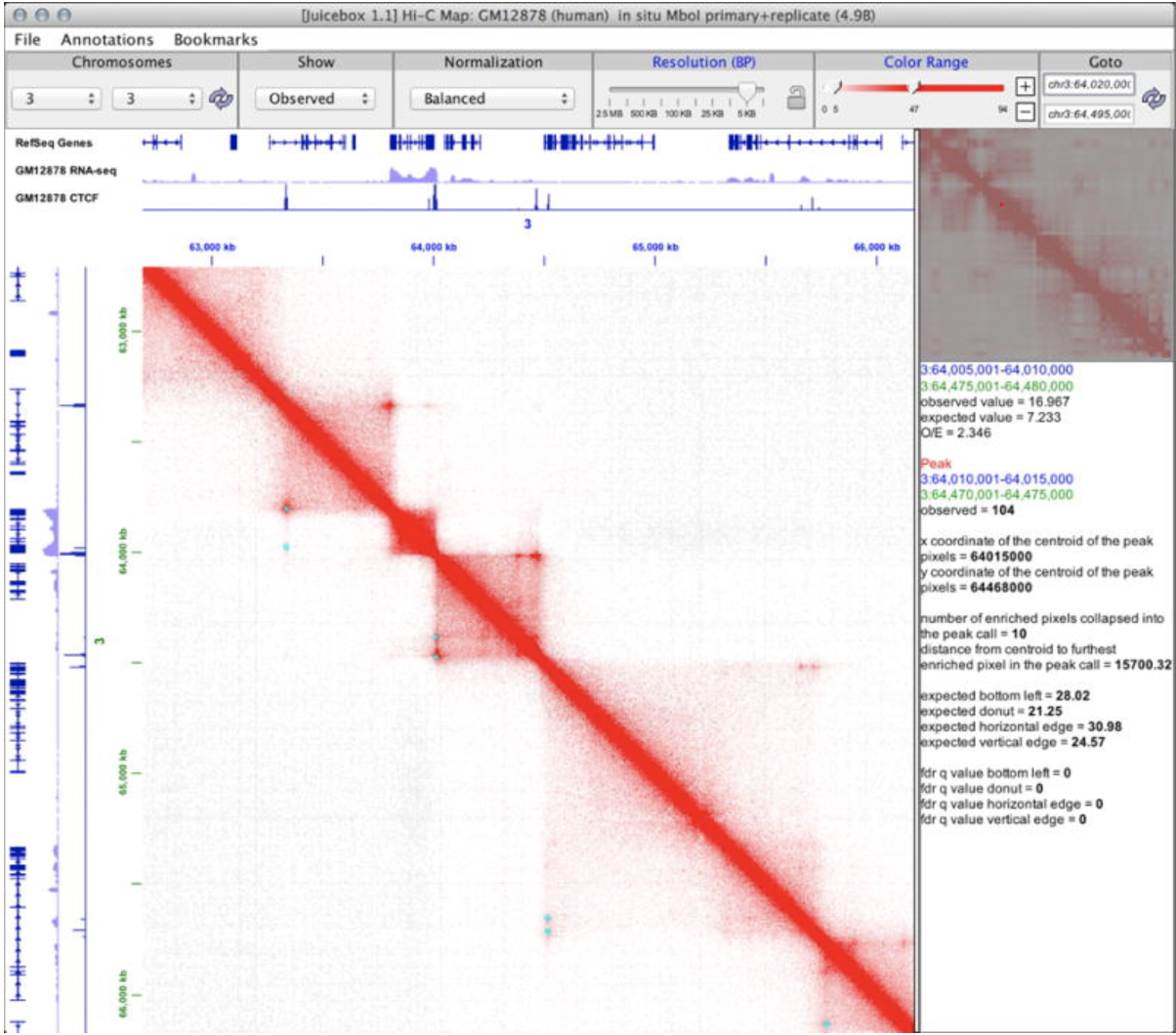
Juiceboxjs
Lollipop Plot cBio
MAGI
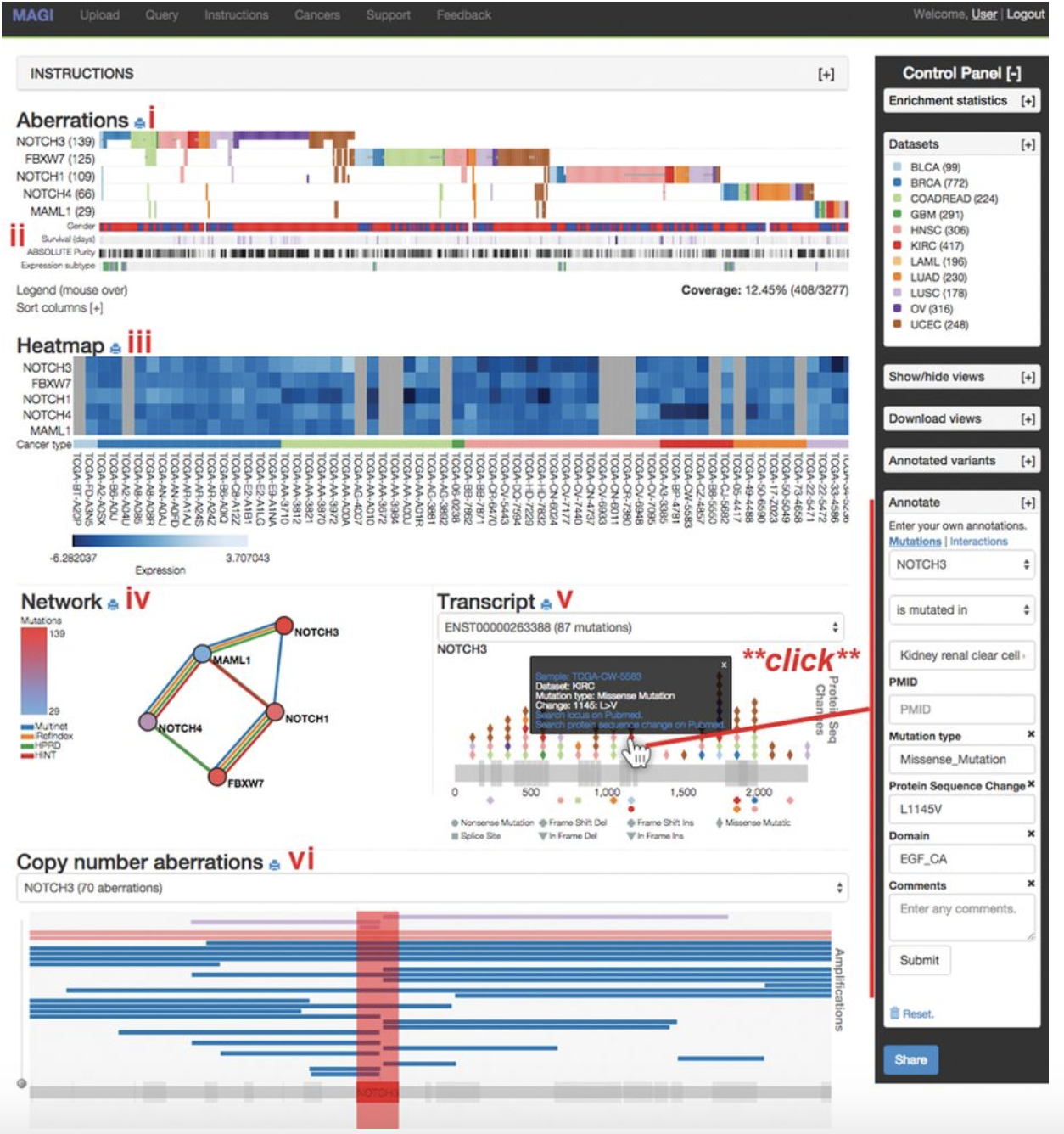
MEME
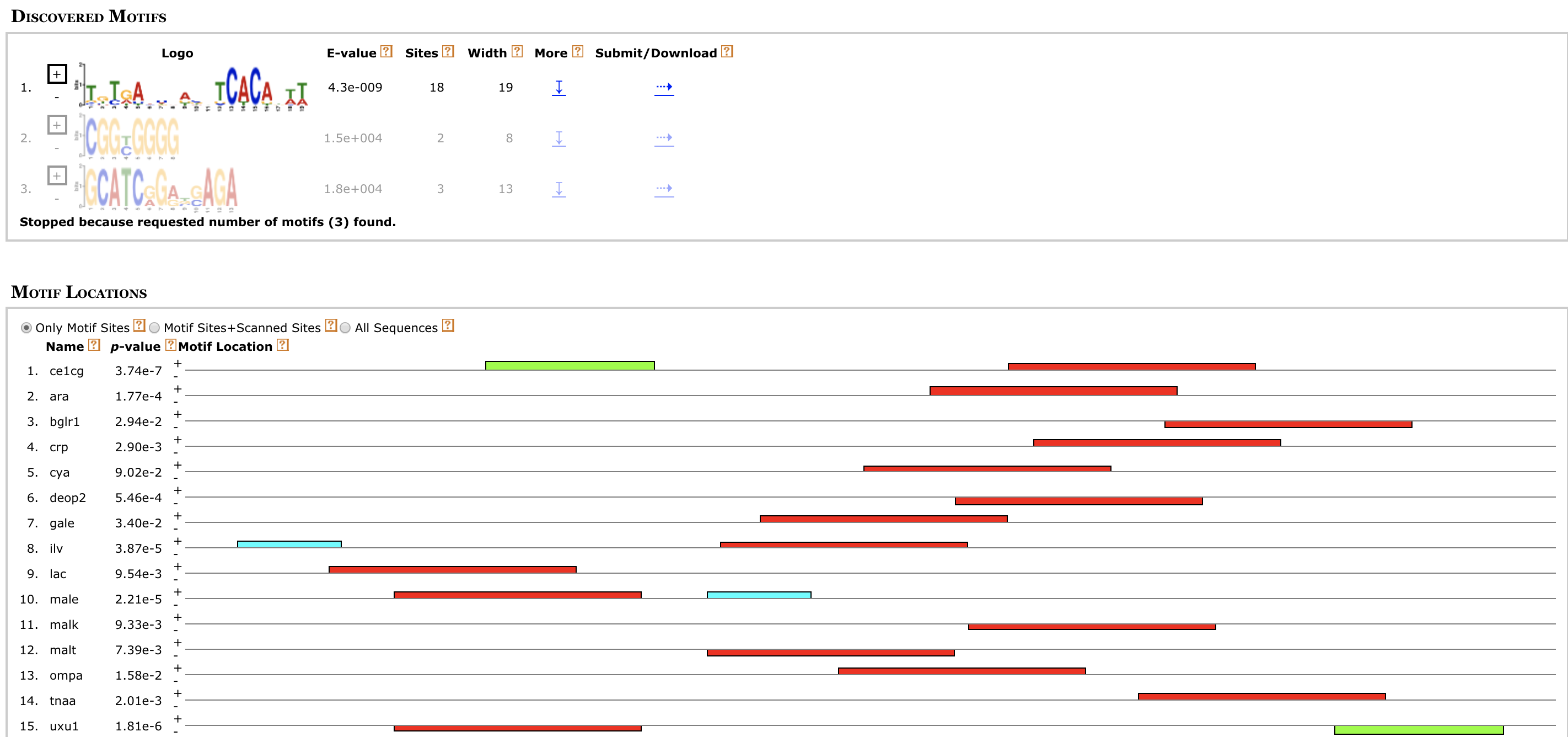
MEXPRESS
MGcV
MicroScope
MizBee
MochiView
MSAViewer
my5c
NCBI Genome Viewer
NCBI Sequence Viewer
ngs.plot
Oviz-Bio
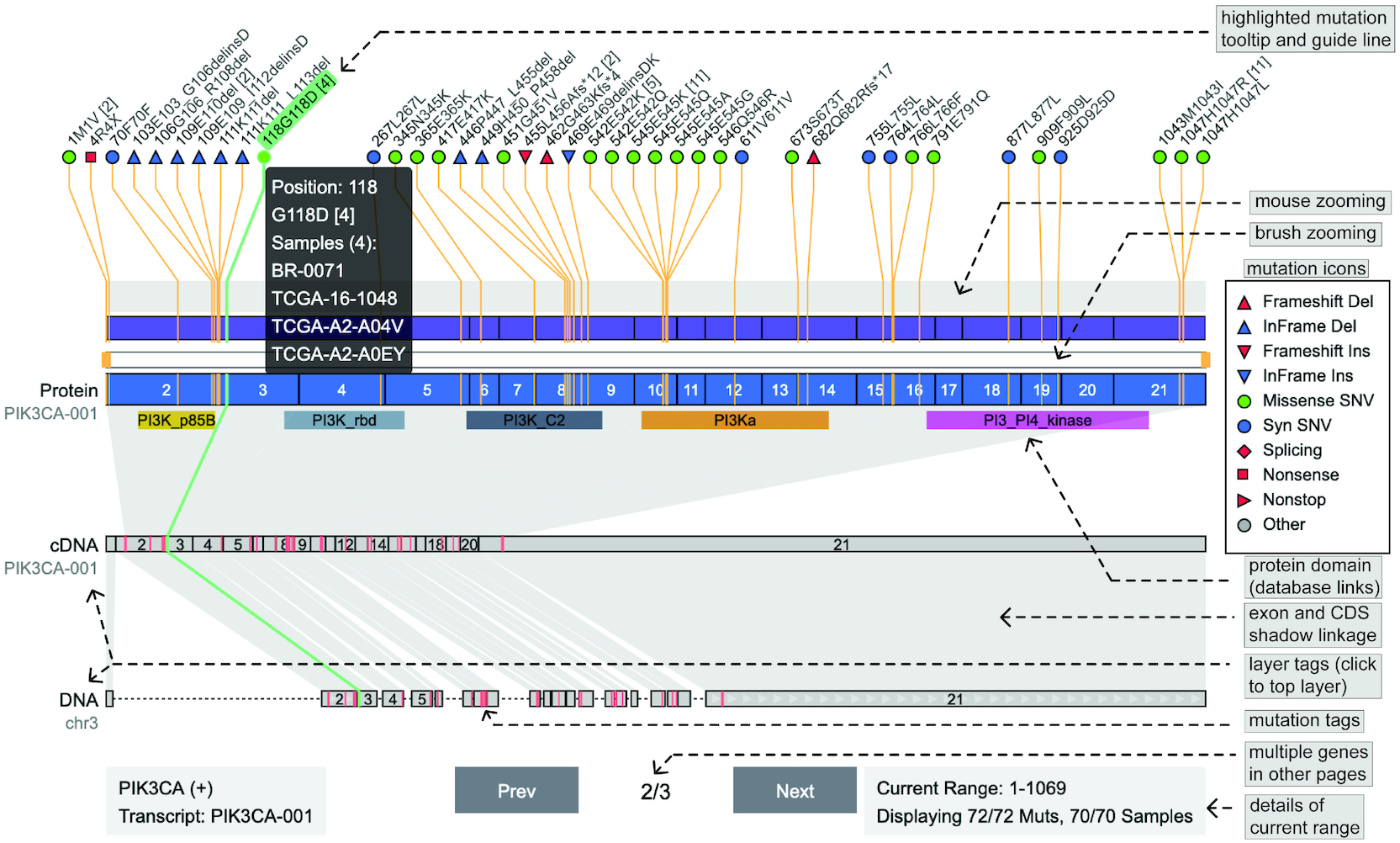
Persephone
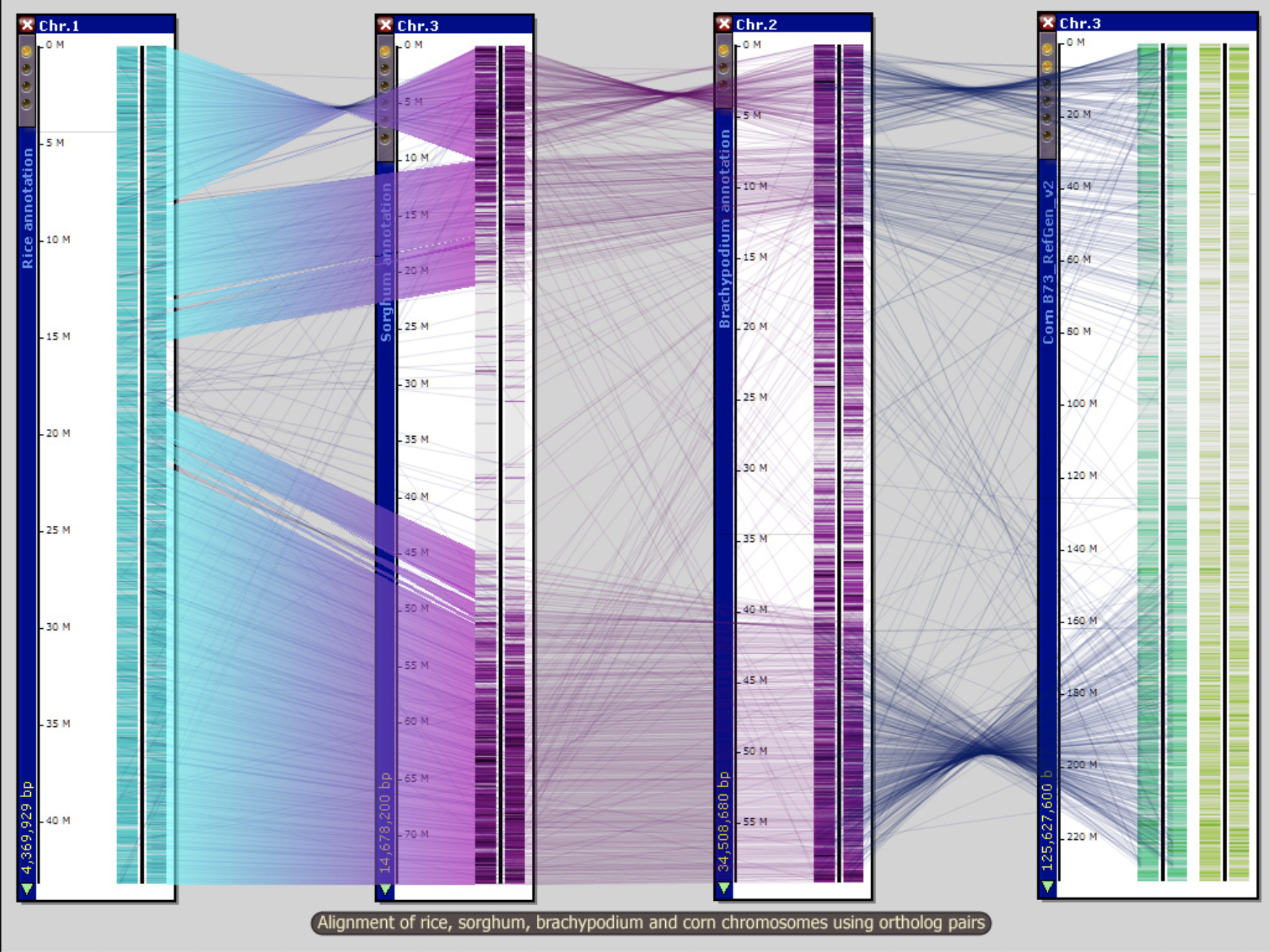
pLogo
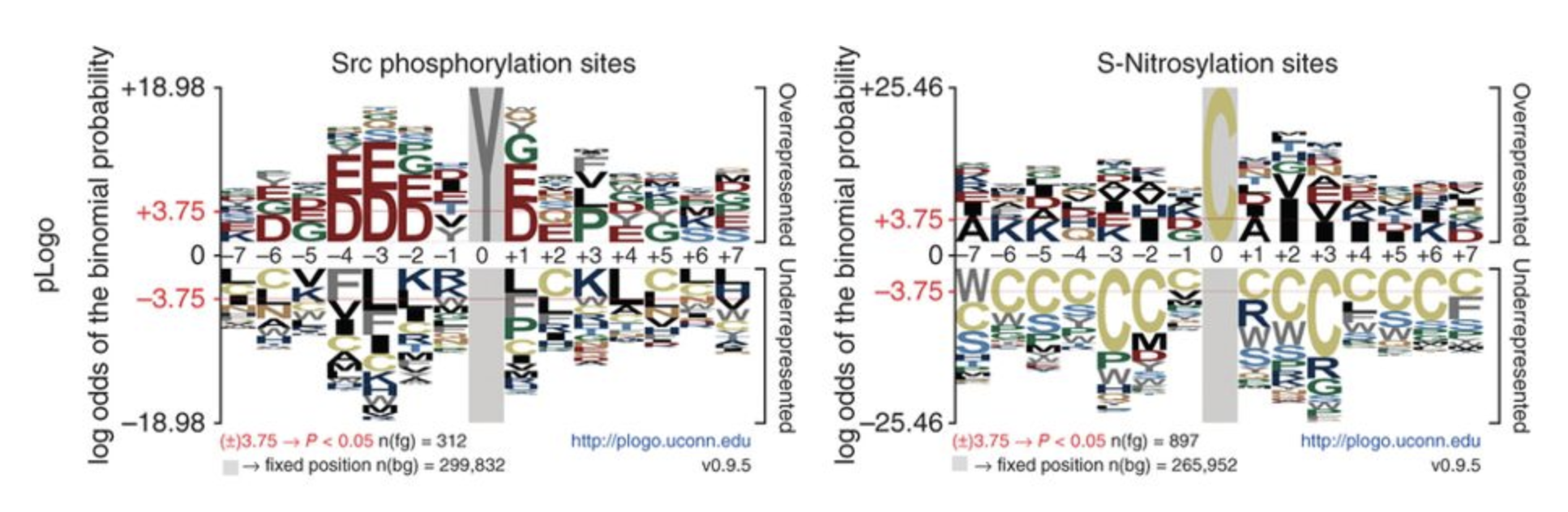
PSU 3D Genome Browser
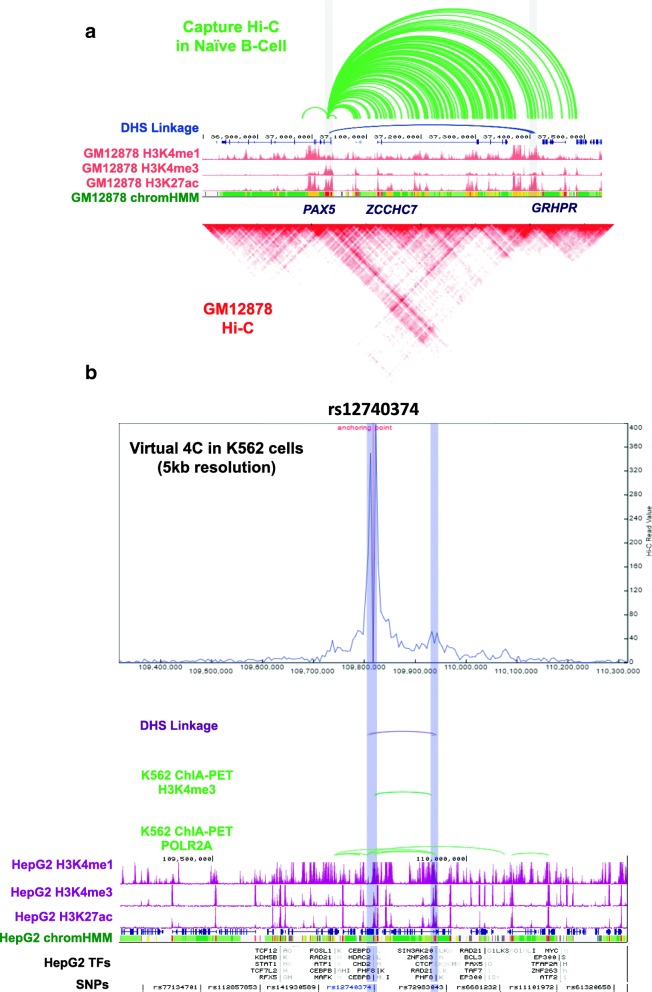
ReadXplorer
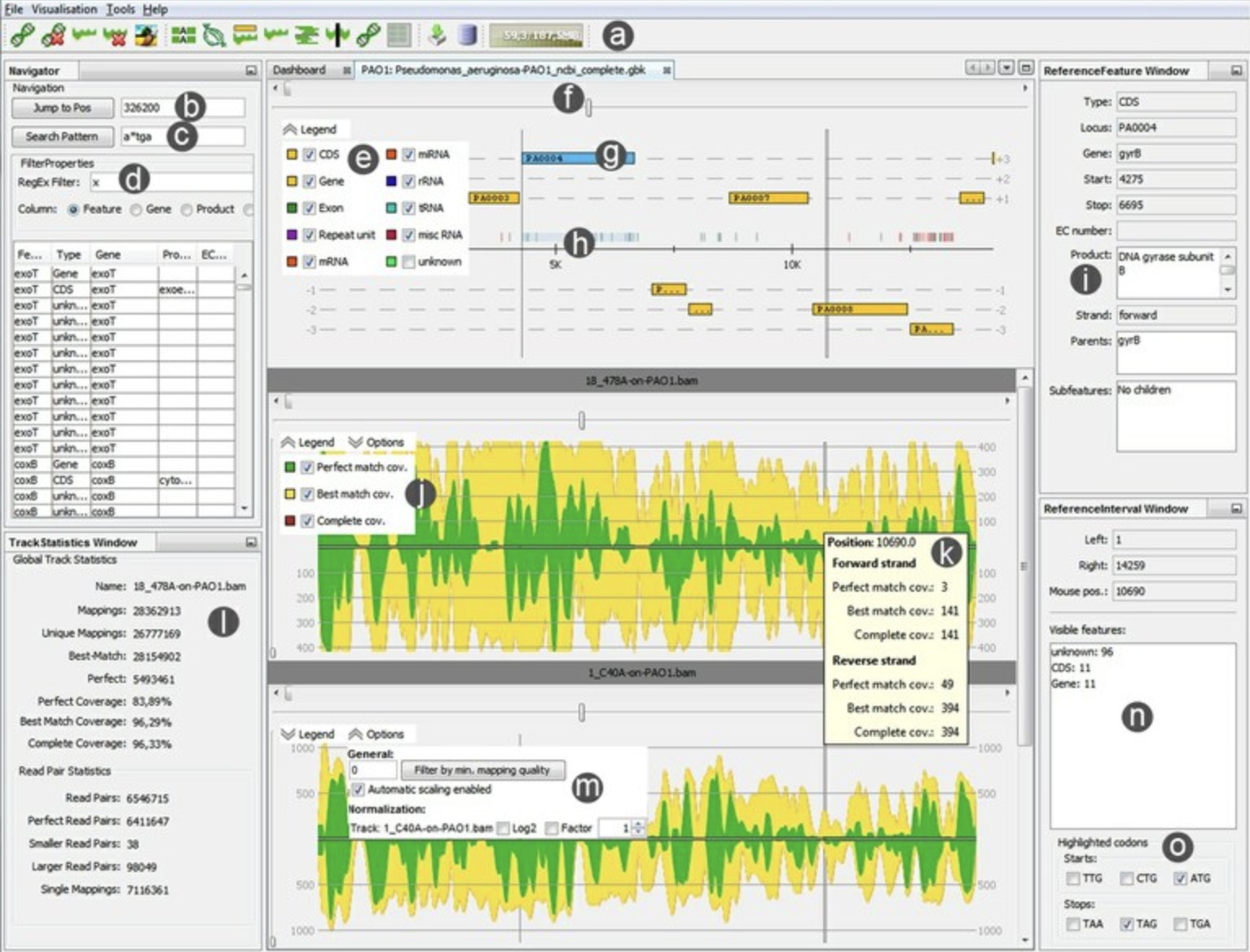
RIdeogram
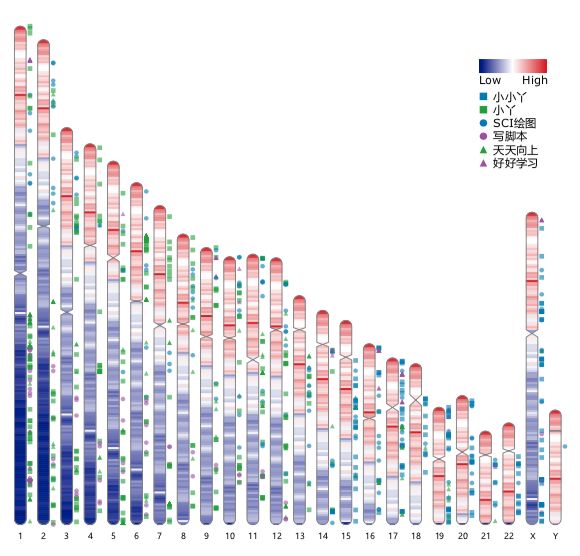
Sashimi Plot
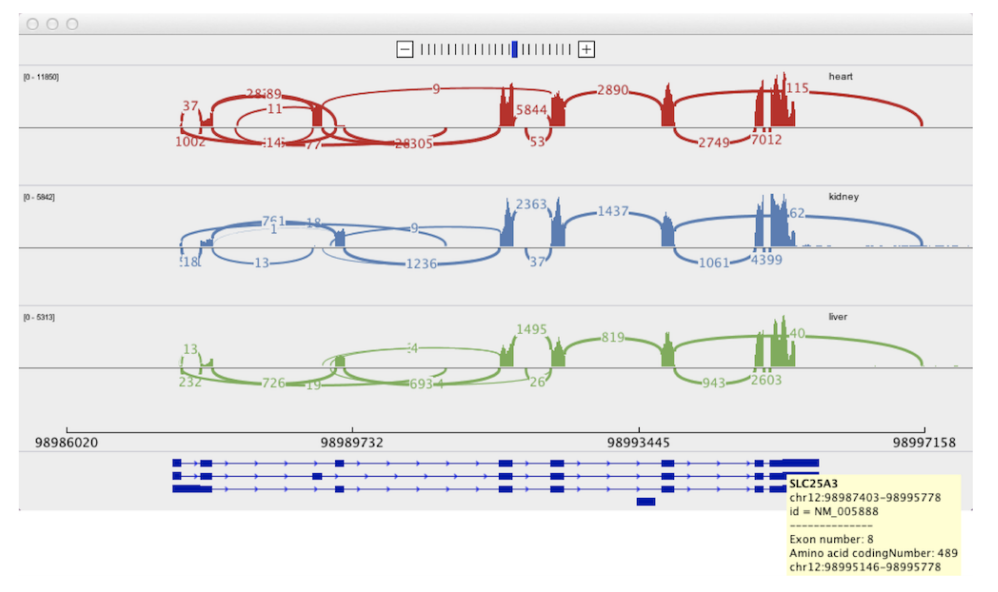
Savant Genome Browser 2
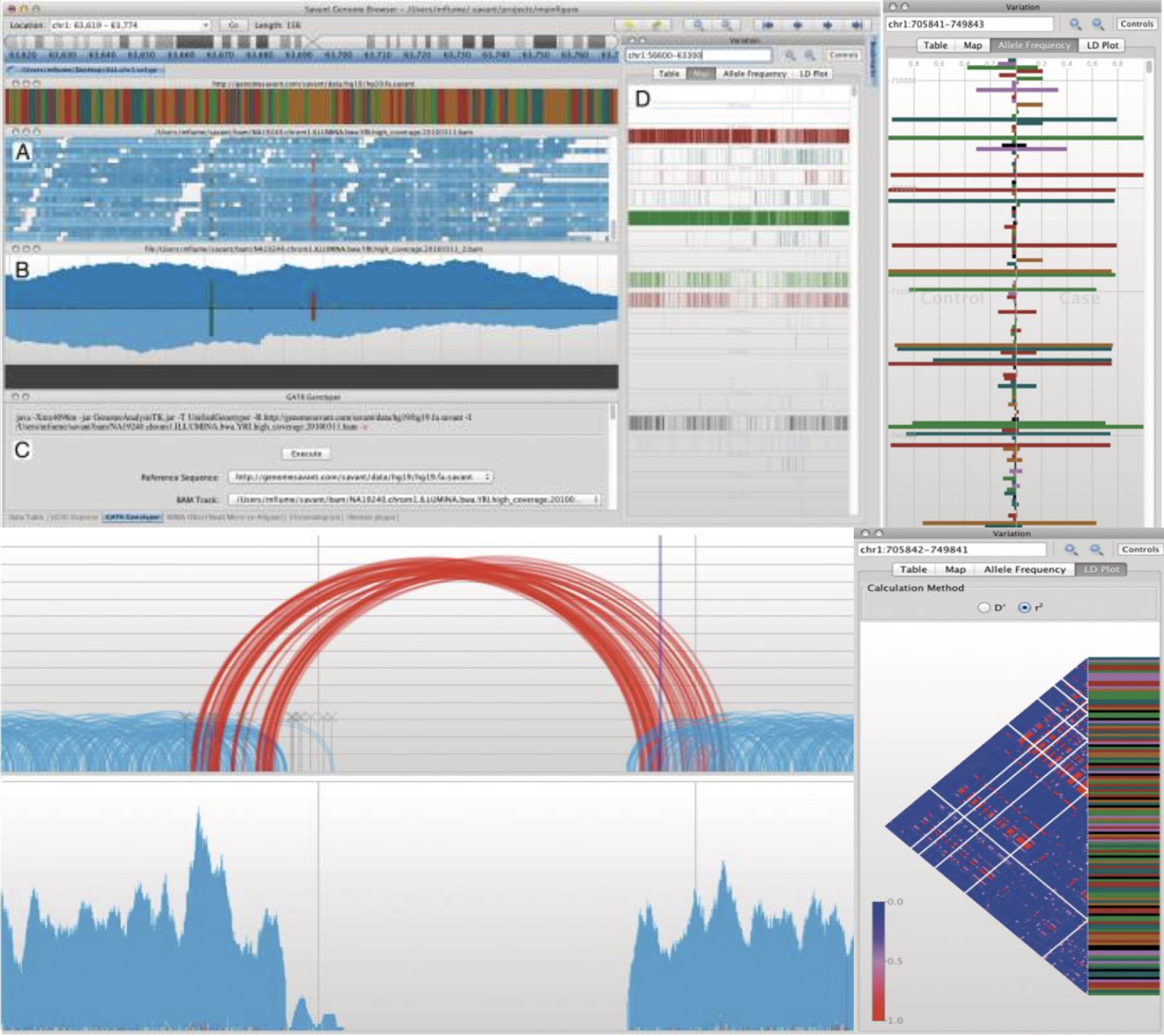
SCGV
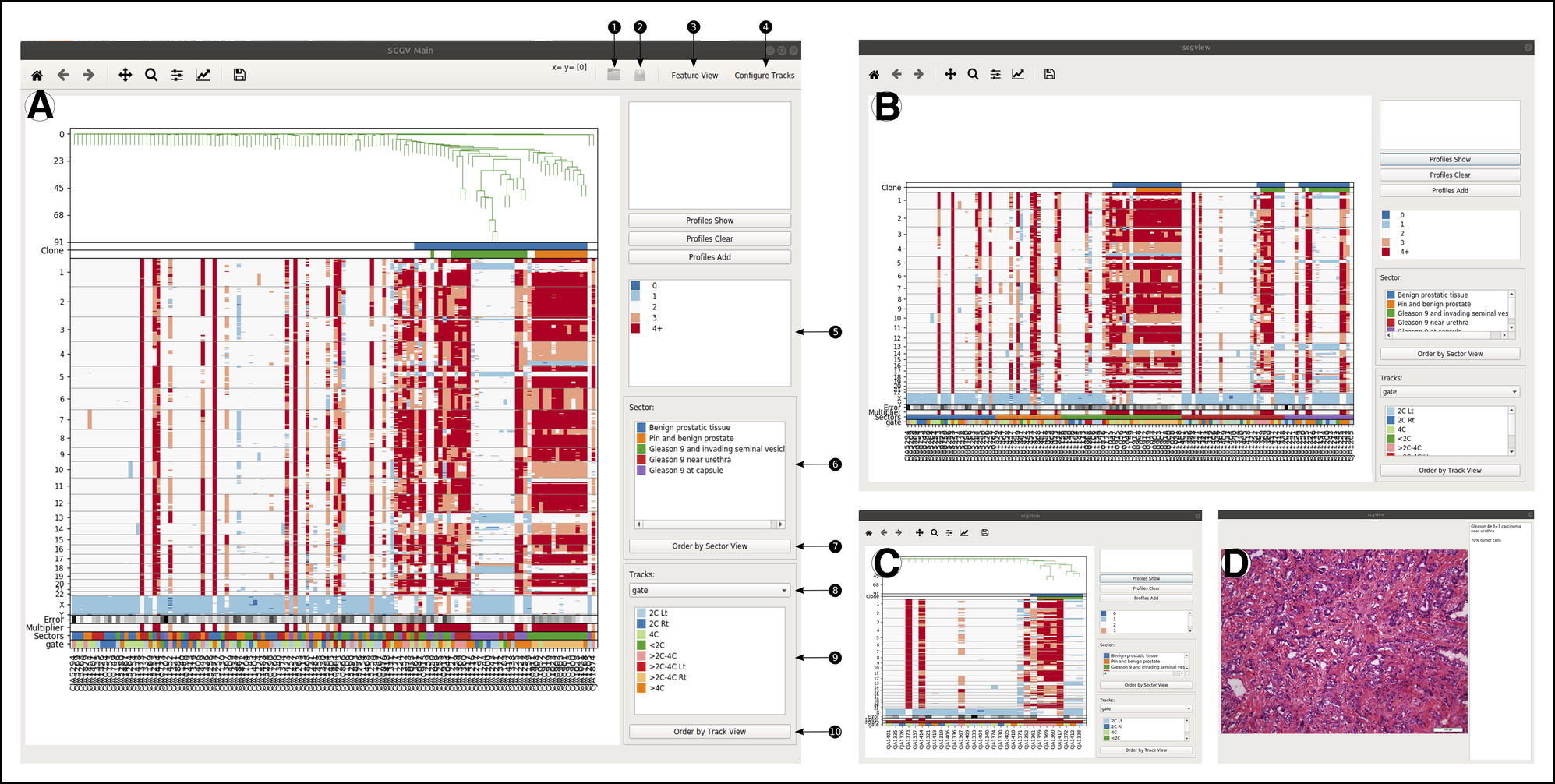
Sequence Bundles
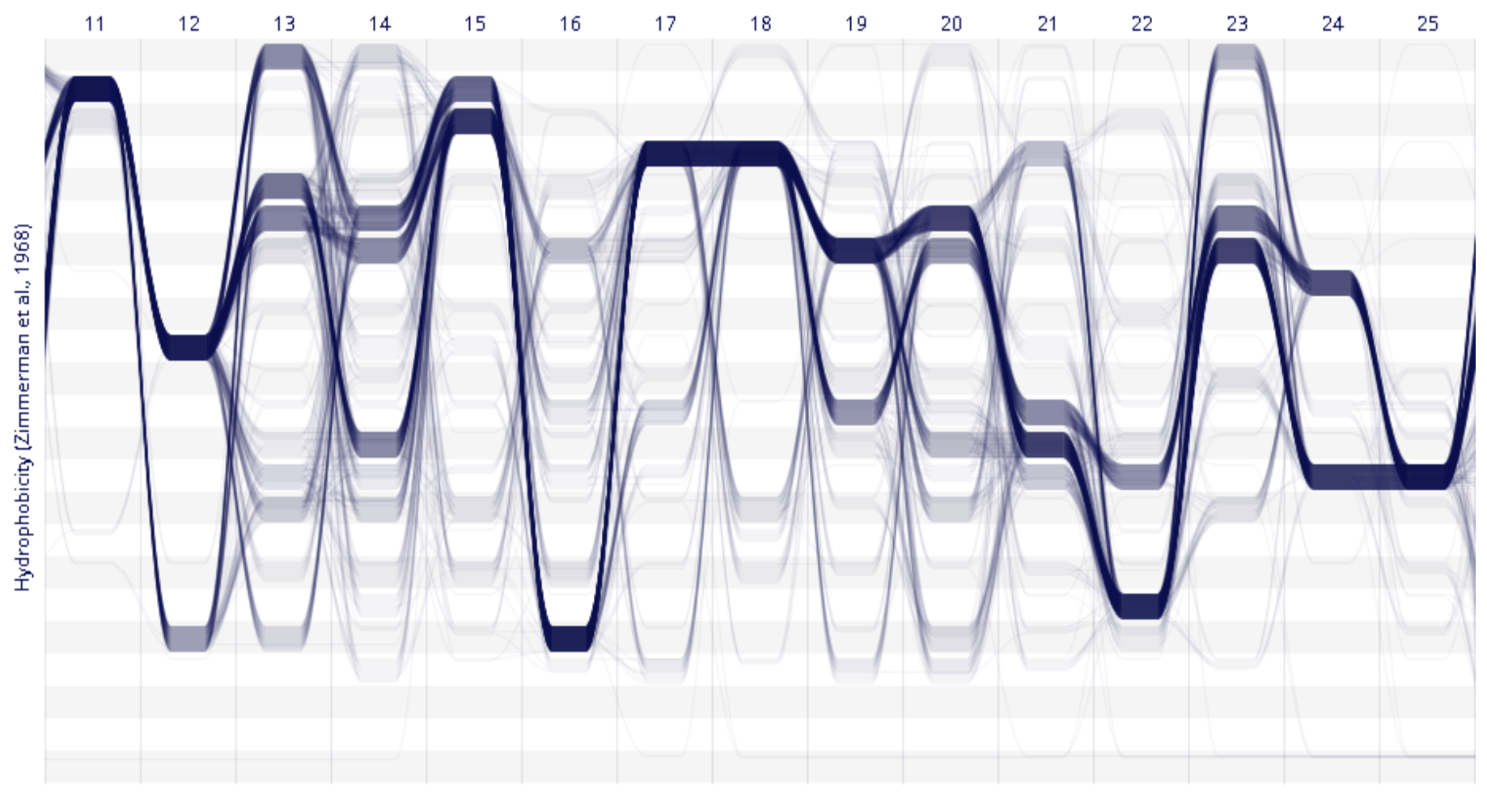
Sequence Surveyor
SilkDB 3.0
Spatial DB
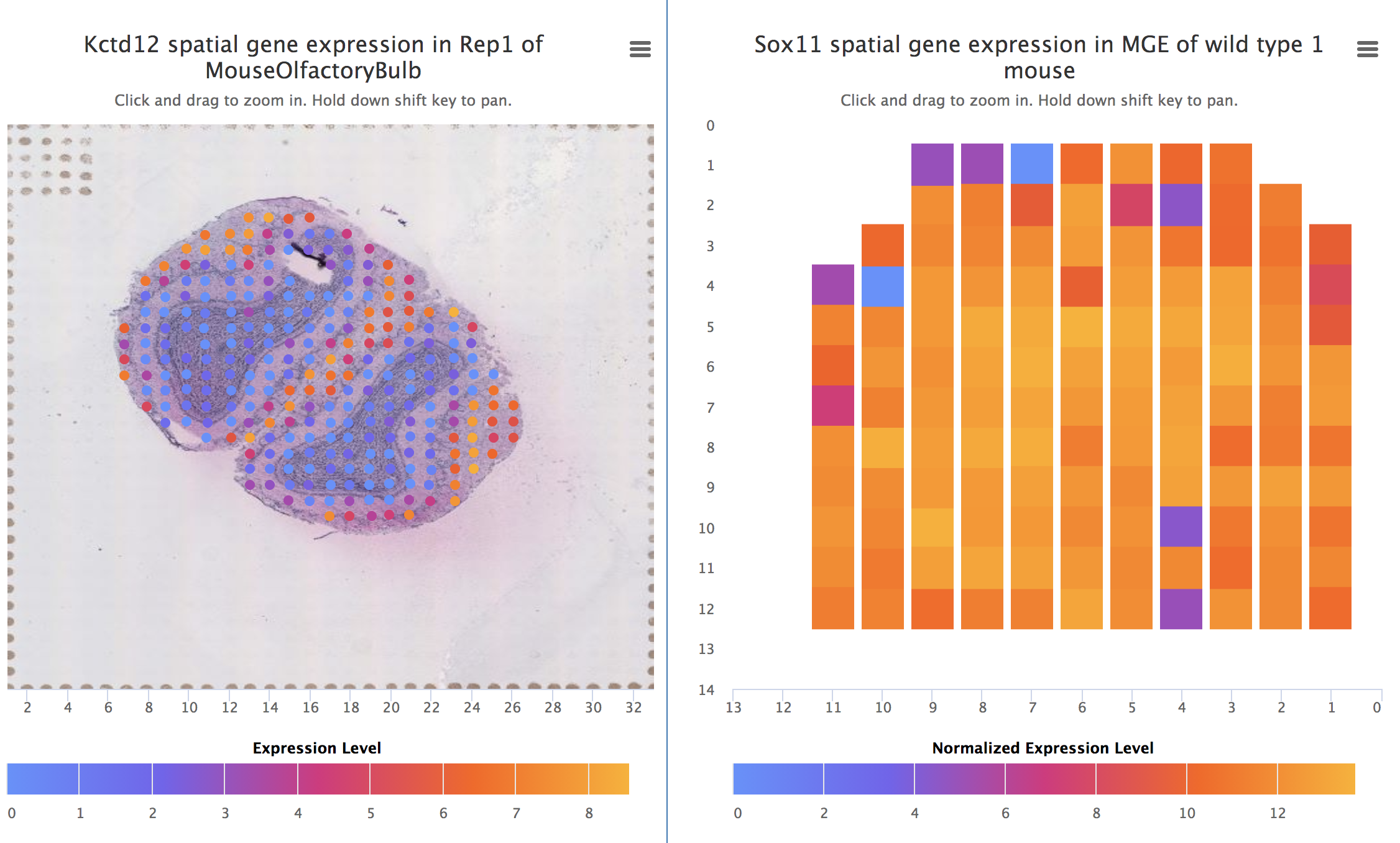
SpliceGrapher
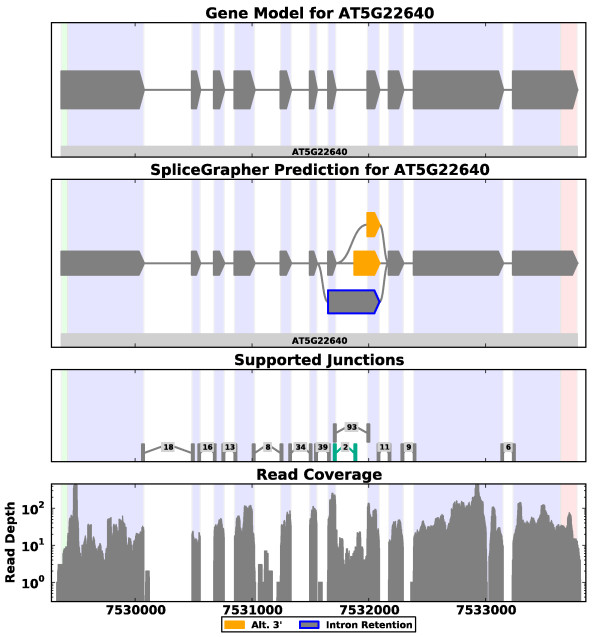
SplicePlot
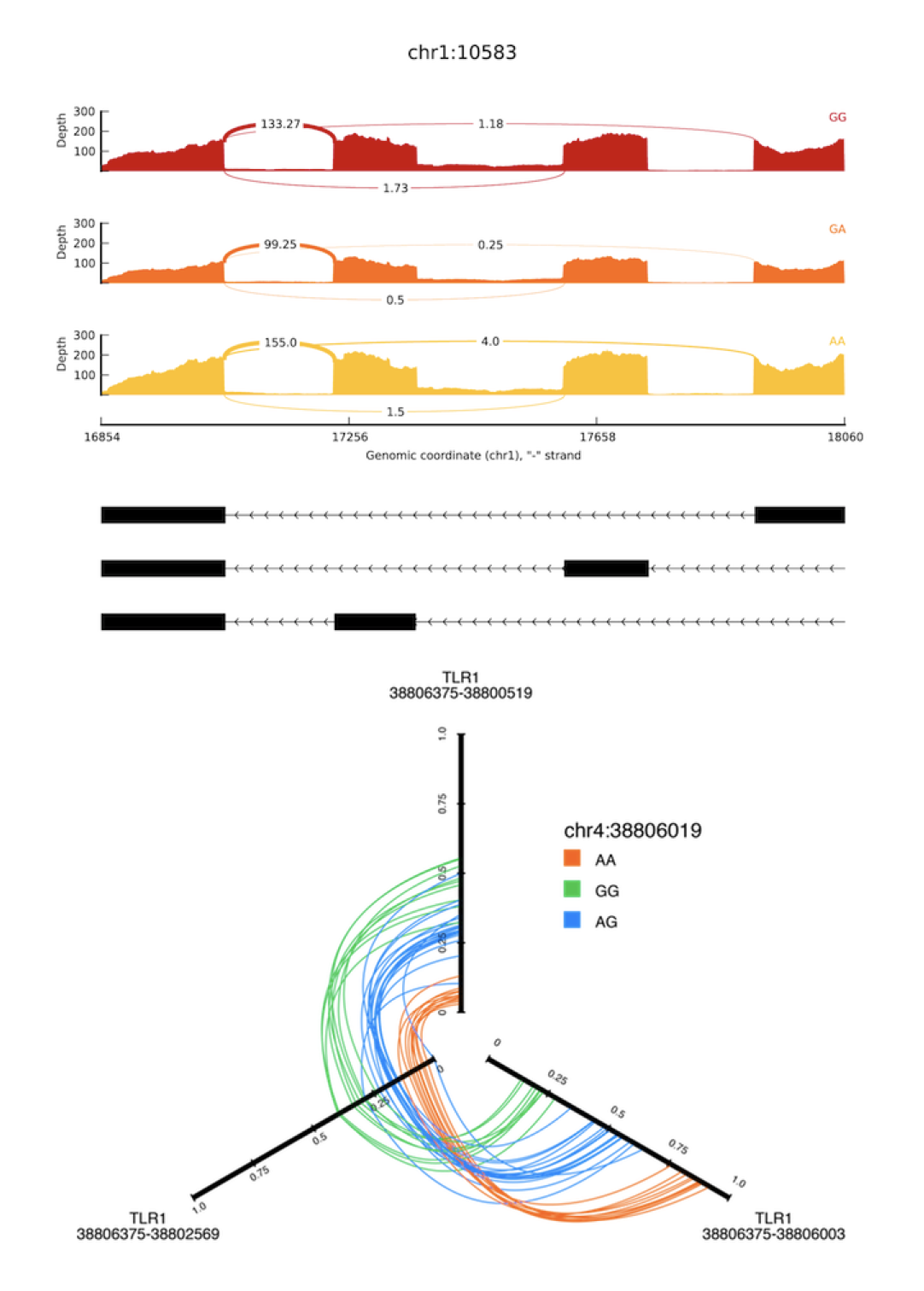
SpliceSeq
svist4get
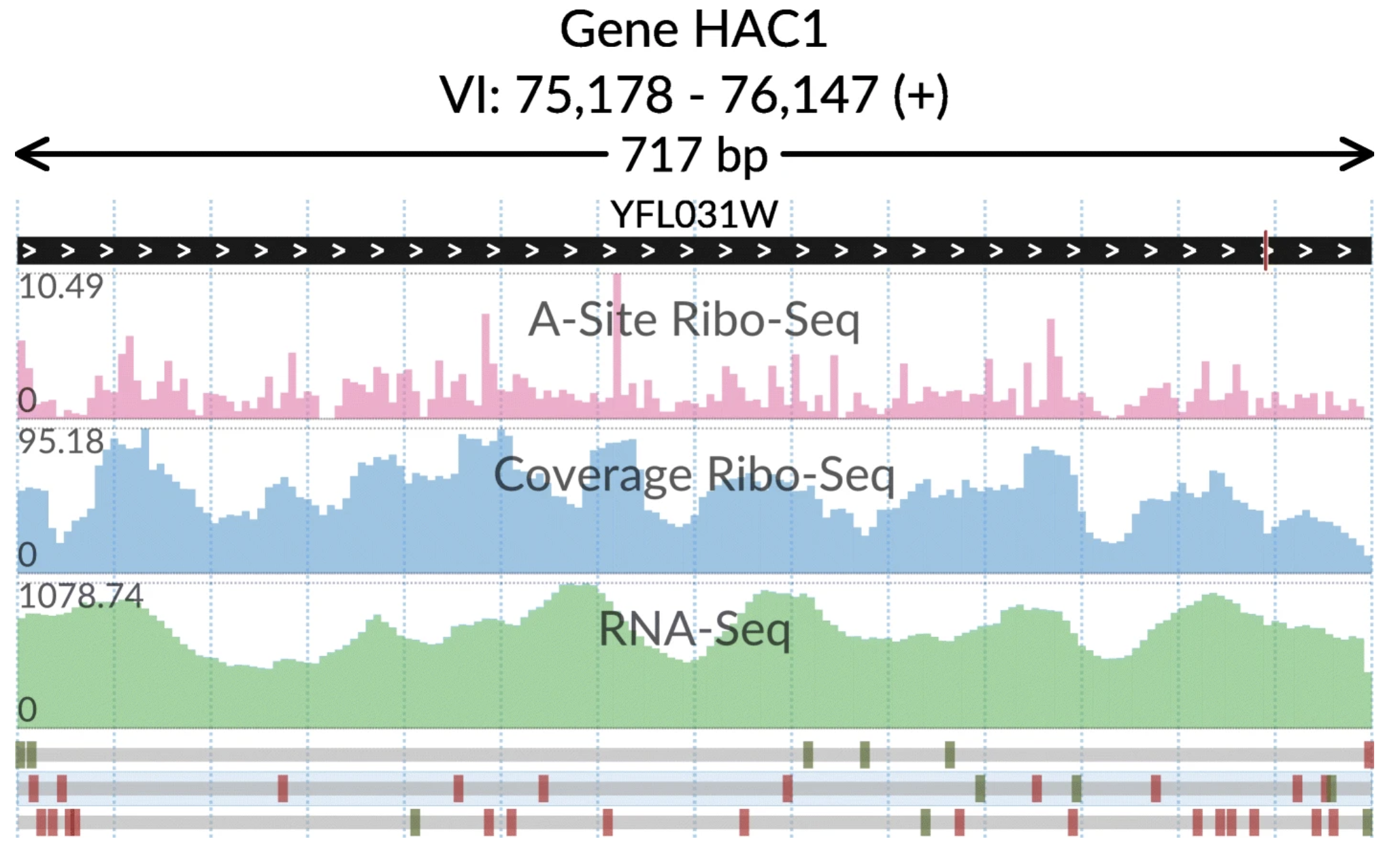
SWAV
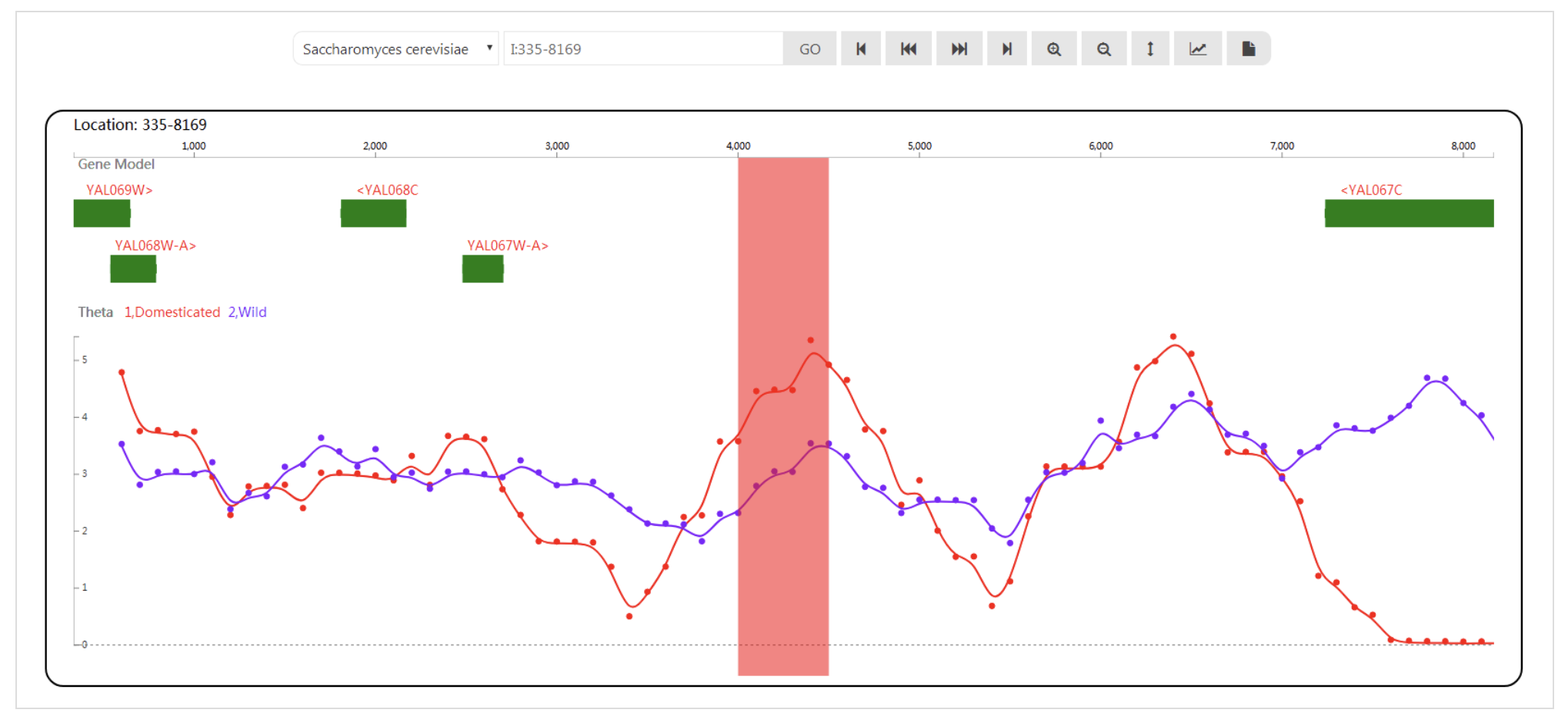
SynMap2
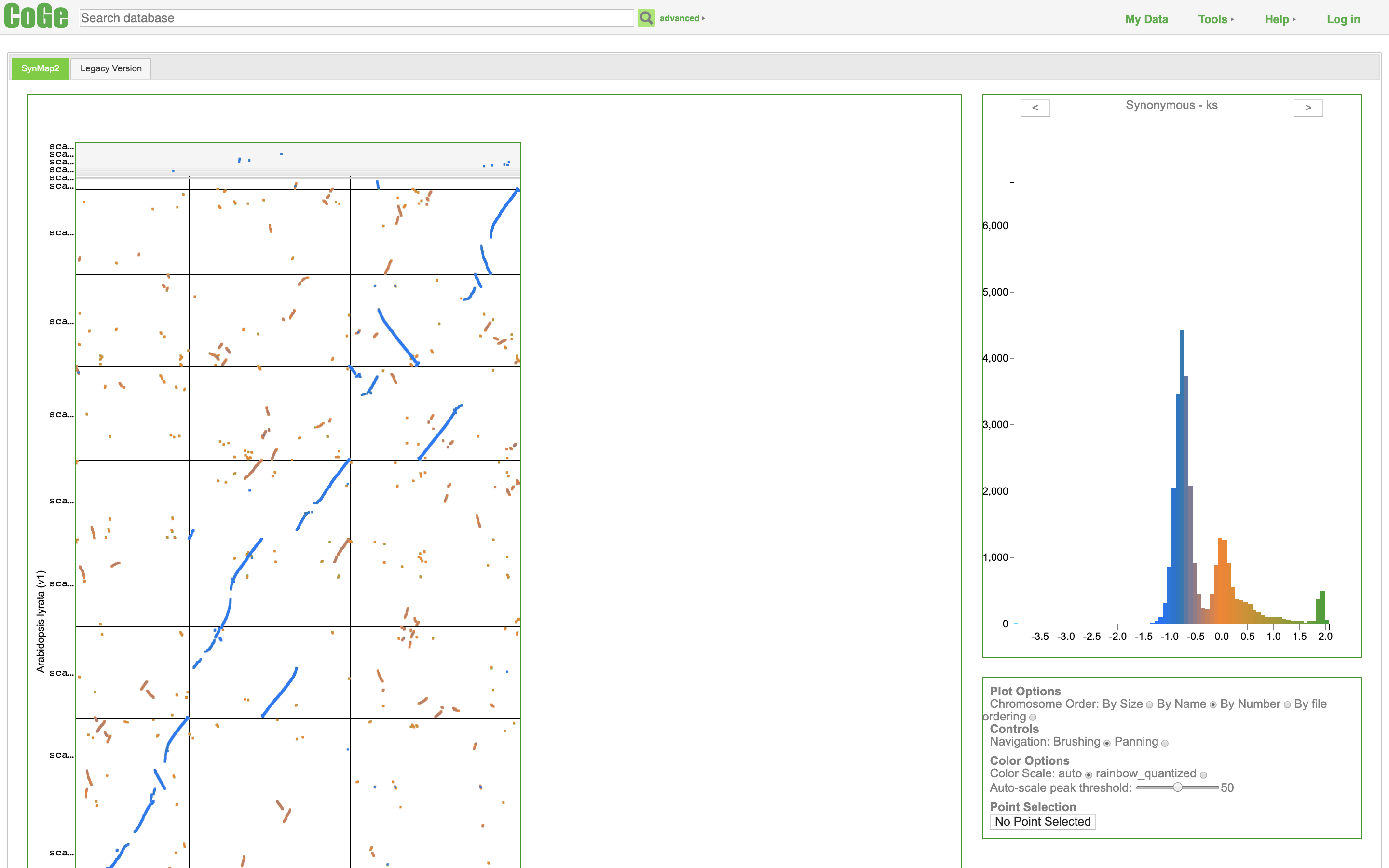
SynteBase and SynteView
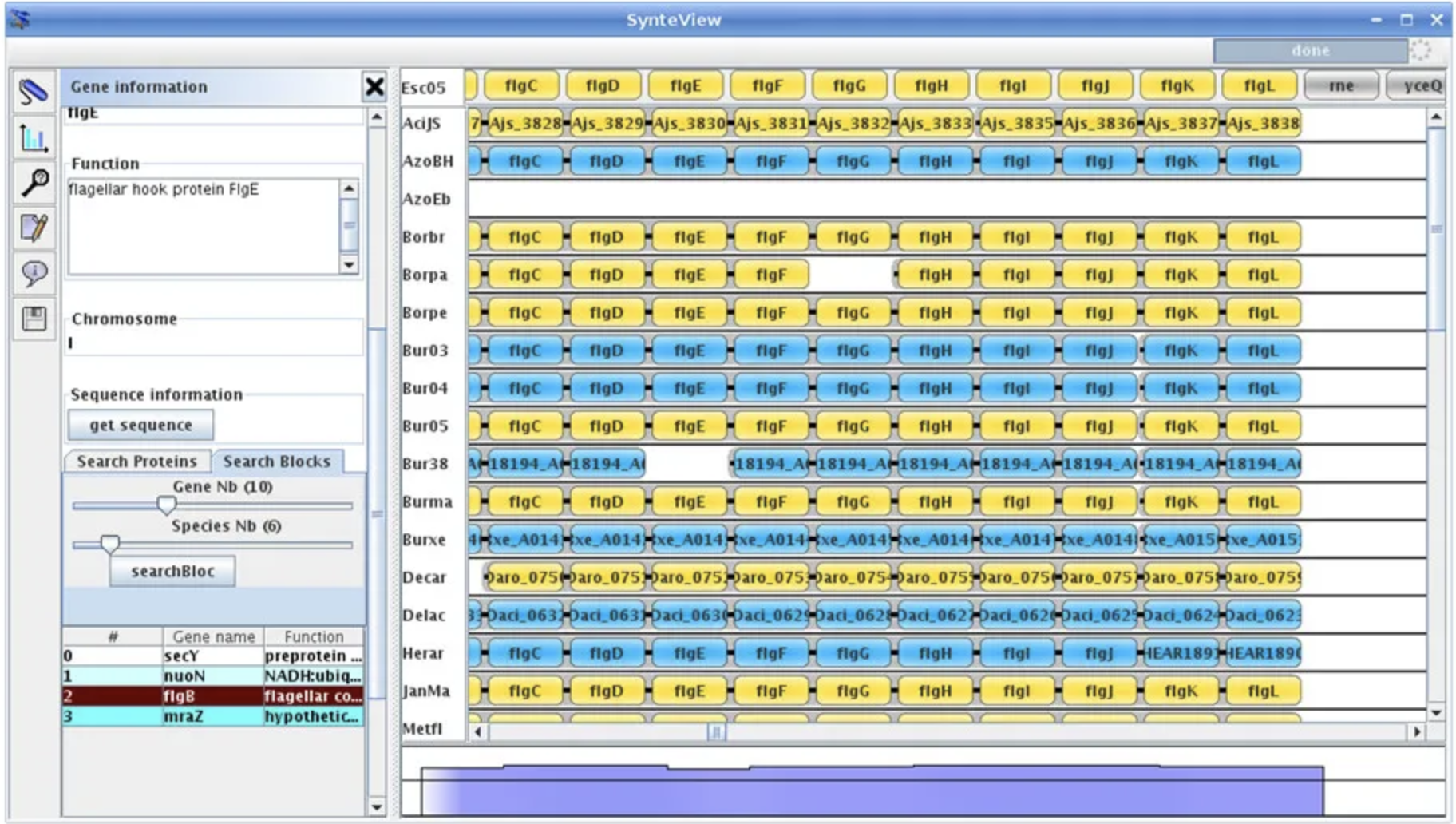
Synteny Explorer
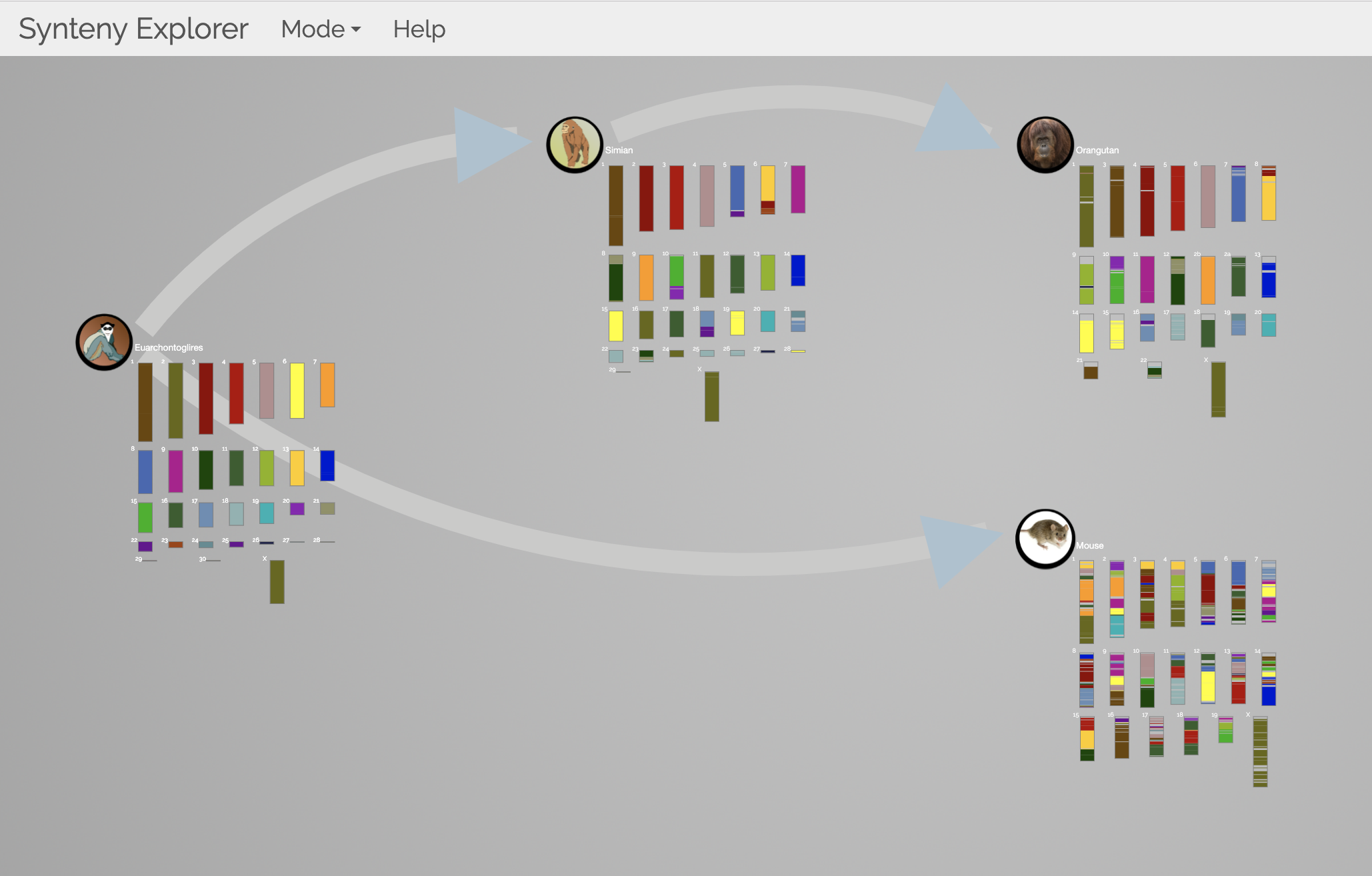
TFmotifView
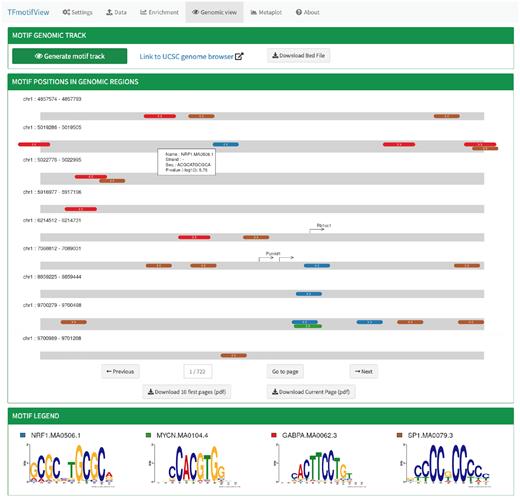
trackViewer
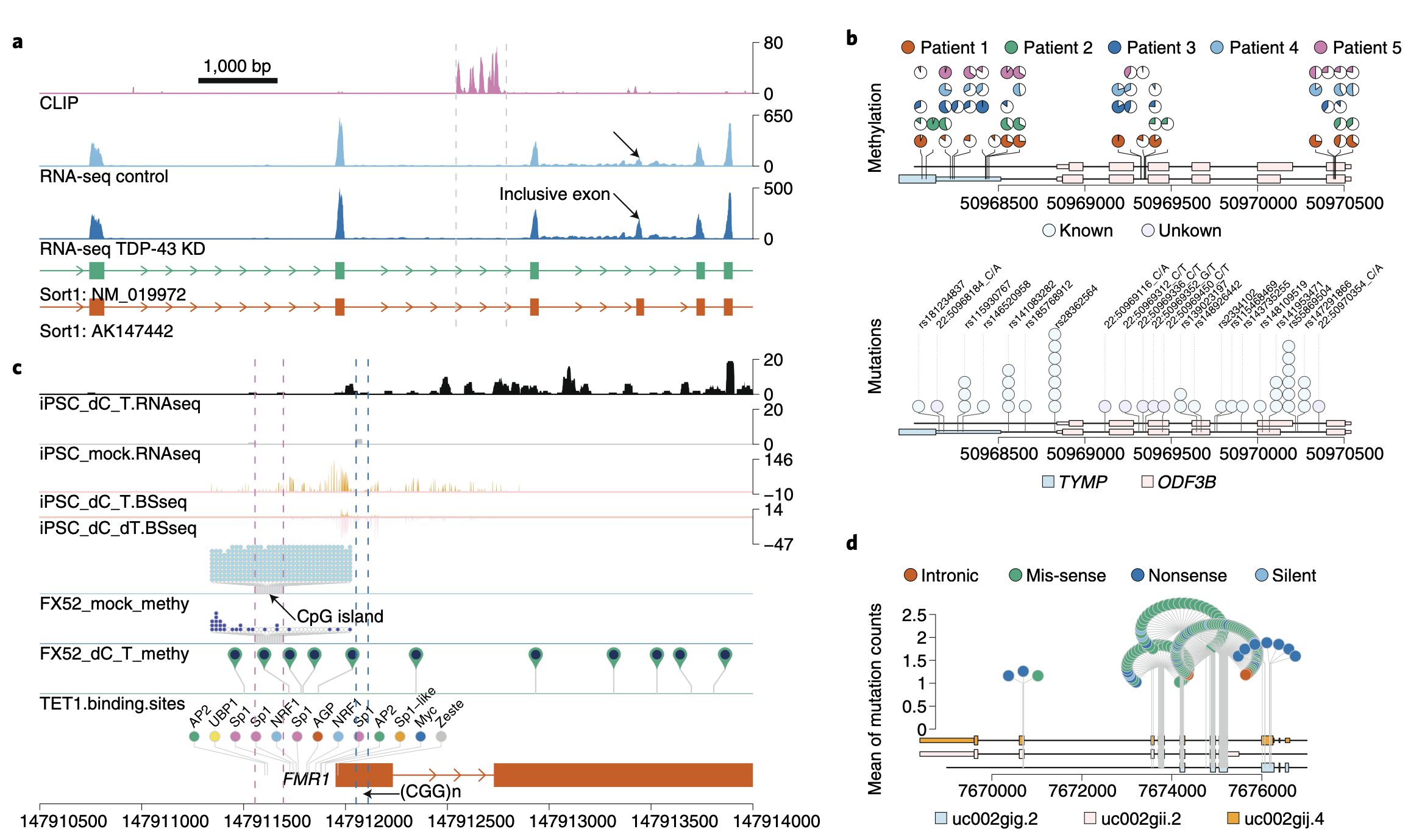
Two Sample Logo
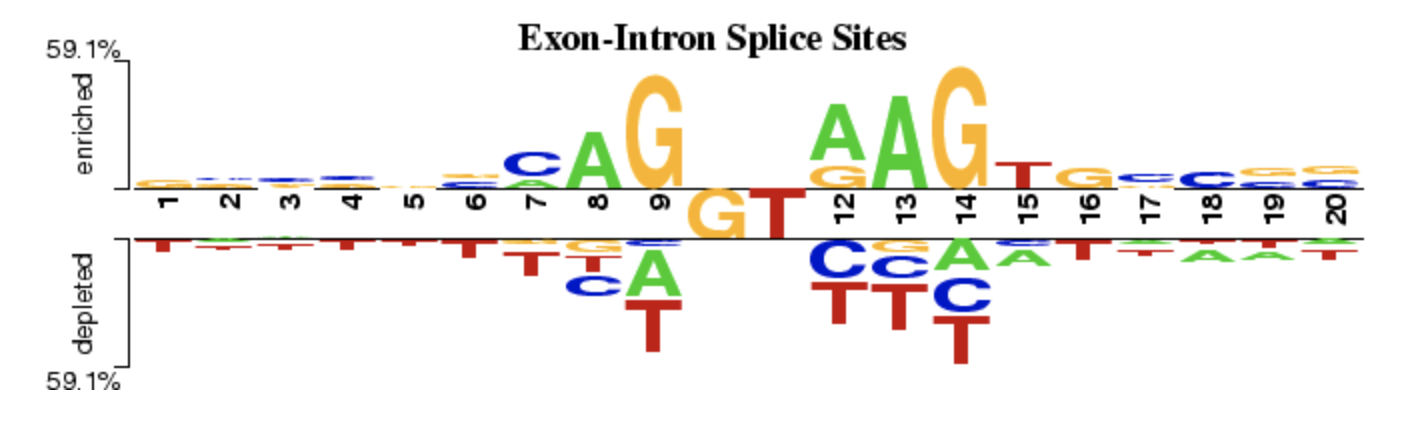
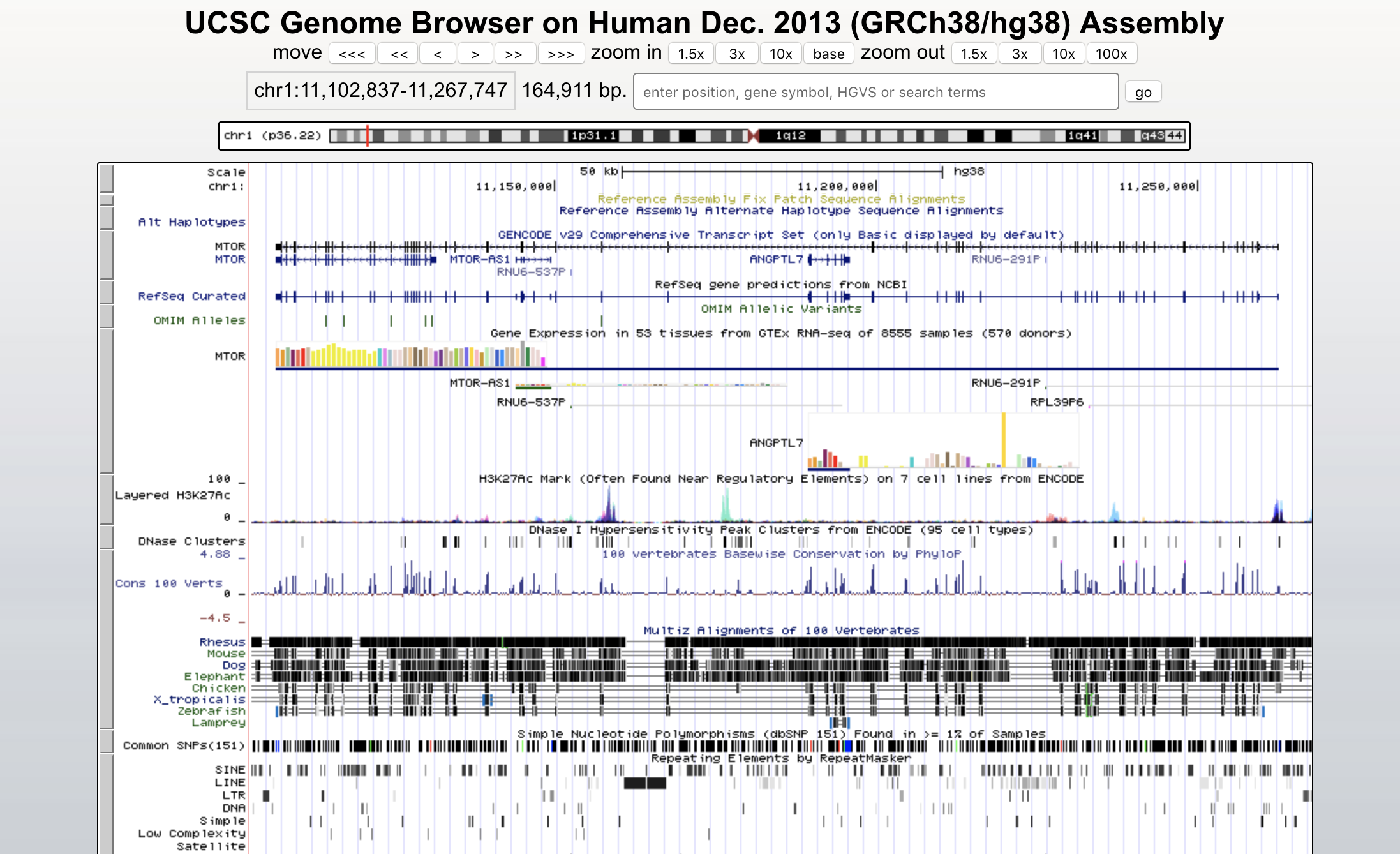
UCSC Genome Browser
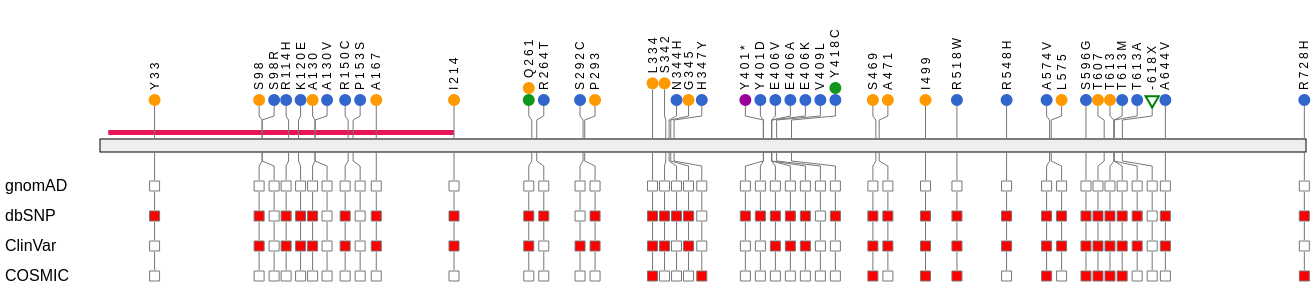
Variant View
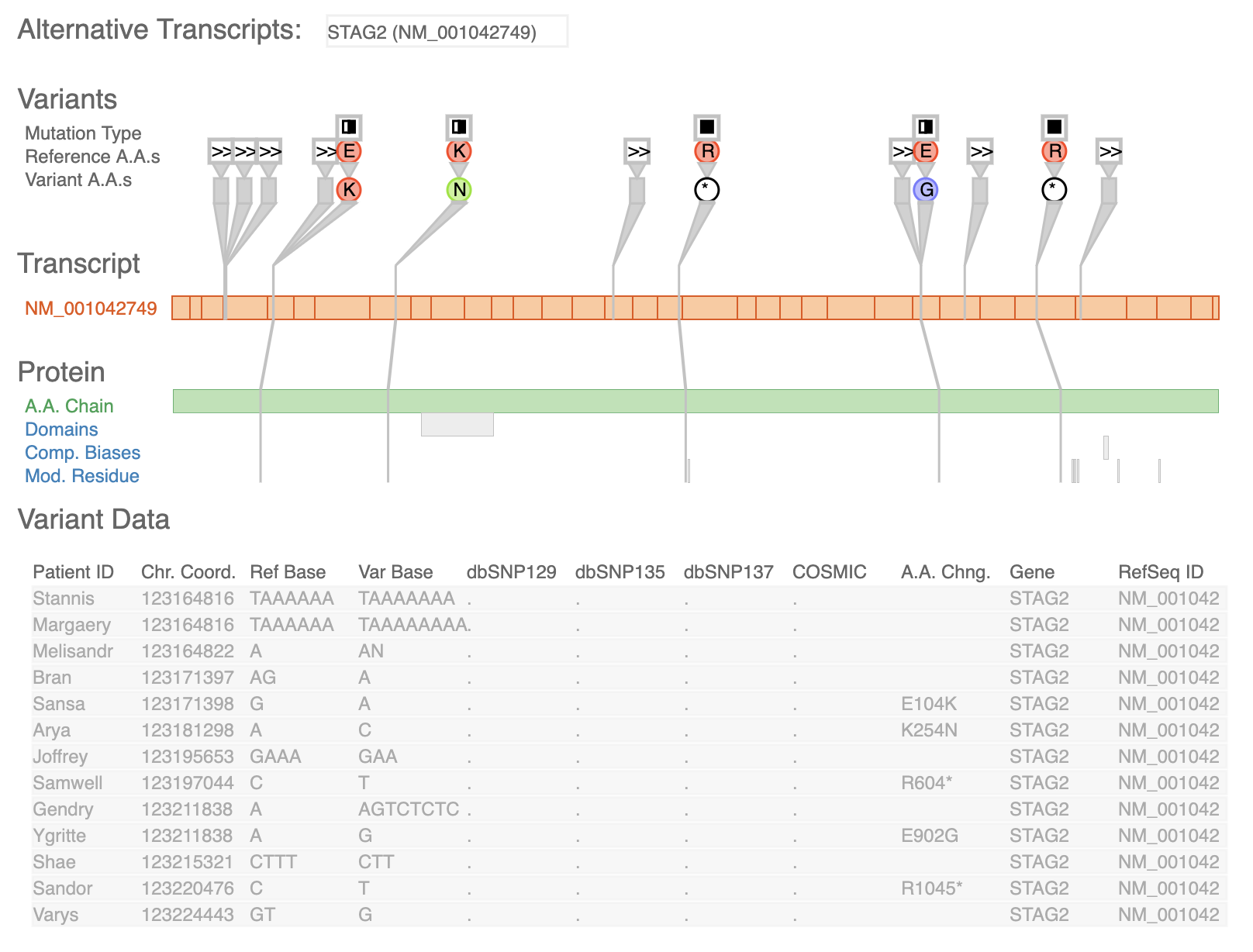
VCF Plotein
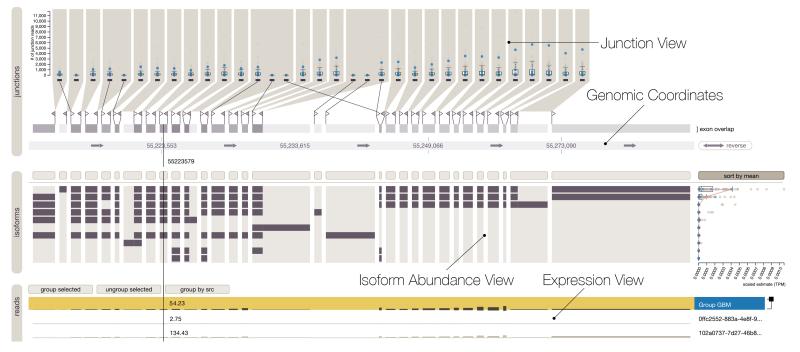
Vials
Vista Dot
Vista Synteny
VistaPoint
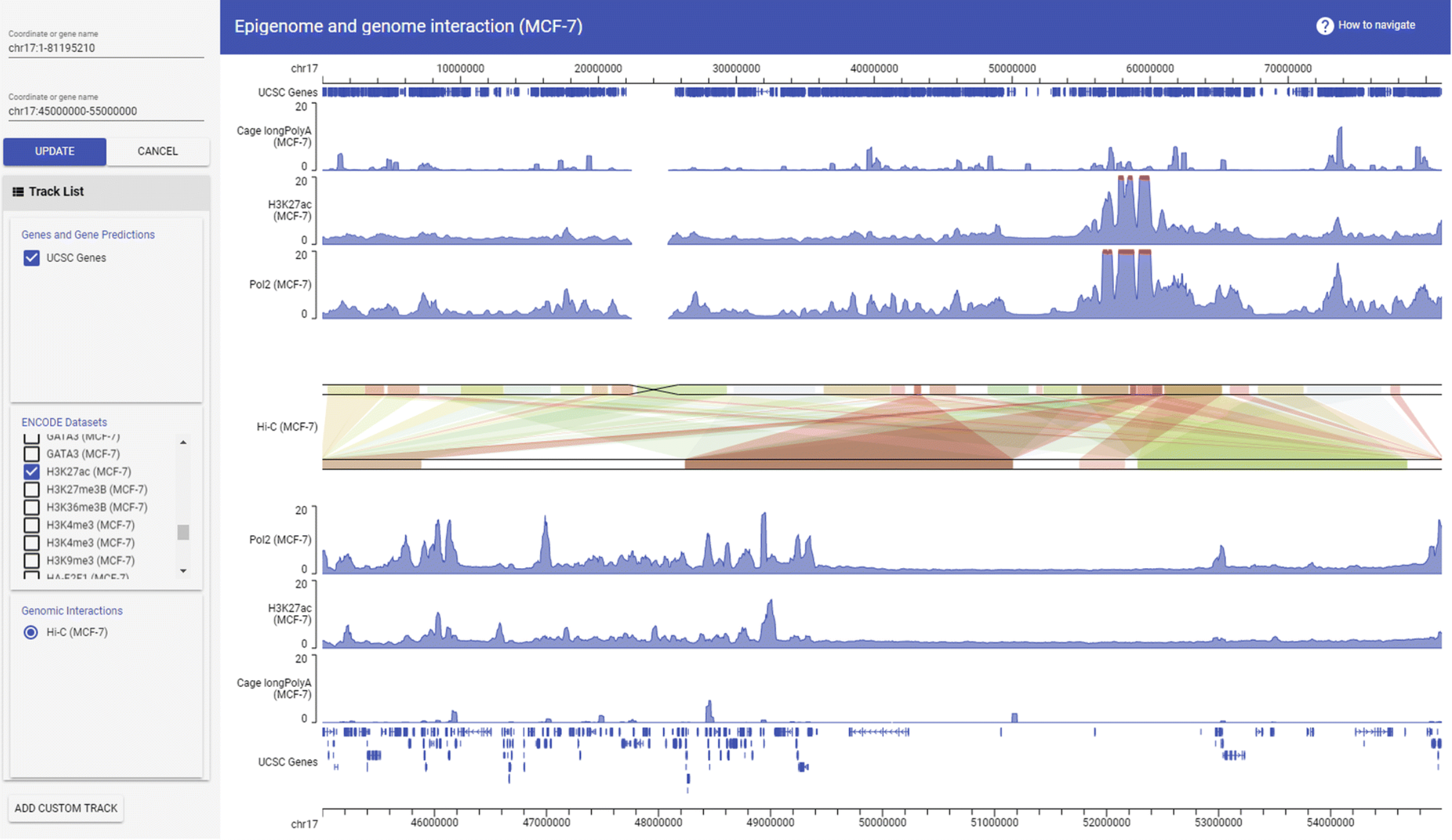
WashU Epigenome Browser
WebLogo
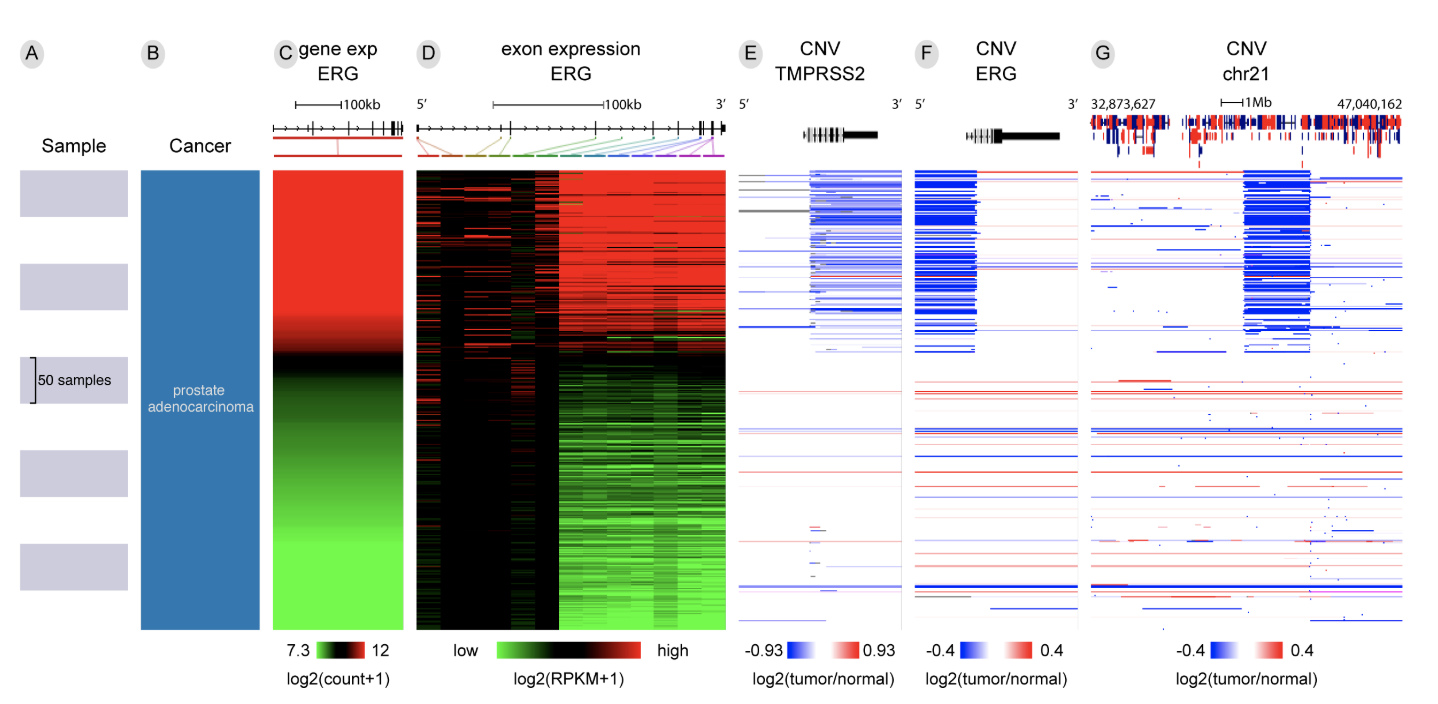
Xena
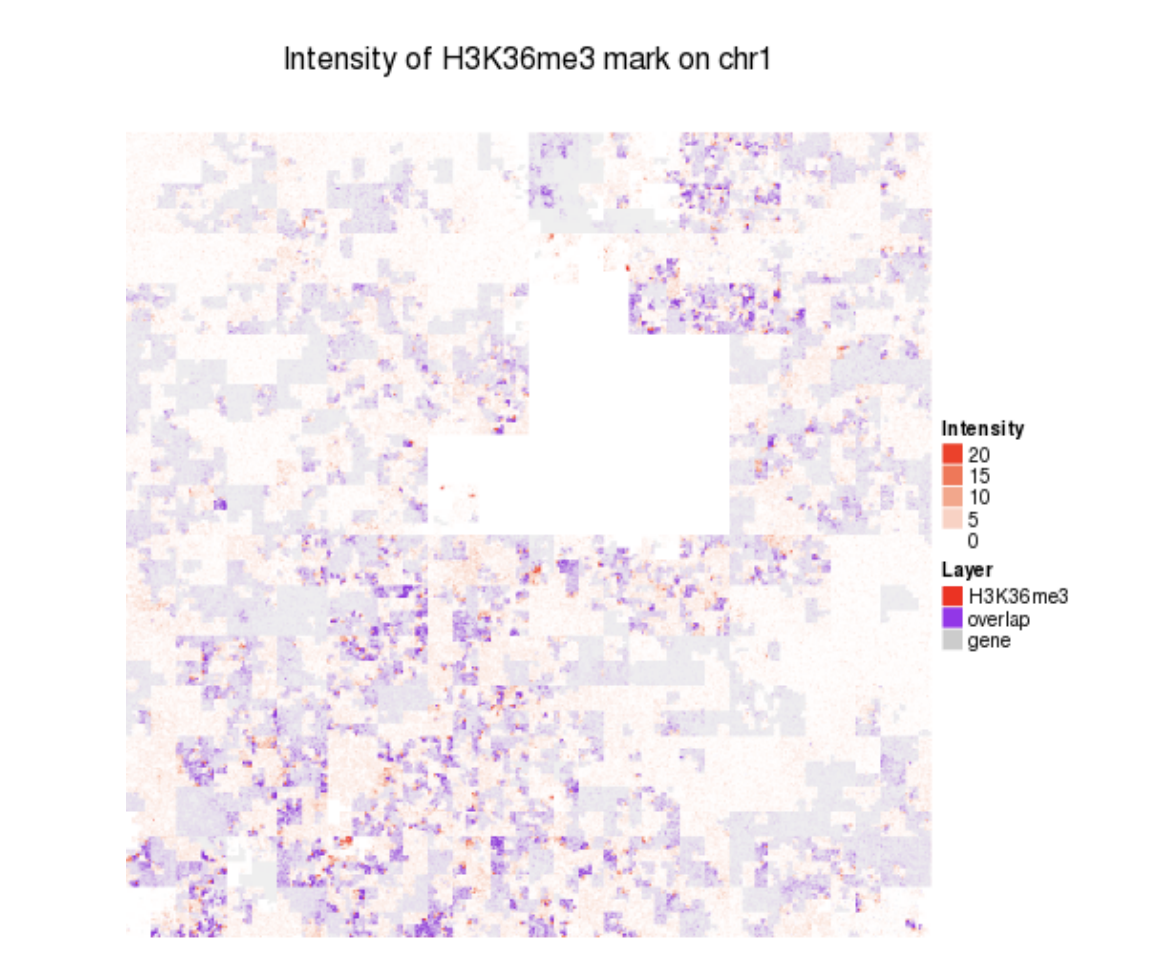
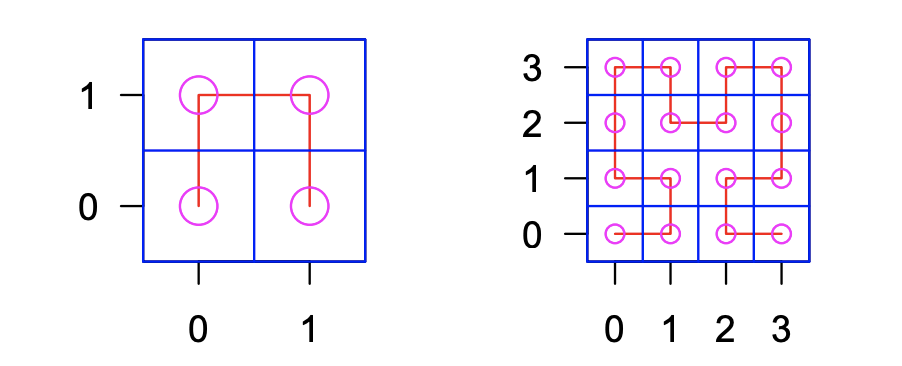
Space Filling
The space-filling curve is more space efficient than a circular layout and is often used to display a global overview of the genome while maintaining the spatial distribution of features. However, space-filling curves can only show one feature set, and it's hard to visually estimate the distances between two positions in a sequence.
2 tools
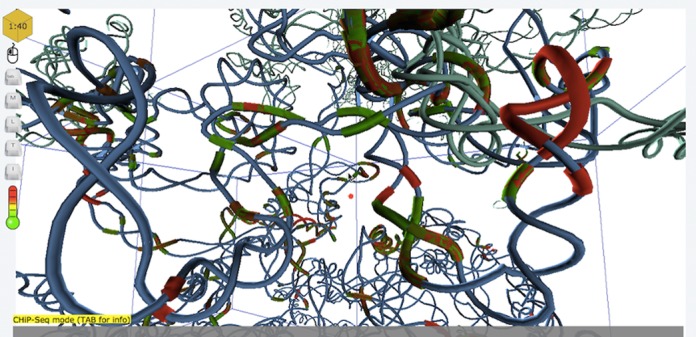
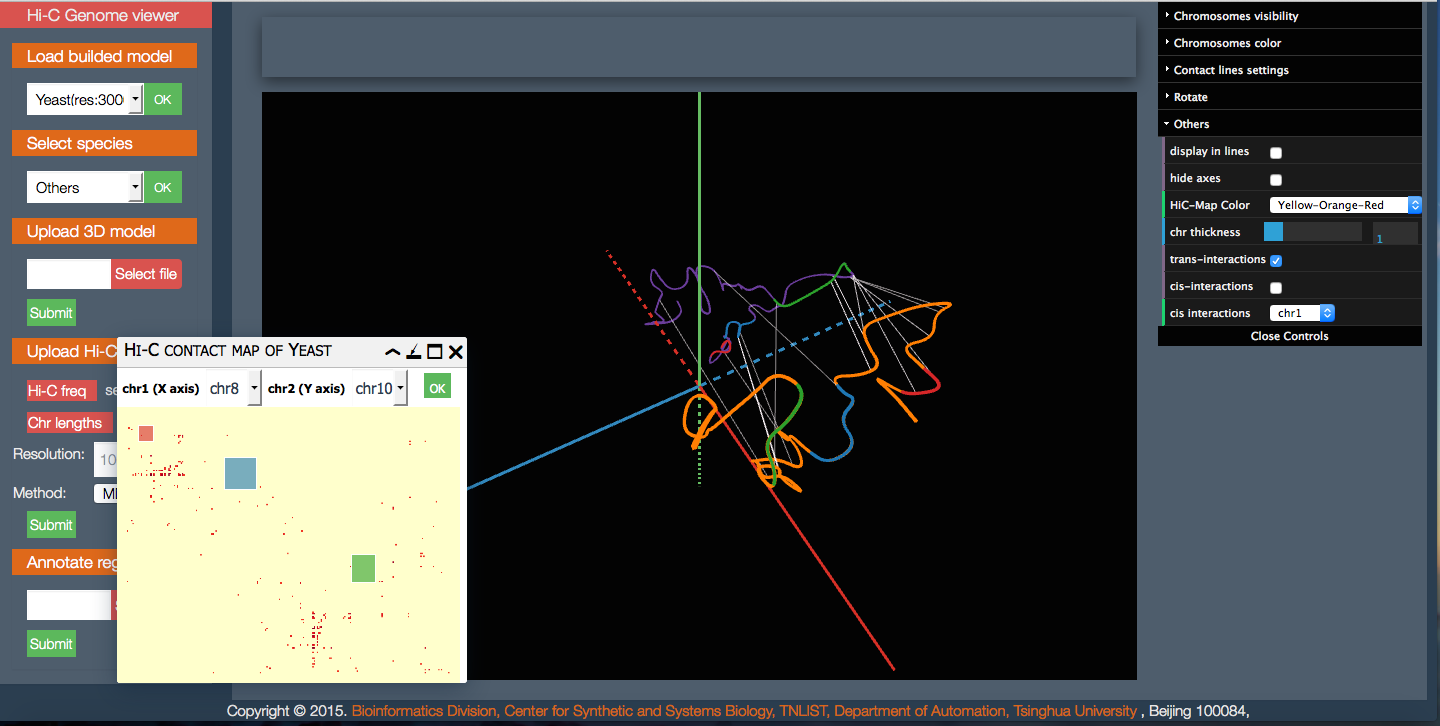
Spatial
Spatial layouts display sequences in a 3-dimensional structure.
2 tools